The Galleries
Earth Science Galleries
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
Heliophysics Galleries
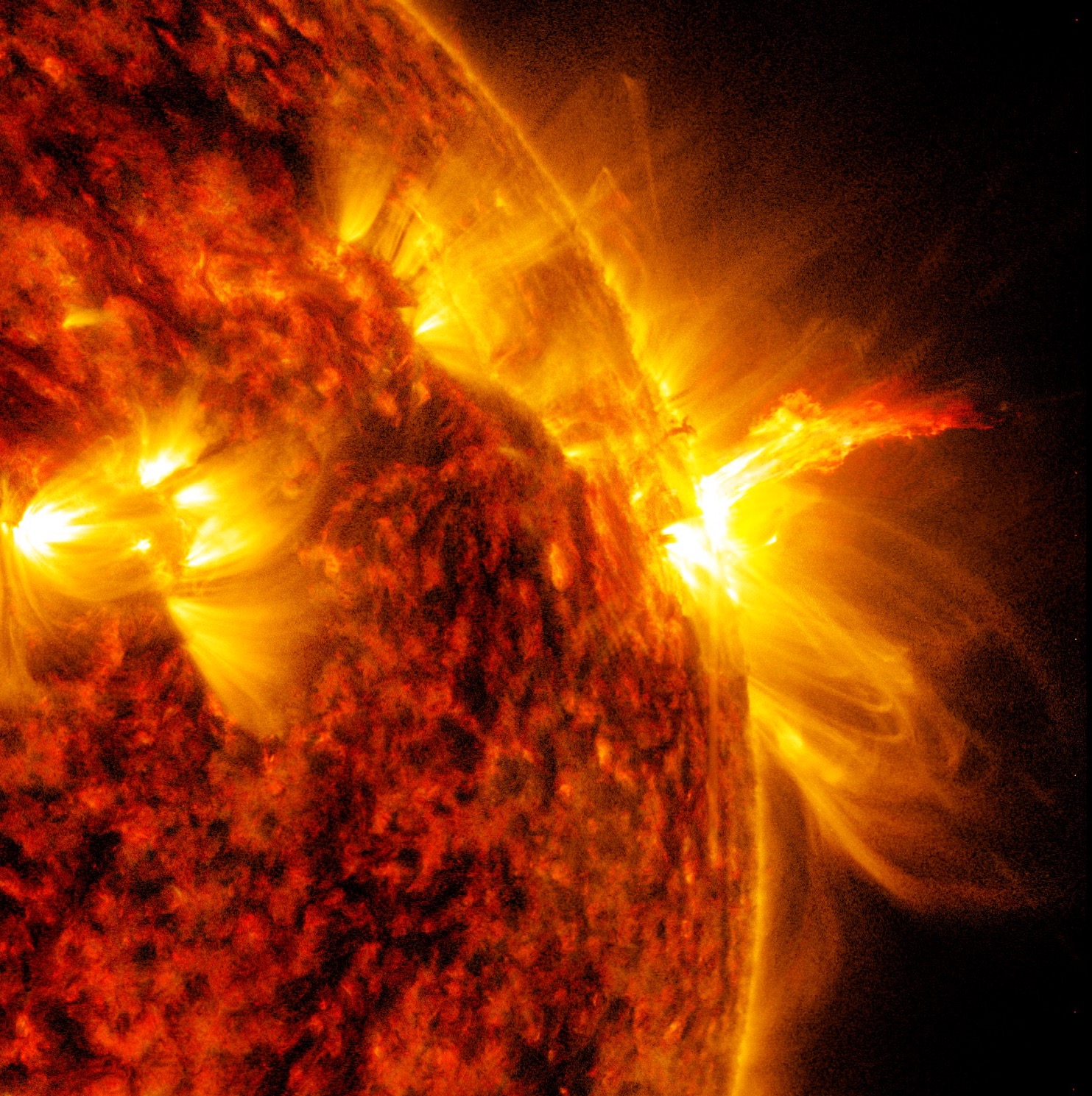
NASA's Heliophysics Gallery
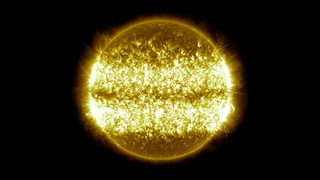
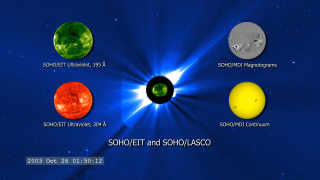
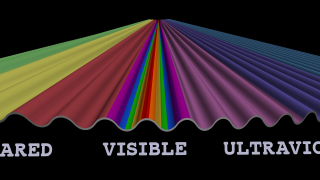
Go to this pageThe Sun is a major influence on Earth's weather and climate. The focus of NASA's Sun-Solar System Connection is to understand this relationship from the perspective of the entire system. You can find out more by visiting the Heliophysics Page, the NASA Living with a Star program, and the Solar-Terrestrial Probe web site.
