Earth
ID: 2216
The Erythemal Index is a measure of ultraviolet radiation (UV) at ground level on the Earth. UV exists to the left of the visible spectrum and is divided into three components (UV-A, UV-B and UV-C). UV-B (290-320 wavelengths) is the most dangerous form of UV radiation that can reach ground level. Atmospheric ozone shields life at the surface from most of the harmful components of solar radiation. Chemical processes in the atmosphere can effect the level of protection provided by the ozone in the upper atmosphere. This thinning of the atmospheric ozone in the stratosphere leads to elevated levels of UV-B at ground level and increases the risks of DNA damage in living organisms.
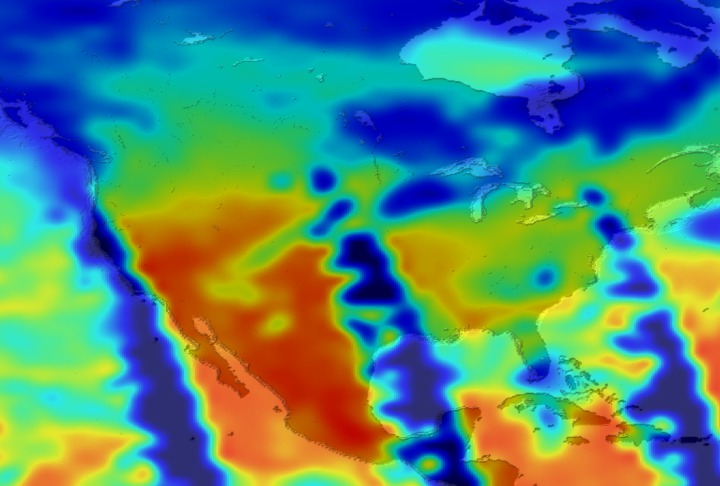
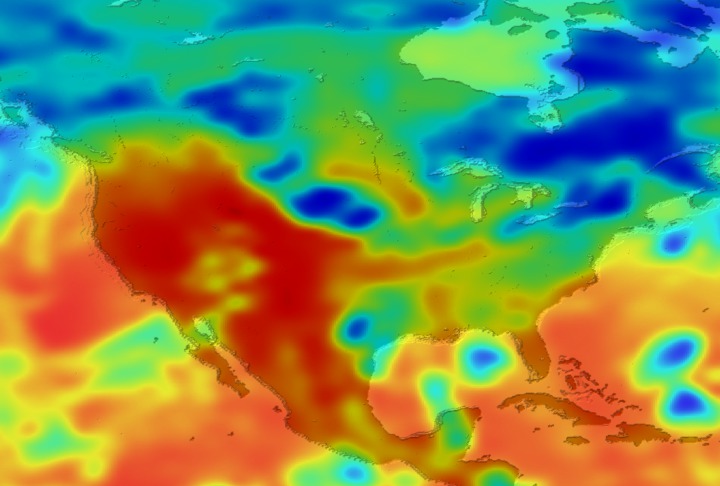
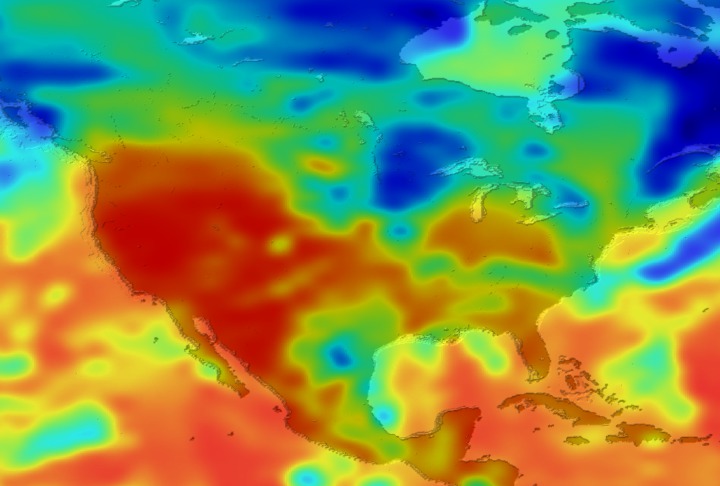
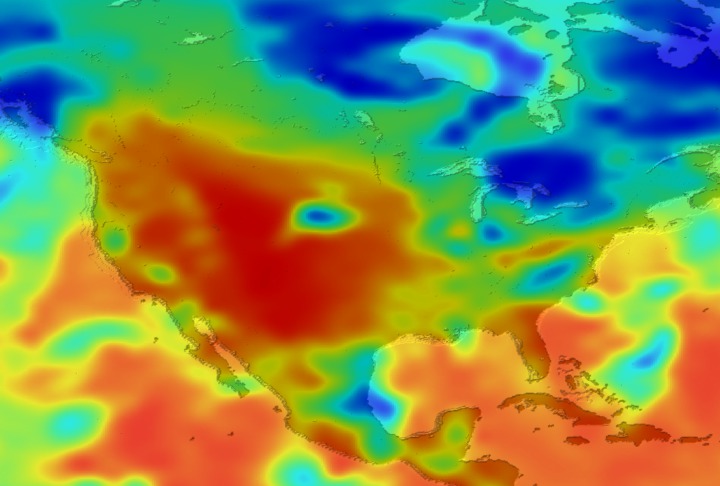
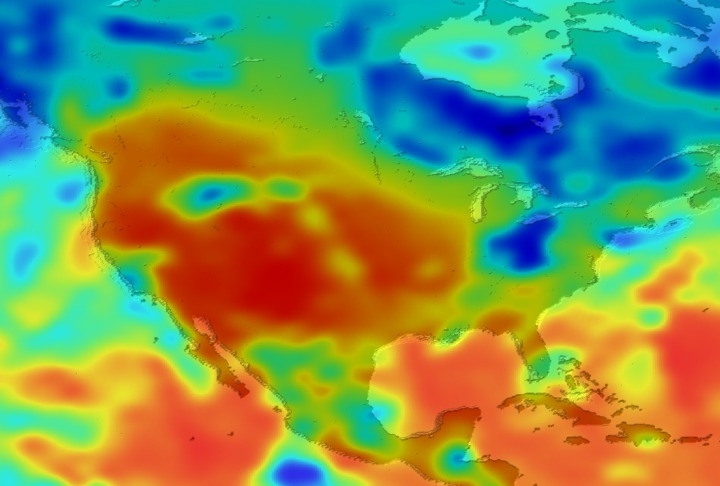
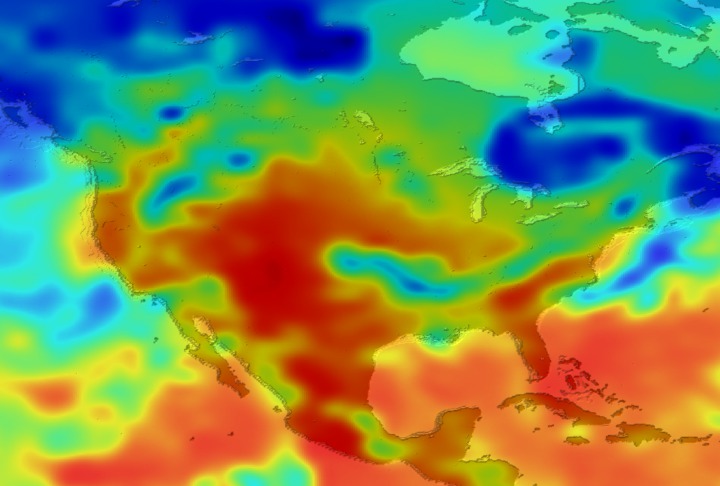
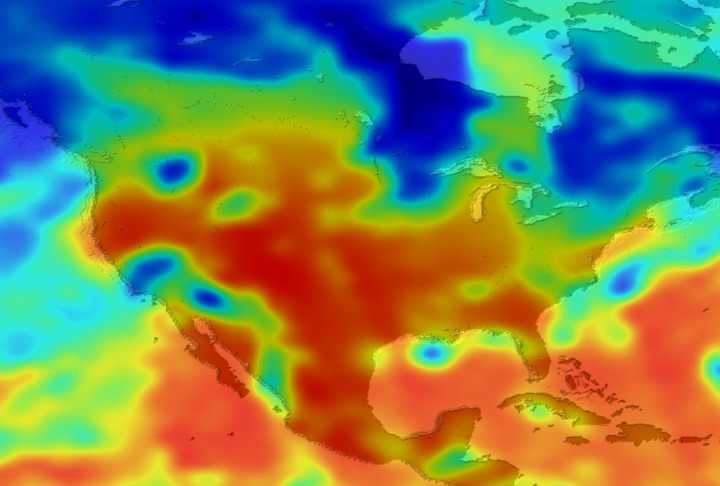
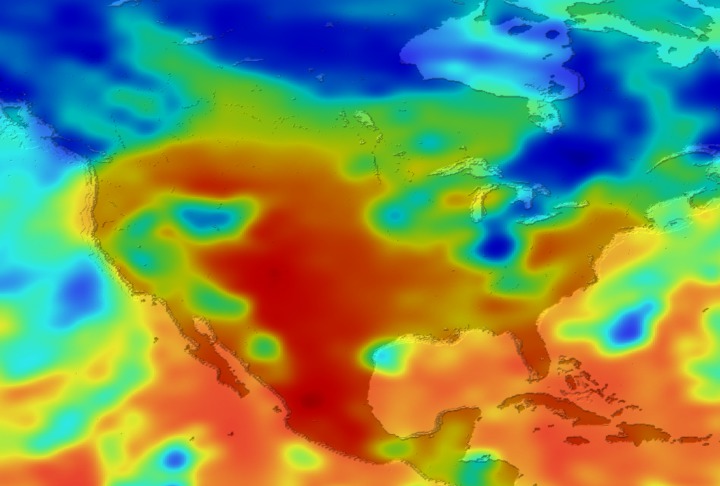
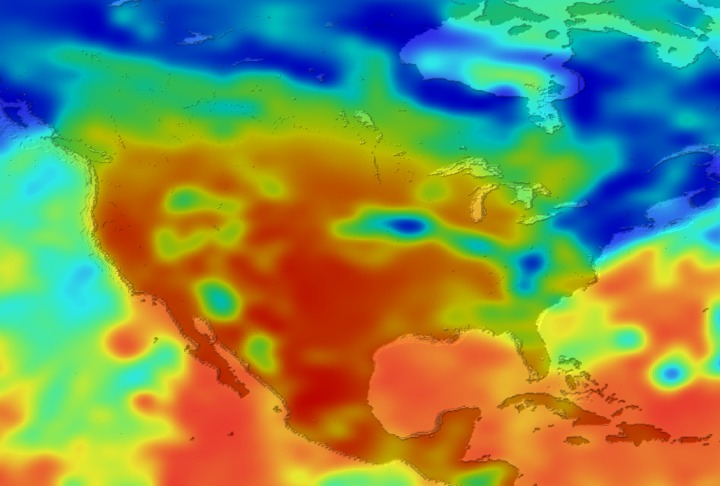

