Earth
ID: 11893
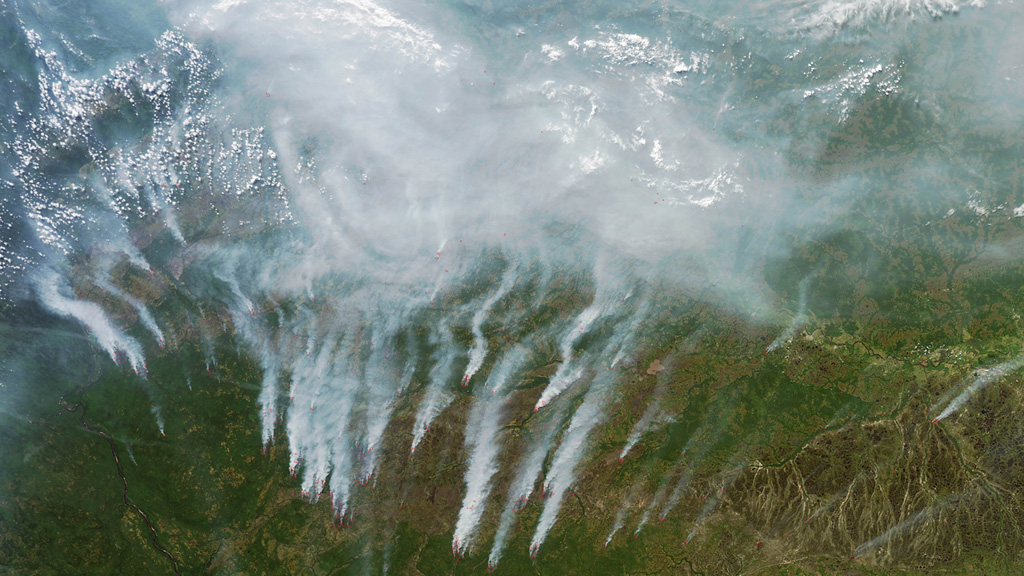

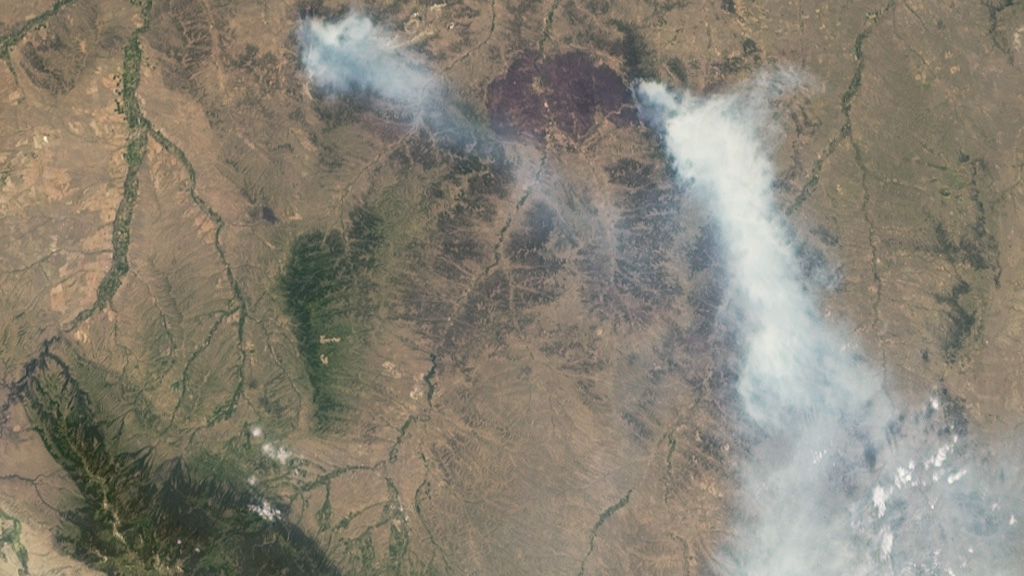
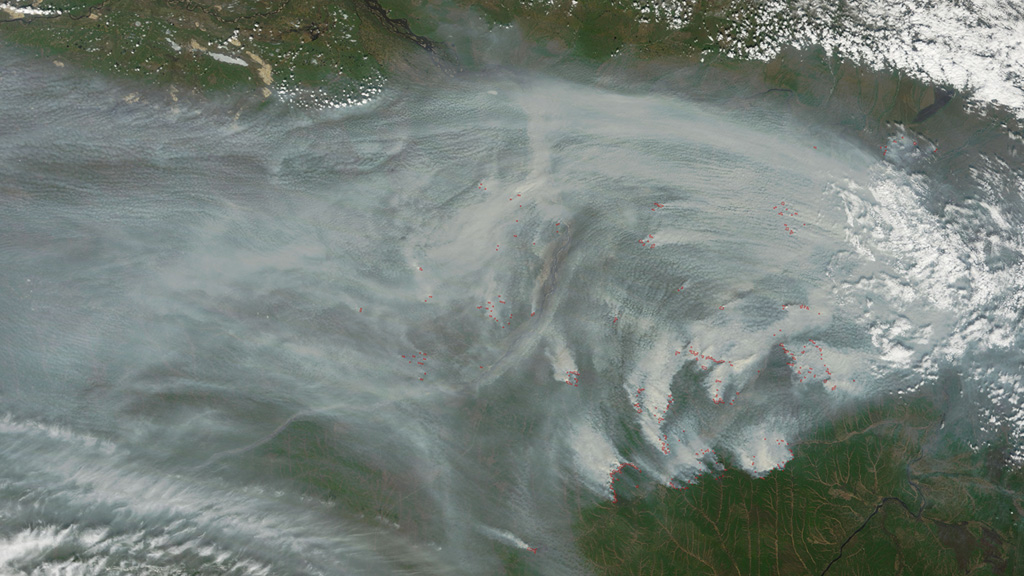
Wildfires in the Northern Hemisphere consume hundreds of thousands of acres of land each year. Temperature, dryness and lightning strikes are all factors that play a role in the number of fires sparked and total area burned. Sensors aboard NASA satellites can not only detect the heat given off by wildfires and number of active fires around the globe at any given time, but they also collect data and imagery of their smoke plumes. Smoke from wildfires can be carried by winds across state, country and even continental borders, impacting air quality in regions far from its source. Satellite observations have been instrumental in helping scientists learn more about how the smoke is transported in the atmosphere and measuring how far it travels. Explore the images to see views of wildfires taken from space.




Up In Smoke





Story Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
Cover image courtesy of NASA/GSFC/LANCE MODIS Rapid Response/J. Schmaltz
California wildfires image courtesy of NASA/GSFC/LaRC/JPL/MISR Team
Montana wildfires image courtesy of NASA/GSFC/LaRC/JPL/MISR Team
Canada wildfires image courtesy of NASA/GSFC/LANCE EODIS Rapid Response/J. Schmaltz
Russia wildfires image courtesy of NASA/GSFC/MODIS Rapid Response/J. Schmaltz
NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
Cover image courtesy of NASA/GSFC/LANCE MODIS Rapid Response/J. Schmaltz
California wildfires image courtesy of NASA/GSFC/LaRC/JPL/MISR Team
Montana wildfires image courtesy of NASA/GSFC/LaRC/JPL/MISR Team
Canada wildfires image courtesy of NASA/GSFC/LANCE EODIS Rapid Response/J. Schmaltz
Russia wildfires image courtesy of NASA/GSFC/MODIS Rapid Response/J. Schmaltz
Short URL to share this page:
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/11893
Keywords:
SVS >> App
NASA Science >> Earth
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/11893
Keywords:
SVS >> App
NASA Science >> Earth