2024 Total Solar Eclipse
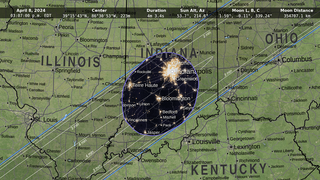
Go to this pageOn April 8, 2024, a total solar eclipse will cross North America, passing over Mexico, the United States, and Canada. A total solar eclipse happens when the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth, completely blocking the face of the Sun. The sky will darken as if it were dawn or dusk.A total solar eclipse happens when the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth, completely blocking the face of the Sun. People viewing the eclipse from locations where the Moon’s shadow completely covers the Sun – known as the path of totality – will experience a total solar eclipse. The sky will darken, as if it were dawn or dusk. Weather permitting, people along the path of totality will see the Sun’s corona, or outer atmosphere, which is usually obscured by the bright face of the Sun.Learn more about this total solar eclipse: solarsystem.nasa.gov/eclipses/2024
2023 Annular Solar Eclipse
Go to this pageOn Oct. 14, 2023, an annular solar eclipse will cross North, Central, and South America. Visible in parts of the United States, Mexico, and many countries in South and Central America, millions of people in the Western Hemisphere can experience this eclipse. An annular solar eclipse happens when the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth while it is at or near its farthest point from Earth. Because the Moon is farther away from Earth than usual, it appears smaller than the Sun and does not completely cover the star. Because of this, the Sun will appear like a “ring of fire” in the sky for those in the path of annularity. During an annular eclipse, it is never safe to look directly at the Sun without specialized eye protection designed for solar viewing. Learn more about this annular solar eclipse: solarsystem.nasa.gov/eclipses/2023
Heliophysics Breaking News
Go to this pageThis gallery contains an archive of breaking news solar events such as flares, CMEs, solar storms, and comet passes. The most recent material is at the top left, and it progresses back in time left-to-right and top-down. Each page contains video and/or stills of a distinct event or series of linked events.The videos are available at multiple resolutions and compressions, including Apple ProRes 422. Where applicable, there are links to 4k x 4k tif frames.For sun-related background, animations, visualizations and informational content, go here.For pre-recorded, frequently-asked-question interviews with NASA scientists, go here.
The Solar Cycle
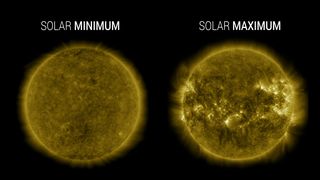
Go to this pageSolar Cycle 25 has begun. The Solar Cycle 25 Prediction Panel announced solar minimum occurred in December 2019, marking the transition into a new solar cycle. In a press event, experts from the panel, NASA, and NOAA discussed the analysis and Solar Cycle 25 prediction, and how the rise to the next solar maximum and subsequent upswing in space weather will impact our lives and technology on Earth. A new solar cycle comes roughly every 11 years. Over the course of each cycle, the star transitions from relatively calm to active and stormy, and then quiet again; at its peak, the Sun’s magnetic poles flip. Now that the star has passed solar minimum, scientists expect the Sun will grow increasingly active in the months and years to come. Understanding the Sun’s behavior is an important part of life in our solar system. The Sun’s outbursts—including eruptions known as solar flares and coronal mass ejections—can disturb the satellites and communications signals traveling around Earth, or one day, Artemis astronauts exploring distant worlds. Scientists study the solar cycle so we can better predict solar activity.