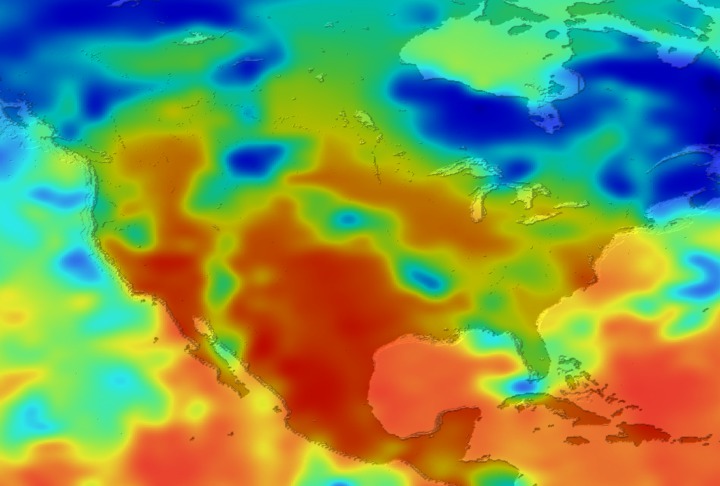
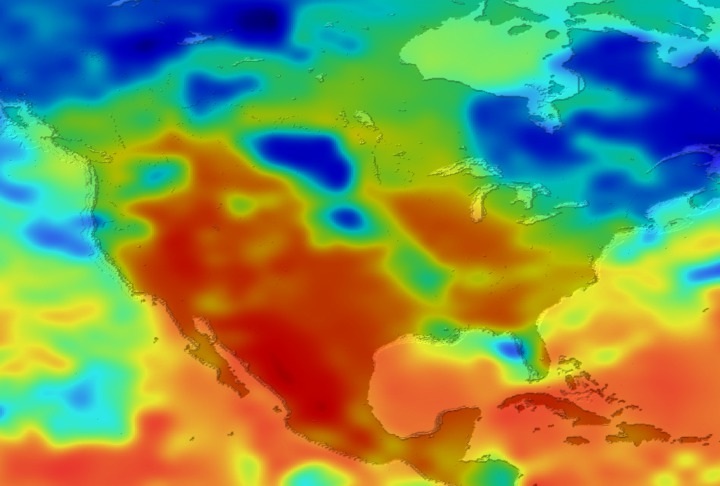
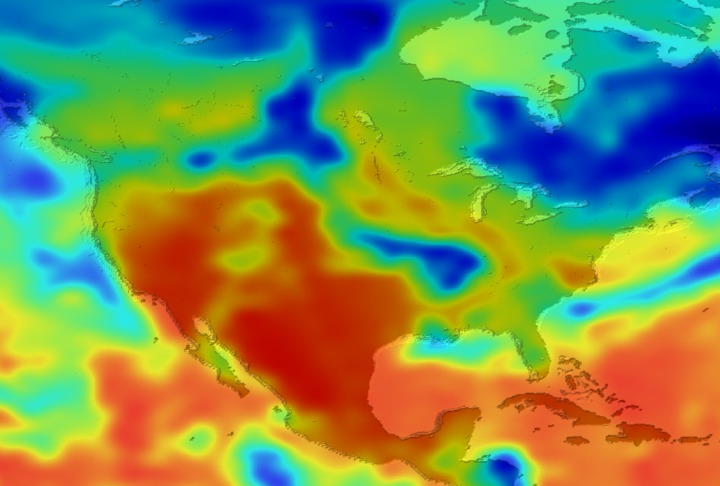
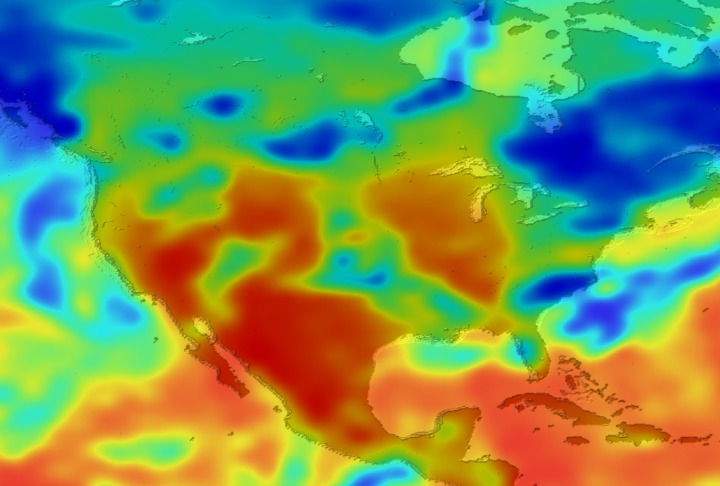
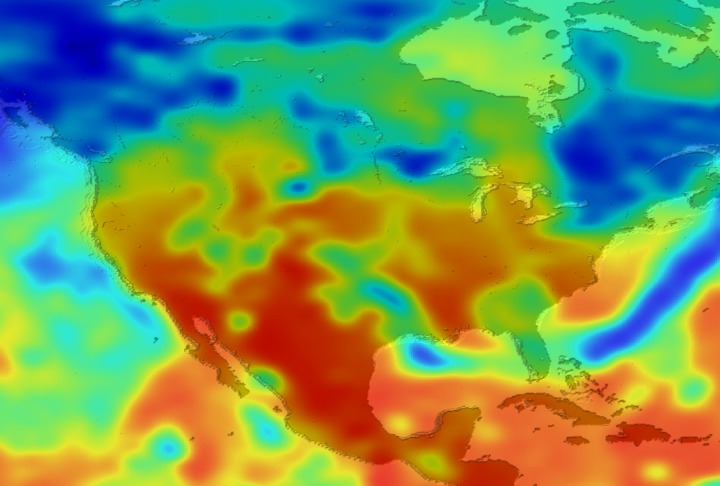
