The Orion Nebula: Visible and Infrared Views
This animation showcases the Orion Nebula, first in infrared light (Spitzer), then in visible light (Hubble), and finally a blend of the two images in a multi-color mosaic.
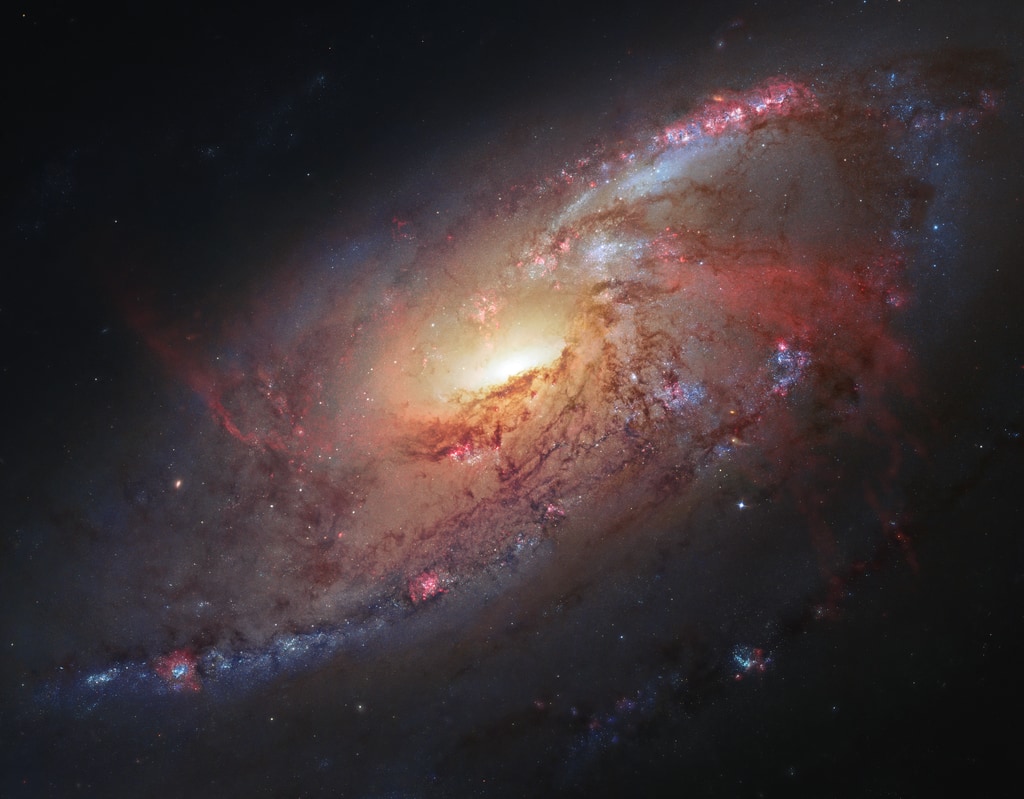
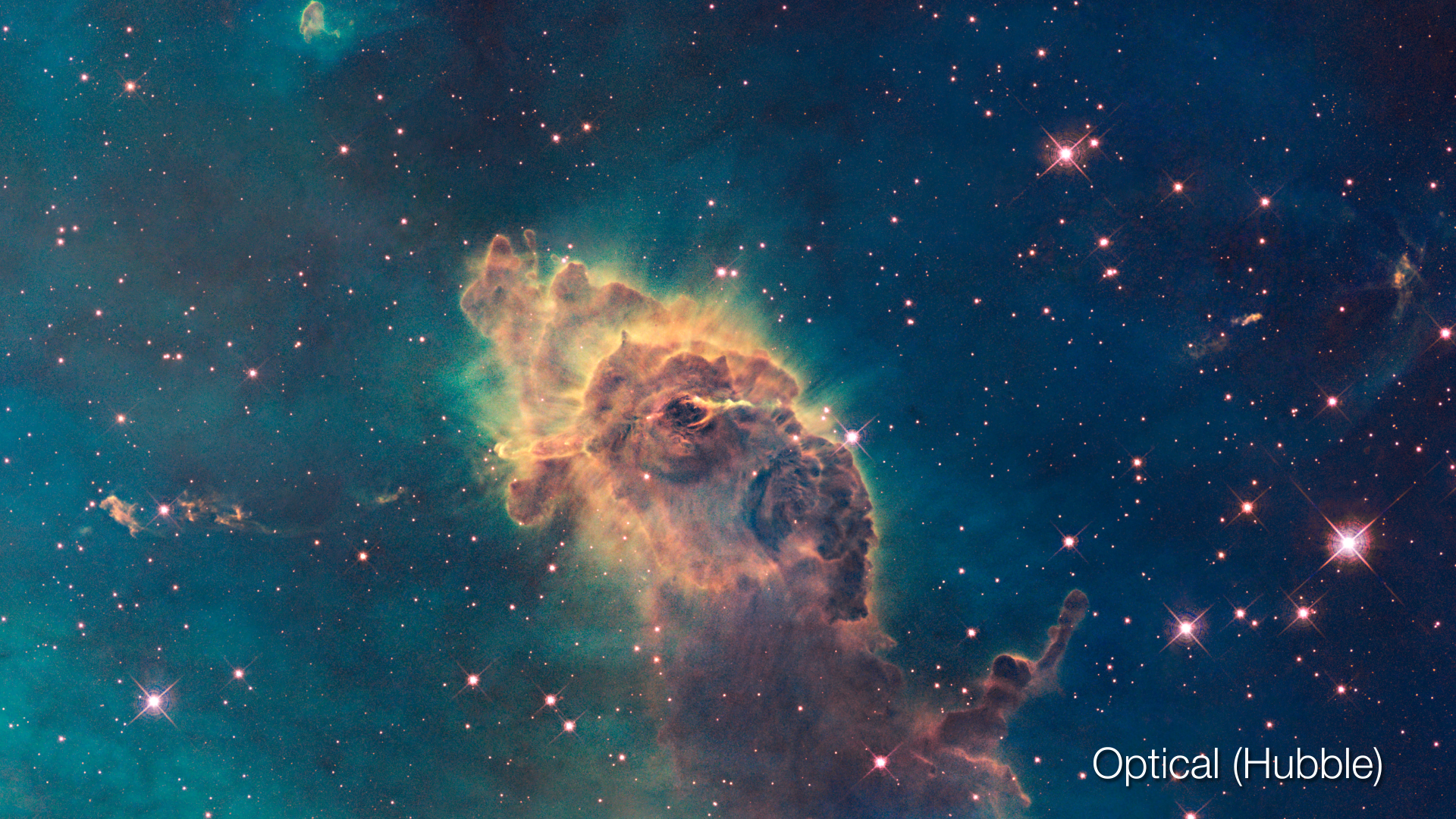
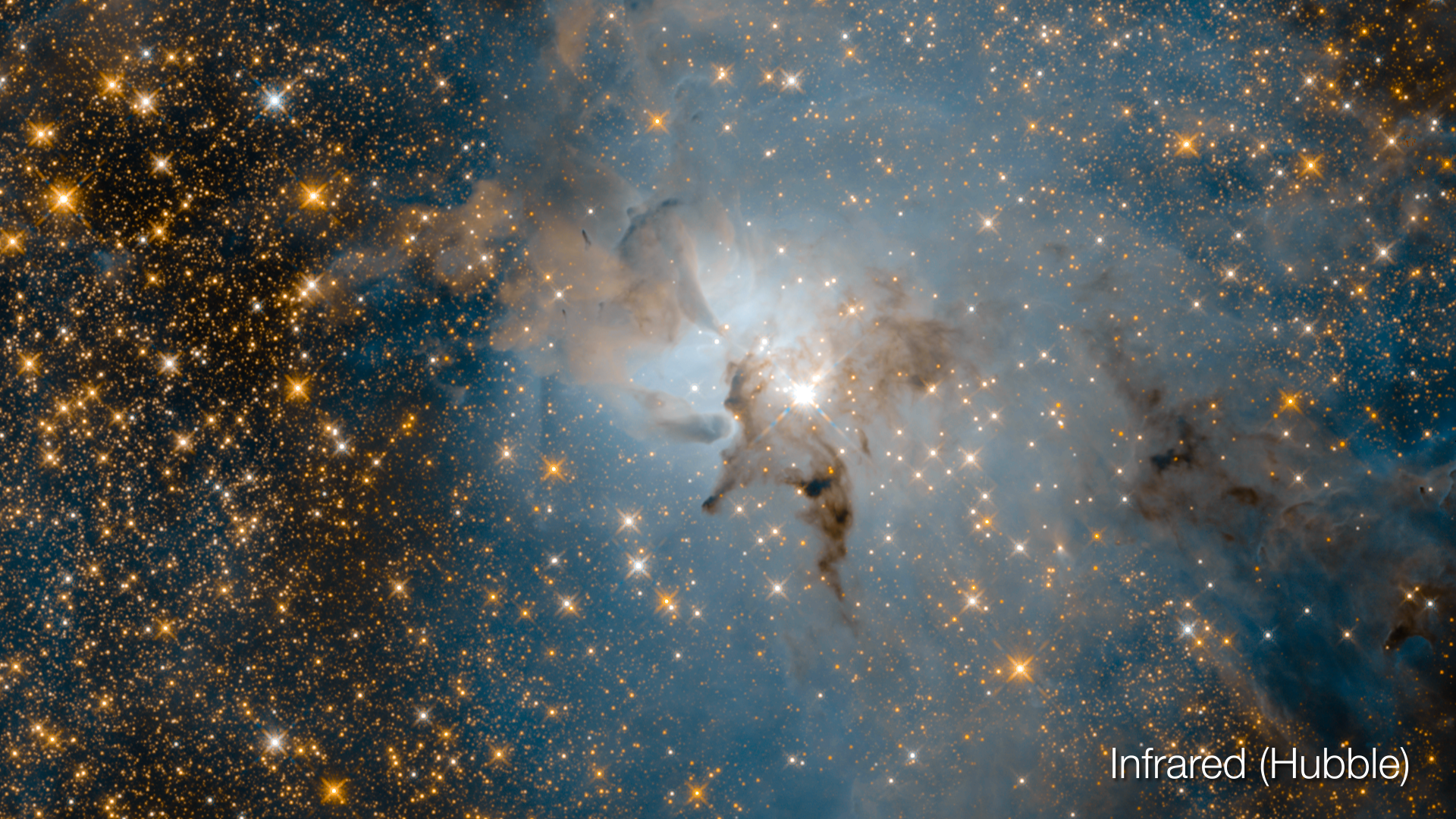
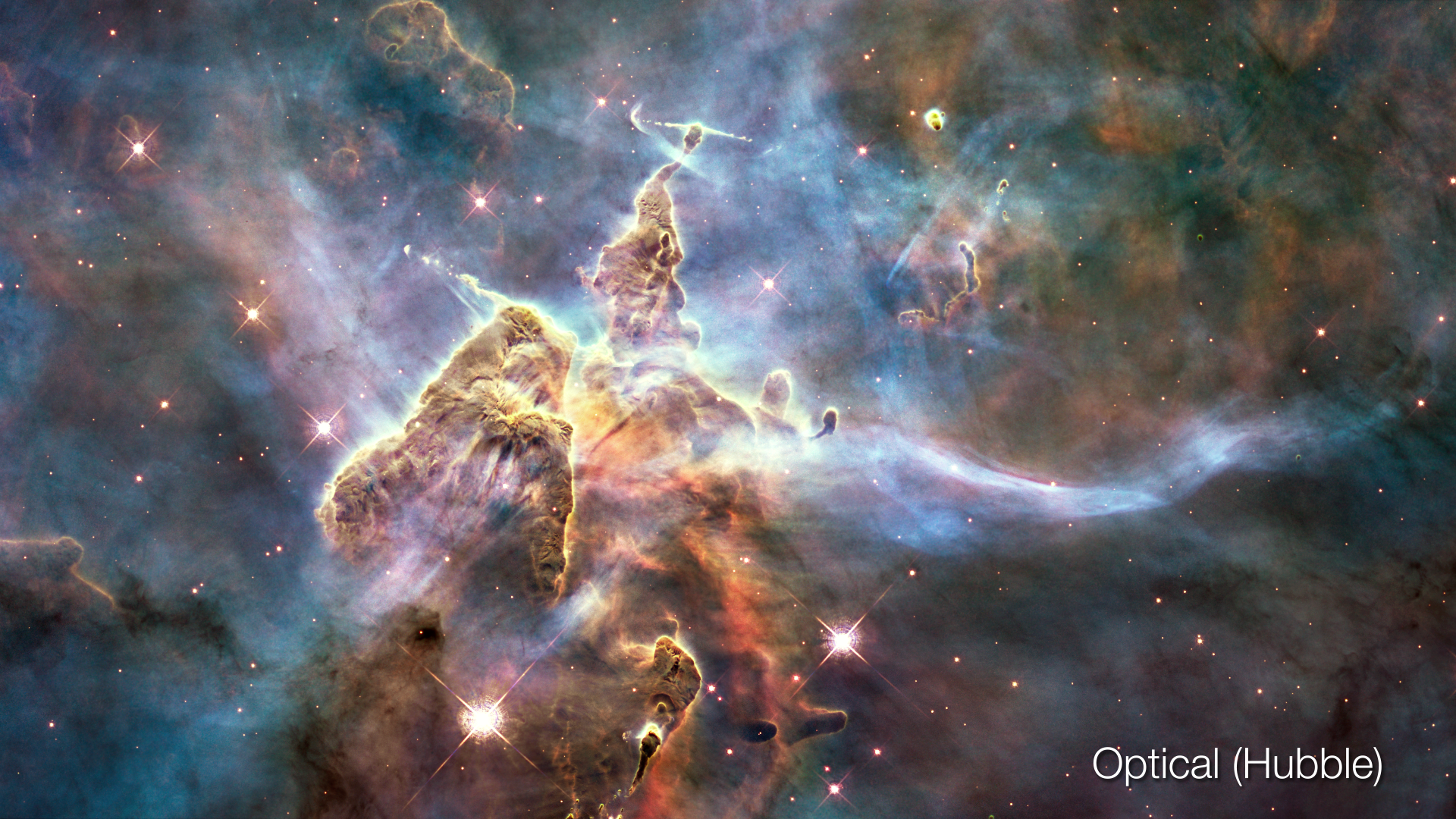
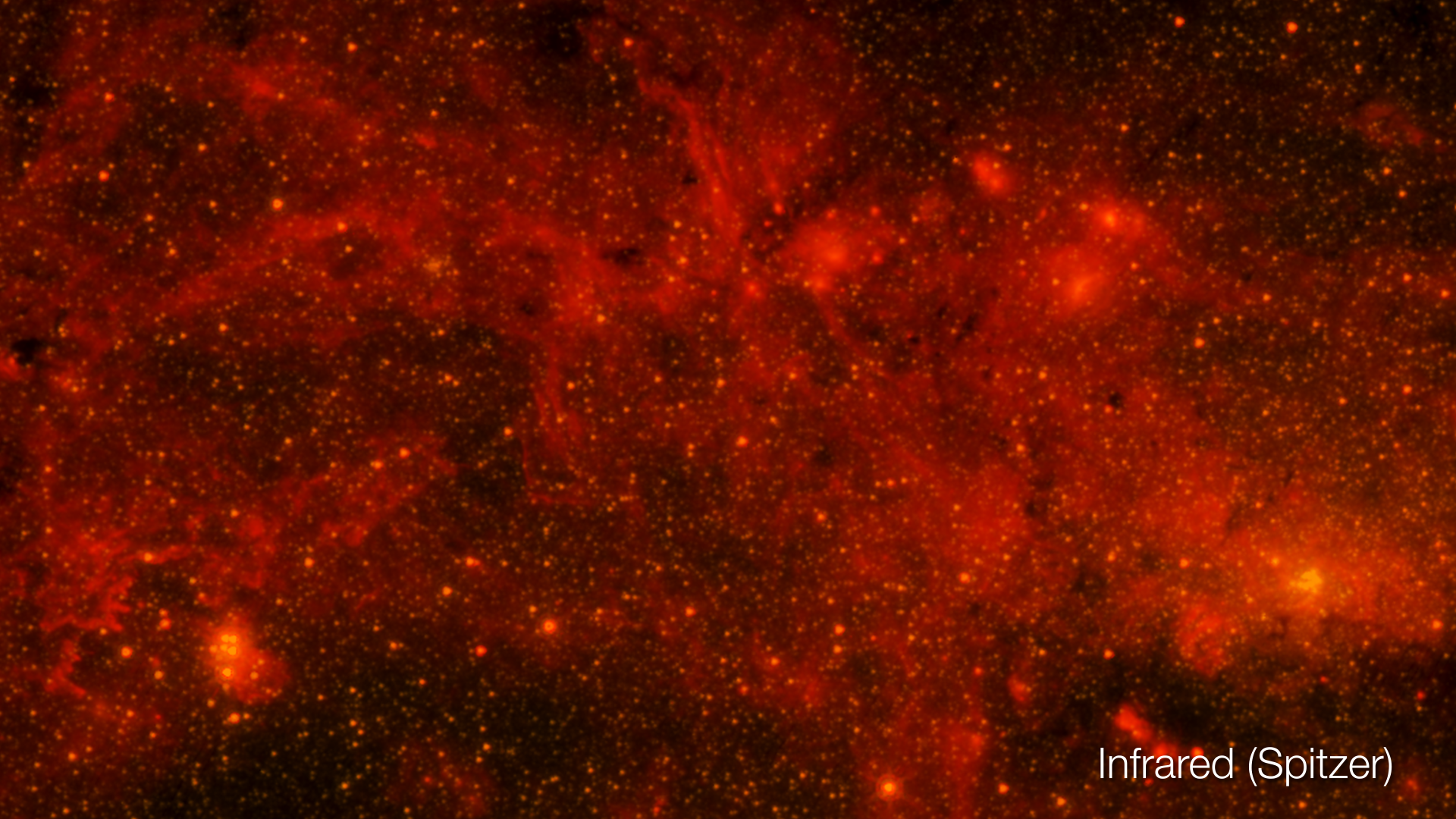