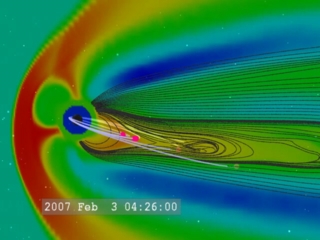
Space Weather
Go to this pageThe term "space weather" was coined not long ago to describe the dynamic conditions in the Earth's outer space environment, in the same way that "weather" and "climate" refer to conditions in Earth's lower atmosphere. Space weather includes any and all conditions and events on the sun, in the solar wind, in near-Earth space and in our upper atmosphere that can affect space-borne and ground-based technological systems and through these, human life and endeavor. Heliophysics is the science of space weather. This gallery organizes satellite footage, animations, visualizations, and edited videos produced at the Goddard Space Flight Center. Visualizations are different from pure animations because they are data-driven. They present a way of "seeing" the data. In the case of orbit visualizations, they are based on actual orbit information. Most of the animations and visualizations are available as frames and all the recent ones are HD quality. All videos are available in several formats and qualities including Apple ProRes for broadcast quality. Unless specifically marked otherwise, all these materials are public domain and free to use. For more infomation about NASA's media use guidelines see this page. The content is organized in two ways. Under "Facets of Space Weather" you will find our visuals grouped by the subject they address. Under "NASA Spacecraft" you will find our visuals grouped by the satellite they were collected by, or that they refer to. This group also contains animations of the spacecraft themselves. For breaking news solar events, go to this gallery.For frequently-asked-question interviews with NASA scientists, go here.
Planetary Science Galleries
Moon Phase and Libration
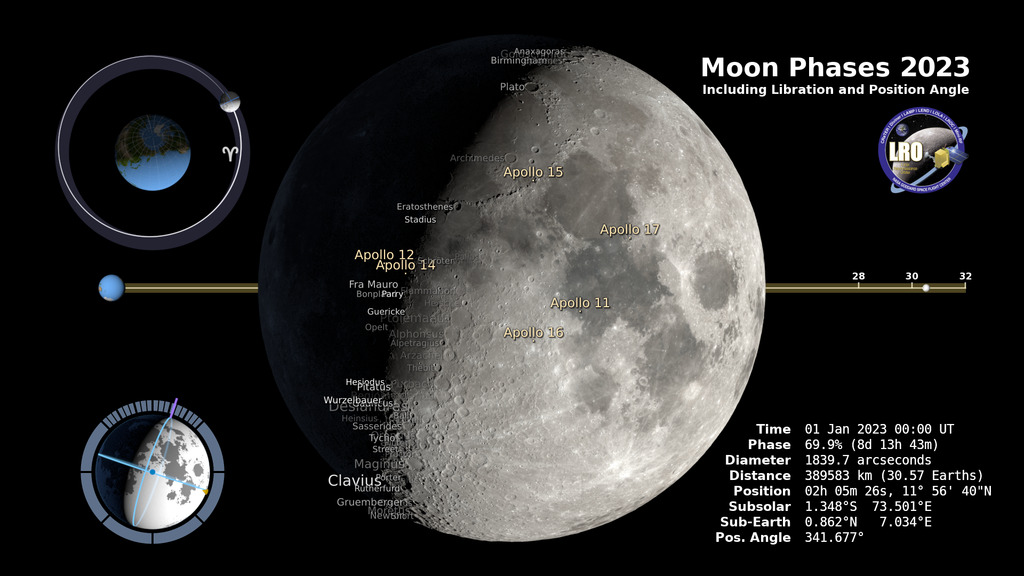
Go to this pageEvery year since 2011, the SVS produces its annual visualization of the Moon's phase and libration comprising 8760 hourly renderings of the precise size, orientation, and illumination of our nearest neighbor in space. The above displays the current state of the Moon. Click on the image to download a much larger version with labeled craters and additional graphics. Follow the links below to see the Moon at any hour of the year, play the animations, access the frames at multiple resolutions, and read detailed explanations.
Mars Missions and Science
Go to this pageThis multimedia gallery assembles and organizes Mars content on the Scientific Visualization Studio website. Highlights of NASA Goddard Space Flight Center’s animations, visualizations, videos, images and graphics relating to Mars science and missions can be found here.
Project Apollo
Go to this pageThis is a collection of the media resources available on the Scientific Visualization Studio website relating to NASA's Apollo missions to the Moon. More information and media can be found at NASA.gov Apollo Lunar Surface Journal Apollo Flight Journal Apollo Landing Sites photographed by Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Apollo in Real TimeProject Apollo Archive on Flickr
Lunar Eclipse
Go to this pageThis gallery contains videos and visualizations related to Lunar Eclipses
Astrophysics Galleries
Goddard's Astrophysics Gallery
Go to this pageThis multimedia gallery assembles and organizes the astrophysics content on the Scientific Visualization Studio website. All of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center's animations, visualizations, videos and still images relating to the universe beyond our Solar System are here. Browse through the basic categories or find Goddard's most recent releases under each specific astronomical feature. Find all the content relating to a particular satellite under "Missions." Most entries have multiple downloadable formats and several resolutions.