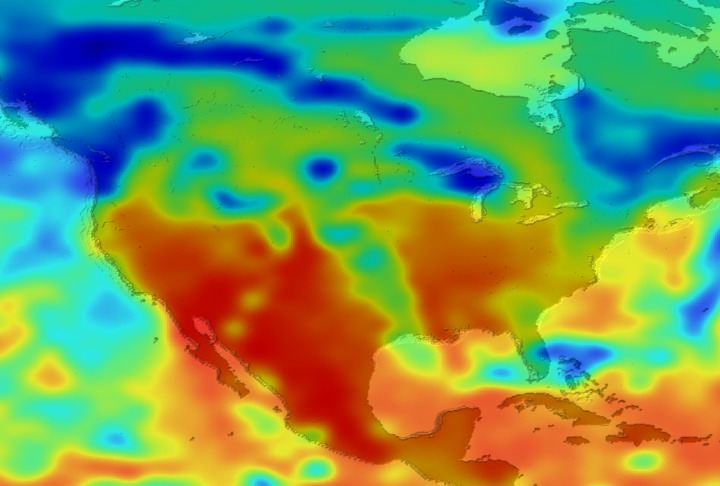
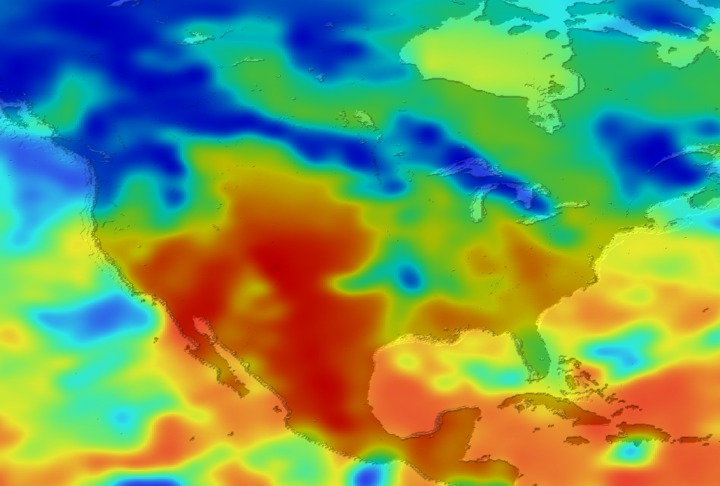
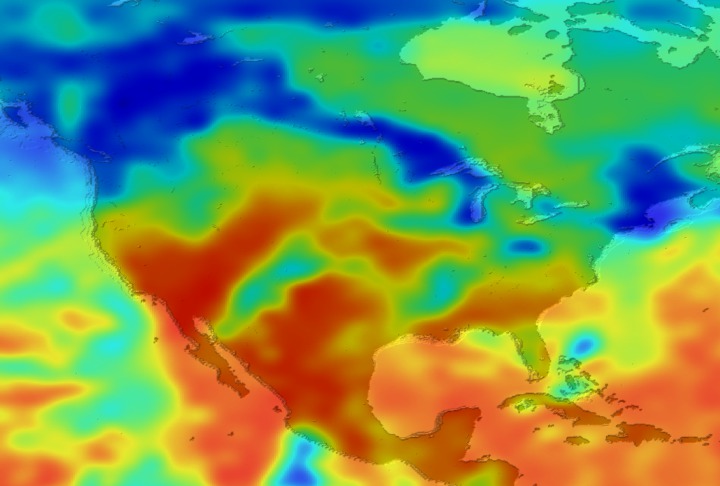
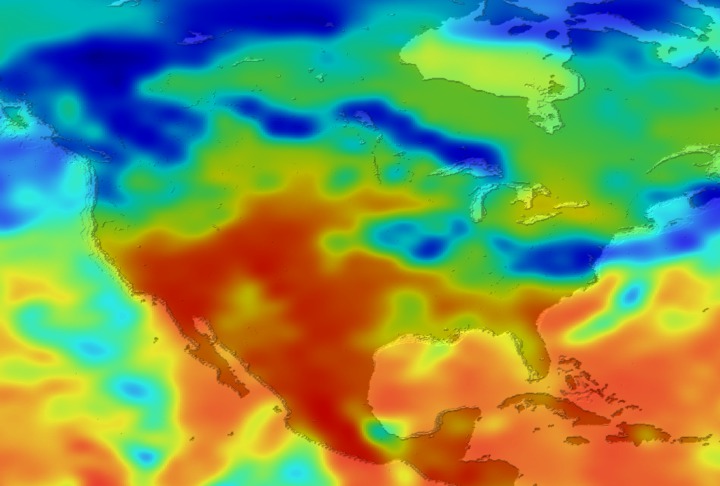

