Earth
ID: 4447
These visuals were created in anticipation of the 2016 Korean United States Air Quality study (KORUS-AQ) field campaign which will combine observations from aircraft, satellties, ships and ground stations with air quality models to assess and monitor air quality acorss urban, rural and coastal areas.
Ozone gas and particle pollution are two of the main factors that contribute to poor air quality around the world.
While ozone gas located high in the stratosphere protects us from the sun’s harmful UV rays, pollution from cars and other human emissions near ground level can cause chemical reactions that lead to ozone formation near the surface. Breathing in high levels of ozone is also bad for human health, causing lung diseases and health impacts on sensitive populations such as children, the elderly and people with asthma.
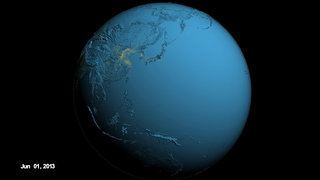
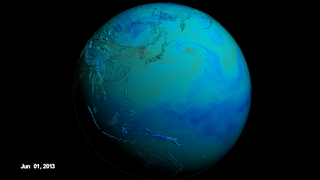
These visuals are showing the ozone that formed near the surface, or 'surface ozone', over the Korean peninsula in June 2013 according to the GEOS-5 Nature Run chemistry model data. Peak ozone in Korea occurs between April and June.
Since Seoul is located on a peninsula, the metropolitan area and the pollution produced here are separated from other sources of emissions. In addition, Seoul’s human-produced emissions are concentrated in its urban areas but are surrounded by more rural agricultural areas. The contrast between urban and rural zones on the peninsula allow scientists to study and differentiate human and naturally-produced emissions and better understand how they interact chemically. Understanding the chemical reactions between urban and agricultural emissions is extremely important for improving models that forecast air quality.
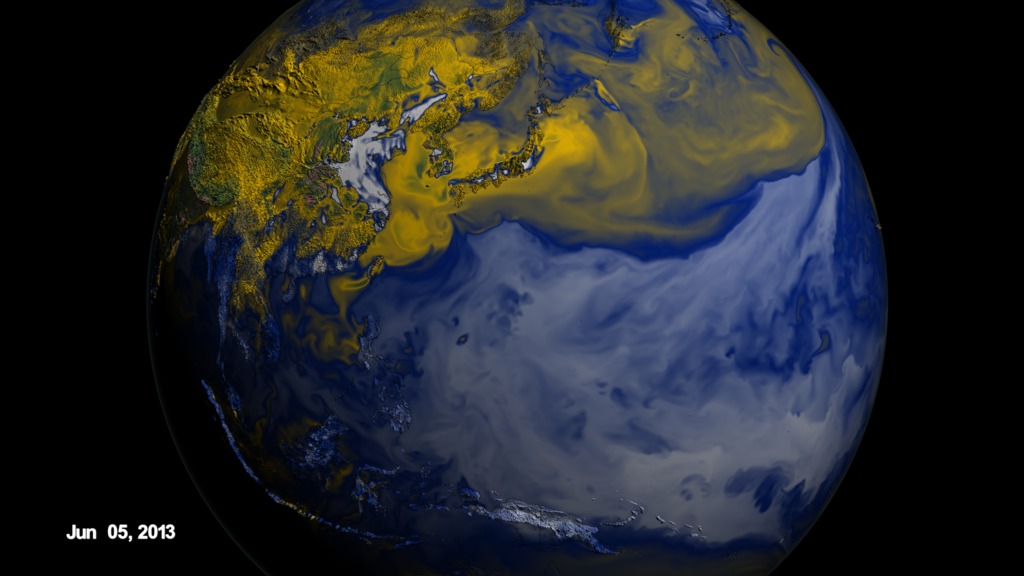
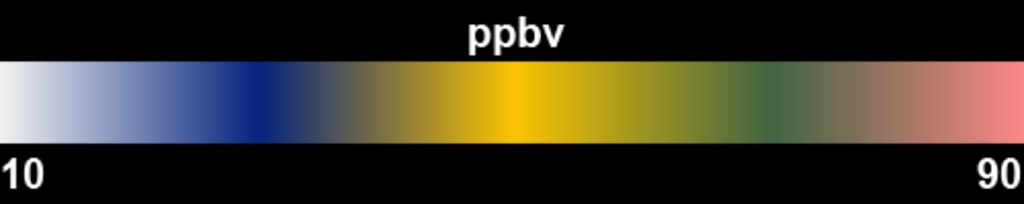
KORUS-AQ: Surface Ozone Levels Over the Korean Peninsula in June 2013
Ozone gas and particle pollution are two of the main factors that contribute to poor air quality around the world.
While ozone gas located high in the stratosphere protects us from the sun’s harmful UV rays, pollution from cars and other human emissions near ground level can cause chemical reactions that lead to ozone formation near the surface. Breathing in high levels of ozone is also bad for human health, causing lung diseases and health impacts on sensitive populations such as children, the elderly and people with asthma.
These visuals are showing the ozone that formed near the surface, or 'surface ozone', over the Korean peninsula in June 2013 according to the GEOS-5 Nature Run chemistry model data. Peak ozone in Korea occurs between April and June.
Since Seoul is located on a peninsula, the metropolitan area and the pollution produced here are separated from other sources of emissions. In addition, Seoul’s human-produced emissions are concentrated in its urban areas but are surrounded by more rural agricultural areas. The contrast between urban and rural zones on the peninsula allow scientists to study and differentiate human and naturally-produced emissions and better understand how they interact chemically. Understanding the chemical reactions between urban and agricultural emissions is extremely important for improving models that forecast air quality.


Related
For More Information
Visualization Credits
Cheng Zhang (USRA): Lead Visualizer
Laurence Schuler (ADNET Systems, Inc.): Technical Support
Ian Jones (ADNET Systems, Inc.): Technical Support
Greg Shirah (NASA/GSFC): Animator
Jefferson Beck (USRA): Lead Producer
Samson K. Reiny (Wyle Information Systems): Lead Writer
Emily Schaller (University of North Dakota/AFRC): Writer
Laurence Schuler (ADNET Systems, Inc.): Technical Support
Ian Jones (ADNET Systems, Inc.): Technical Support
Greg Shirah (NASA/GSFC): Animator
Jefferson Beck (USRA): Lead Producer
Samson K. Reiny (Wyle Information Systems): Lead Writer
Emily Schaller (University of North Dakota/AFRC): Writer
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio
NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio
Short URL to share this page:
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/4447
Data Used:
Note: While we identify the data sets used in these visualizations, we do not store any further details nor the data sets themselves on our site.
Keywords:
SVS >> Hyperwall
NASA Science >> Earth
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/4447
Data Used:
GEOS-5/Nature Run/Chemistry also referred to as: G5NR-Chem
Model - NASA GMAOKeywords:
SVS >> Hyperwall
NASA Science >> Earth