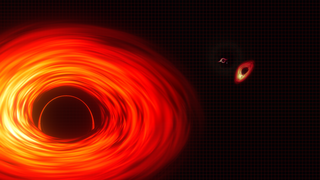
Black Hole Week
Go to this pageThis gallery brings together resources related to NASA’s Black Hole Week — videos, social media products, news stories, still images, and assets. This week is a celebration of celestial objects with gravity so intense that even light cannot escape them. Our goal is that no matter where people turn that week they will run into a black hole. (Figuratively, of course — we don’t want anyone falling in!)
Black Holes
Go to this pageThis gallery gathers together visualizations and narrated videos about black holes. A black hole is a celestial object whose gravity is so intense that even light cannot escape it. Astronomers observe two main types of black holes. Stellar-mass black holes contain three to dozens of times the mass of our Sun. They form when the cores of very massive stars run out of fuel and collapse under their own weight, compressing large amounts of matter into a tiny space. Supermassive black holes, with masses up to billions of times the Sun’s, can be found at the centers of most big galaxies. Although a black hole does not emit light, matter falling toward it collects in a hot, glowing accretion disk that astronomers can detect.
The Traveler
Go to this pageOur Traveler can’t wait to explore the universe! It’s hard not to be caught up in their boundless enthusiasm for all the wondrous sights the cosmos has to offer. This gallery brings together resources related to the intrepid blue Traveler and their adventures. This includes videos, videos, social media products, still images, and assets.
Missions and Instrument Galleries
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
Special Productions
Goddard From Above
Go to this pageThis is an expanding collection of aerial images and 4K video of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. Each group contains footage of the specific buildings or campus areas described in its title, along with nearby features, and in most cases includes a brief summary of the shots available in each video sequence.
Fulldome Gallery
Go to this pageVisualizations in fulldome format for display in digital planetariums.
NASA On Air
Go to this pageBroadcast-ready video for TV weathercasters produced by NASA's Earth Science News Team and NASA Goddard Space Flight Center.
Visualizations for Educators
Go to this pagePhenomena are observable events that occur in nature. Data visualizations can offer new ways for students to experience and explore Earth and space phenomena that happen over large scales of time and at great distances. This gallery includes visualizations of phenomena that support topics that are taught in middle and high school and are aligned with select Next Generation Science Standards. This gallery was curated by Anne Arundle County Science Teachers Margaret Graham and Jeremy Milligan with support from Dr. Rachel Connolly during the summer of 2022. A video showing how Jeremy Milligan uses SVS resources to develop a phenomena-based lesson is also available.
Science On a Sphere Gallery
Go to this pageContent for NOAA's Science on a Sphere and related spherical display platforms.
Live Shots Gallery Collection
Go to this pageCollection of live shot pages of b-roll and interviews!
Special Events
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
- Gallery
Hyperwall
Hyperwall Power Playlist - Planetary Science Focus
Go to this pageThis is a collection of our most powerful and most frequently used Hyperwall-ready visualizations, along with several that haven't gotten the attention they deserve. They're especially great for more general or top-level science talks, or to "set the scene" before a deep dive into a more focused topic or dataset. We've tried to cover the subject areas our speakers focus on most. If you're not seeing what you're looking for, there is a huge library of visualizations more localized or specialized in subject - please use the Search function above, and filter "Result type" for "Hyperwall Visual." If you'd like to use one of these visualizations in your Hyperwall presentation, we'll need the ID number overlaid on the preview image (for example "30998" on the SMD fleet graphic below) or the page link, and if there are multiple items, which one you want (i.e. "the third movie down"). Please check our Hyperwall How-To Guide for tips on designing your Hyperwall presentation, file specifications, and Powerpoint/Keynote templates.
Hyperwall Power Playlist - Heliophysics Focus
Go to this pageThis is a collection of our most powerful, newsworthy, and frequently used Hyperwall-ready visualizations, along with several that haven't gotten the attention they deserve. They're especially great for more general or top-level science talks, or to "set the scene" before a deep dive into a more focused subject or dataset. We've tried to cover the subject areas our speakers focus on most. If you're not seeing what you're looking for, there is a huge library of visualizations more localized or specialized in subject - please use the Search function above, and filter "Result type" for "Hyperwall Visual." If you'd like to use one of these visualizations in your Hyperwall presentation, we'll need the ID number overlaid on the preview image (for example "30998" on the SMD fleet graphic below) or the page link, and if there are multiple items, which one you want (i.e. "the third movie down"). Please check our Hyperwall How-To Guide for tips on designing your Hyperwall presentation, file specifications, and Powerpoint/Keynote templates.