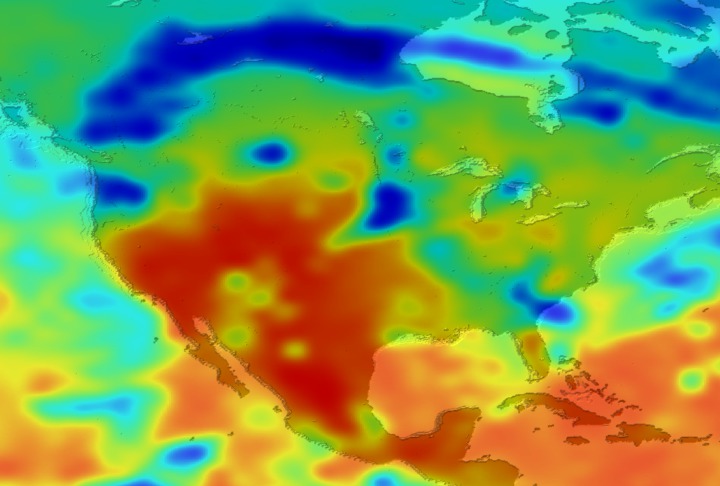
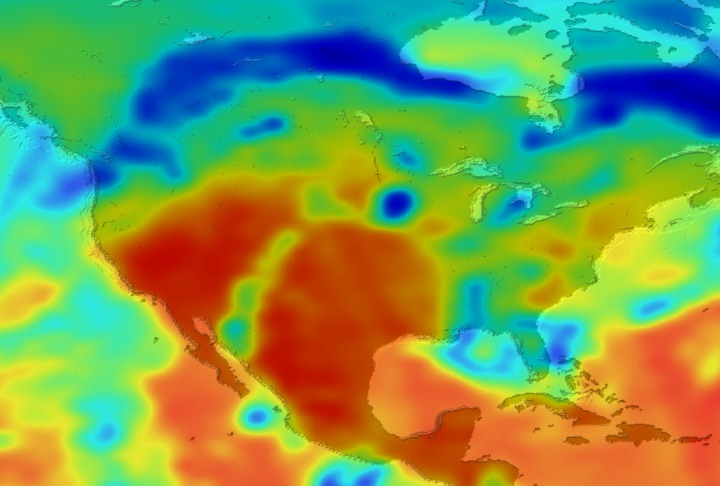
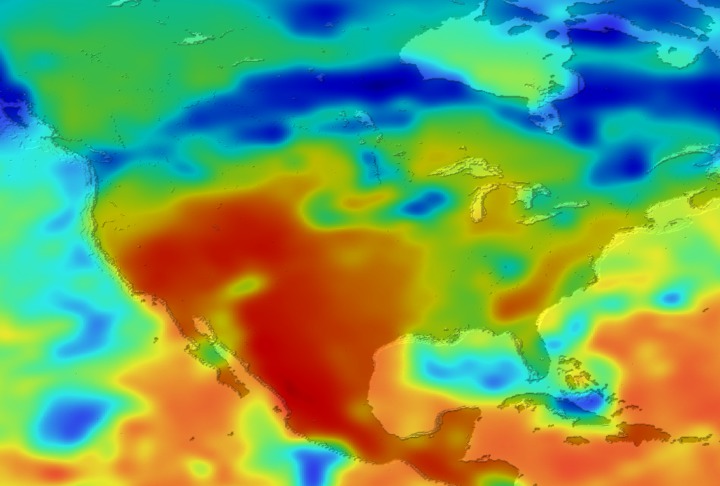
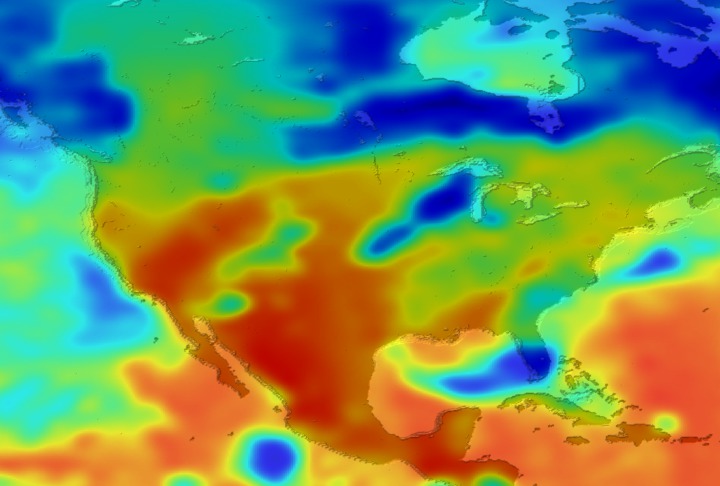
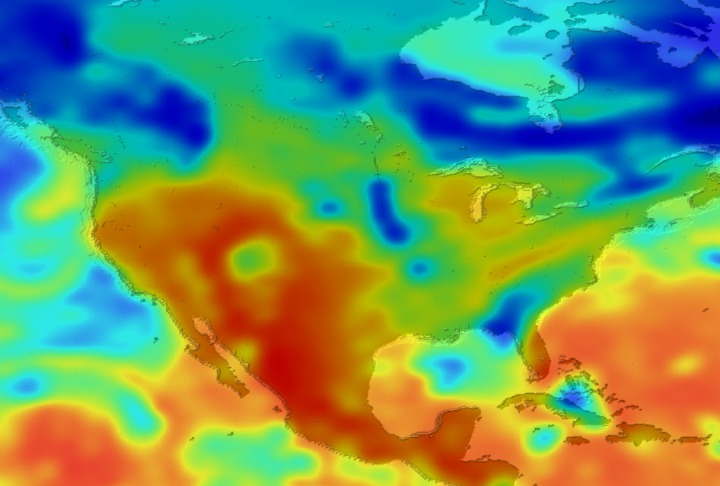

