Universe
ID: 11641

A nova is a sudden, short-lived explosion from a compact star not much larger than Earth. The outburst comes from a collapsed star known as a white dwarf, which circles so close to a normal star that a stream of gas flows between them. This gas piles up into a layer on the white dwarf's surface until it reaches a flash point and detonates in a runaway thermonuclear explosion. Astronomers estimate that between 20 and 50 novae occur each year in our galaxy, but despite their power most go undiscovered. NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope has observed several nearby novae and found that each blast produces gamma rays, the most energetic form of light. Scientists think the gamma rays result from collisions among multiple shock waves that race from the site of the explosion in a rapidly expanding shell of debris. Watch the video to see an animation of a nova eruption.
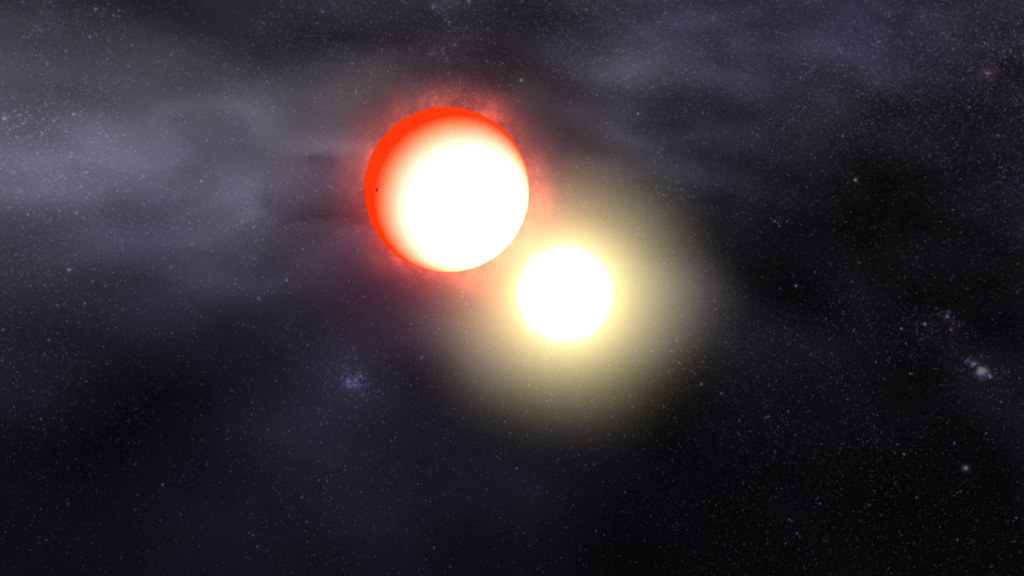


Cosmic Blast




Related Story
For More Information
Story Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Short URL to share this page:
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/11641
Keywords:
SVS >> Astrophysics
SVS >> App
NASA Science >> Universe
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/11641
Keywords:
SVS >> Astrophysics
SVS >> App
NASA Science >> Universe