Hyperwall Power Playlist - Earth Science Focus
Go to this pageThis is a collection of our most powerful, newsworthy, and frequently used Hyperwall-ready visualizations, along with several that haven't gotten the attention they deserve. They're especially great for more general or top-level science talks, or to "set the scene" before a deep dive into a more focused subject or dataset. We've tried to cover the subject areas our speakers focus on most. If you're not seeing what you're looking for, there is a huge library of visualizations more localized or specialized in subject - please use the Search function above, and filter "Result type" for "Hyperwall Visual." If you'd like to use one of these visualizations in your Hyperwall presentation, we'll need the ID number overlaid on the preview image (for example "30998" on the SMD fleet graphic below) or the page link, and if there are multiple items, which one you want (i.e. "the third movie down"). Please check our Hyperwall How-To Guide for tips on designing your Hyperwall presentation, file specifications, and Powerpoint/Keynote templates.
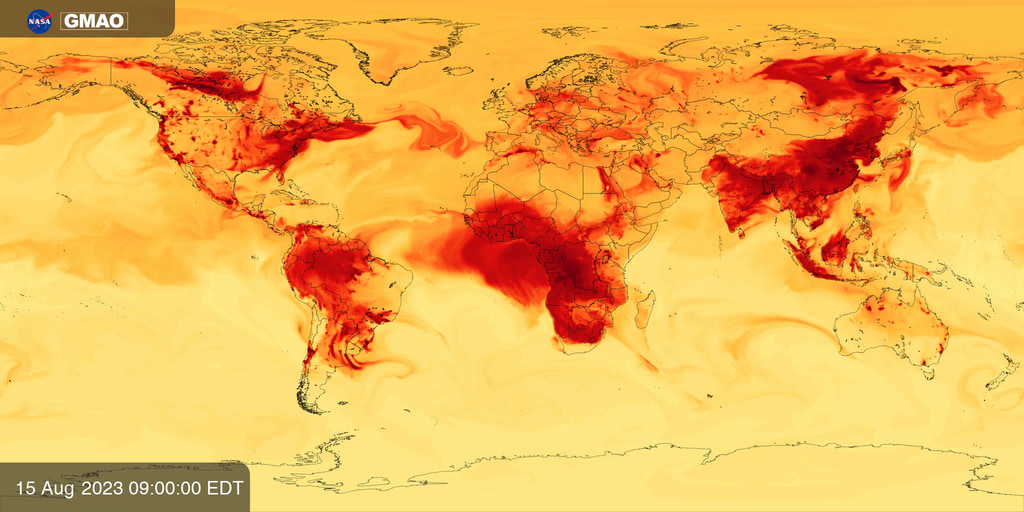
Earth at Night Imagery
Go to this pageDazzling photographs and images from space of our planet’s nightlights have captivated public attention for decades. In such images, patterns are immediately seen based on the presence or absence of light: a distinct coastline, bodies of water recognizable by their dark silhouettes, and the faint tendrils of roads and highways emanating from the brilliant blobs of light that are our modern, well-lit cities. For nearly 25 years, satellite images of Earth at night have served as a fundamental research tool, while also stoking public curiosity. These images paint an expansive and revealing picture, showing how natural phenomena light up the darkness and how humans have illuminated and shaped the planet in profound ways since the invention of the light bulb 140 years ago.
NASA's Heliophysics Gallery
Go to this pageThe Sun is a major influence on Earth's weather and climate. The focus of NASA's Sun-Solar System Connection is to understand this relationship from the perspective of the entire system. You can find out more by visiting the Heliophysics Page, the NASA Living with a Star program, and the Solar-Terrestrial Probe web site.





























![Complete transcript available.Music credits: 'Faint Glimmer' by Andrew John Skeet [PRS], Andrew Michael Britton [PRS], David Stephen Goldsmith [PRS], 'Ocean Spirals' by Andrew John Skeet [PRS], Andrew Michael Britton [PRS], David Stephen Goldsmith [PRS] from Killer Tracks.Watch this video on the NASA Goddard YouTube channel.](/vis/a010000/a012800/a012817/GOLDOverview_YouTube.00001_searchweb.png)