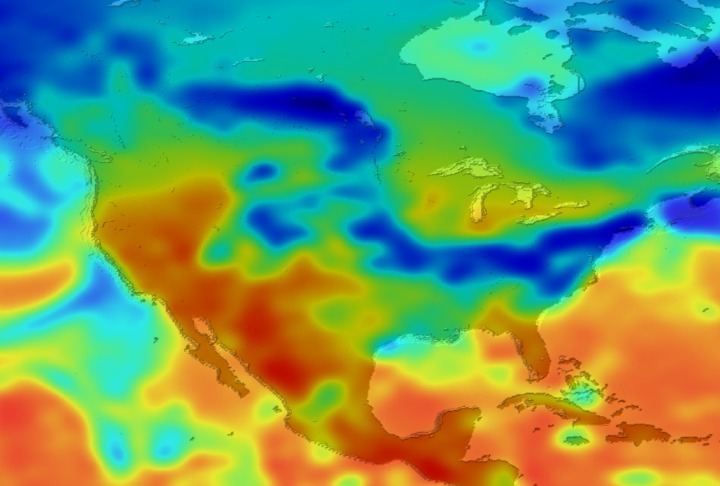

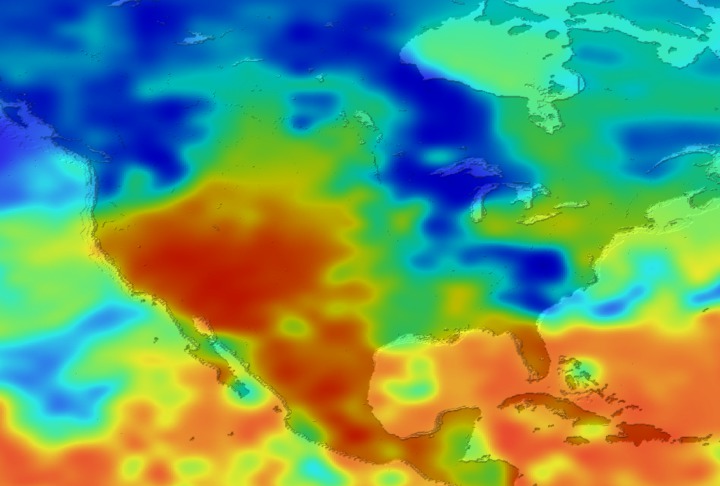
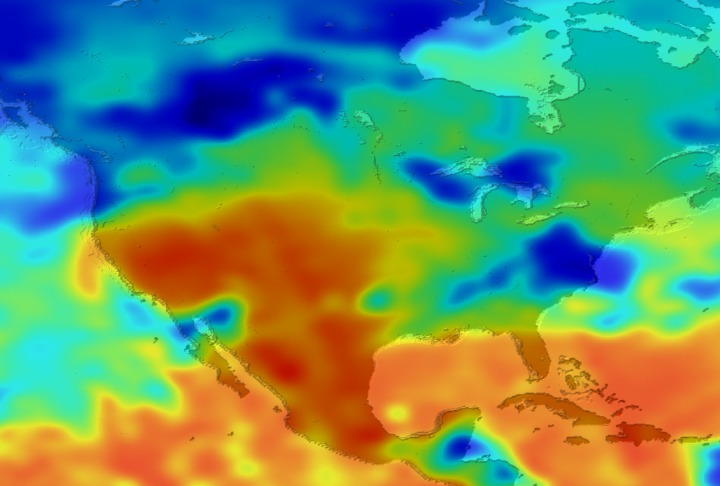
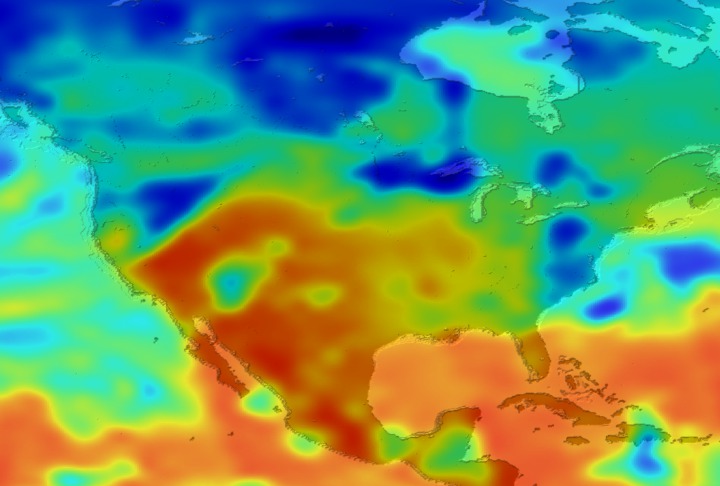
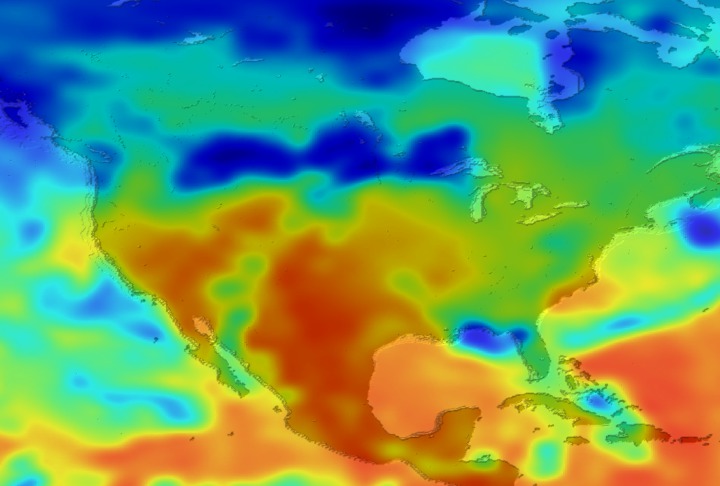
Daily Erythemal Index over the United States for July 2001
View of the United States with red (showing high levels of ground level ultraviolet radiation) covering the Western US and then changing to splotchy yellows, greens and blues as you move East (denoting lower levels of ground level ultraviolet radiation). Daily data is presented for July 1, 2001 through August 2, 2001.

August 1, 2001

August 2, 2001

July 1, 2001

July 2, 2001

July 3, 2001

July 1, 2001

July 5, 2001

July 6, 2001

July 7, 2001

July 8, 2001

July 9, 2001

July 10, 2001

July 11, 2001

July 12, 2001

July 13, 2001

July 14, 2001

July 15, 2001

July 16, 2001

July 17, 2001

July 18, 2001

July 19, 2001

July 20, 2001

July 21, 2001

July 22, 2001

July 23, 2001

July 24, 2001

July 25, 2001

July 26, 2001

July 27, 2001

July 28, 2001

July 29, 2001

July 30, 2001

July 31, 2001
Visualization Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio
NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio
Short URL to share this page:
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/2216
Data Used:
Note: While we identify the data sets used in these visualizations, we do not store any further details nor the data sets themselves on our site.
This item is part of this series:
Erythemal UV
Keywords:
DLESE >> Atmospheric science
SVS >> Erythemal
SVS >> Solar Radiation
SVS >> UV
SVS >> UV-B
NASA Science >> Earth
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/2216
Data Used:
Earth Probe/TOMS
2001/07/01-2001/08/02This item is part of this series:
Erythemal UV
Keywords:
DLESE >> Atmospheric science
SVS >> Erythemal
SVS >> Solar Radiation
SVS >> UV
SVS >> UV-B
NASA Science >> Earth