Earth
ID: 12072
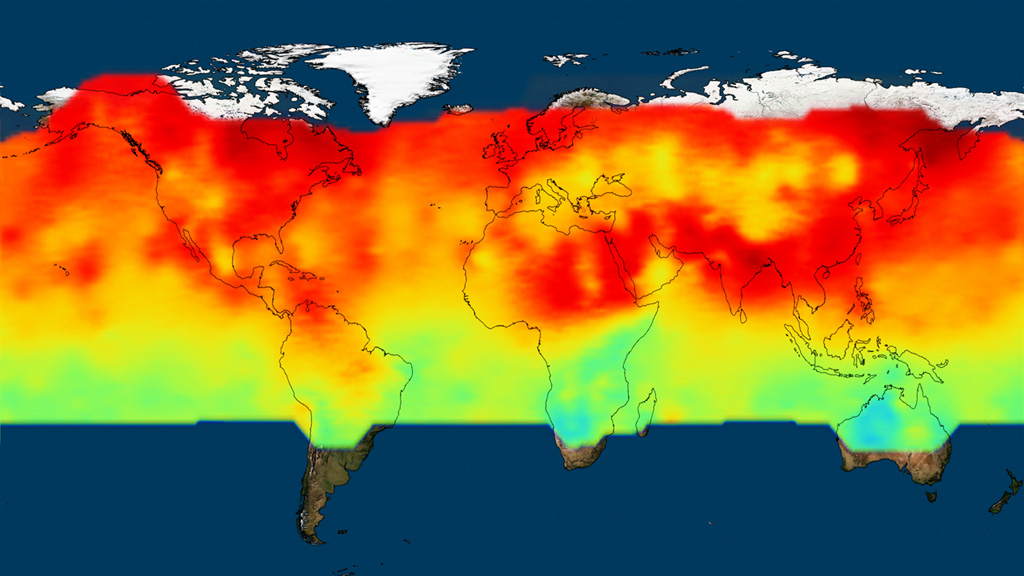
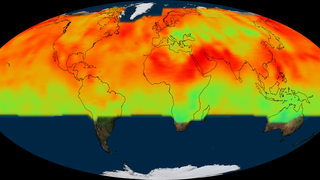
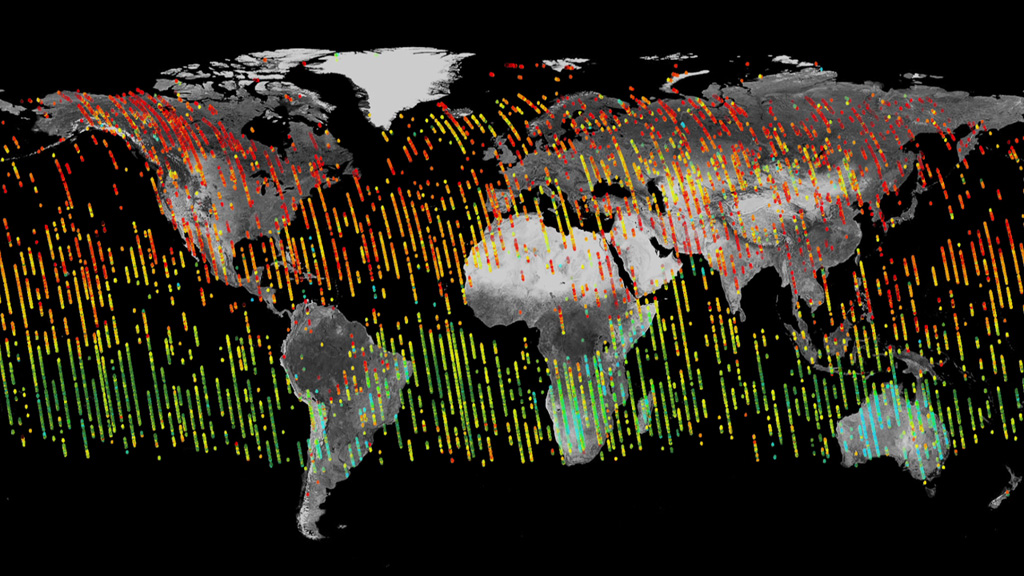
Levels of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide have risen sharply over the last 50 years due to human activity and the burning of fossil fuels. Today, about half of the carbon dioxide that’s emitted into the atmosphere is absorbed by Earth’s land and oceans. But exactly where the carbon ends up is not well understood. To get a clearer picture, NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, satellite is collecting measurements from space of carbon dioxide levels near the planet’s surface. By observing how concentrations vary over time, scientists can pinpoint areas on the globe that take up or release large amounts of the gas, and observe changes from season to season and year to year. The findings will help scientists quantify carbon dioxide sources and reservoirs, and determine what effect rising carbon dioxide levels might have in the future. Watch the video to see a visualization of the satellite’s first year of observations.


A New Picture of Carbon Dioxide




Related Story
For More Information
Story Credits
Lead Visualizer/Animator:
Alex Kekesi (Global Science and Technology, Inc.)
Visualizer/Animator:
Greg Shirah (NASA/GSFC)
Lead Producers:
Michelle Handleman (USRA)
Wade Sisler (NASA/GSFC)
Producer:
Matthew R. Radcliff (USRA)
Lead Scientist:
Annmarie Eldering (NASA/JPL CalTech)
Project Support:
Horace Mitchell (NASA/GSFC)
Lead Writer:
NASA Viz Team
Alex Kekesi (Global Science and Technology, Inc.)
Visualizer/Animator:
Greg Shirah (NASA/GSFC)
Lead Producers:
Michelle Handleman (USRA)
Wade Sisler (NASA/GSFC)
Producer:
Matthew R. Radcliff (USRA)
Lead Scientist:
Annmarie Eldering (NASA/JPL CalTech)
Project Support:
Horace Mitchell (NASA/GSFC)
Lead Writer:
NASA Viz Team
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
OCO-2 satellite and satellite data images courtesy of NASA/JPL
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
OCO-2 satellite and satellite data images courtesy of NASA/JPL
Short URL to share this page:
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/12072
Keywords:
NASA Science >> Earth
SVS >> App
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/12072
Keywords:
NASA Science >> Earth
SVS >> App