This sequence uses infrared (Spitzer) and visible (Hubble) images to reveal the formation of stars within a large cloud of hydrogen gas and dust. The warm gas lights up in the infrared view as red, and the hydrocarbon dust appears in green. The starlight from young stars appears in blue. The flood of starlight provides extra illumination throughout the dusty environment and in front of the cloud. The threads of gas, reminiscent of clouds on Earth, are compressed and pushed into knots by the winds from forming stars throughout the region. The clouds appear as shadows in this visible-light view. However, in areas where the gas has mostly been cleared or thinned, glowing cavities can be seen inside these cocoons. The combined view hints at the nebula’s complex three-dimensional structure.
This animation is the same as above, played twice as fast.

Visible image of the Orion Nebula

Infrared image of the Orion Nebula

Visible and Infrared image of the Orion Nebula
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
Video: NASA, ESA, and G. Bacon (STScI)
Optical image: NASA, ESA, M. Robberto (STScI/ESA) and the Hubble Space Telescope Orion Treasury Project Team (STScI)
Infrared image: NASA/Spitzer/JPL-Caltech
-
Visualizer
- Greg Bacon (STScI)
-
Technical support
- Leann Johnson (Global Science and Technology, Inc.)
Release date
This page was originally published on Monday, May 28, 2018.
This page was last updated on Monday, July 15, 2024 at 12:22 AM EDT.
Missions
This visualization is related to the following missions:Datasets used in this visualization
-
[Spitzer Space Telescope]
ID: 690This dataset can be found at: http://www.spitzer.caltech.edu/
See all pages that use this dataset -
[Hubble Space Telescope]
ID: 831
Note: While we identify the data sets used in these visualizations, we do not store any further details, nor the data sets themselves on our site.