Insolation during the 2024 Eclipse
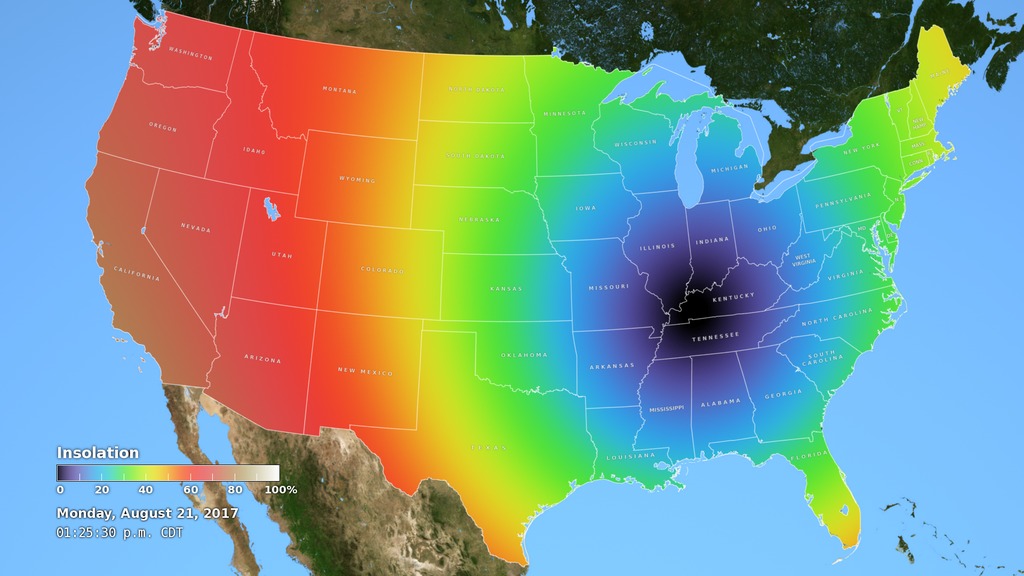
Insolation (the amount of sunlight reaching the ground) is affected dramatically by the Moon's shadow during the April 8, 2024 total solar eclipse.
On an ordinary day, the insolation – the amount of sunlight hitting a given spot on the Earth – is proportional to the sine of the Sun's altitude. When the Sun is 30° above the horizon, the sunlight energy per square meter is half of what it is when the Sun is directly overhead. This relationship is the reason that the tropics are hot and the poles are cold. Combined with day length, it's also the reason for the difference in temperature between the seasons at temperate latitudes.
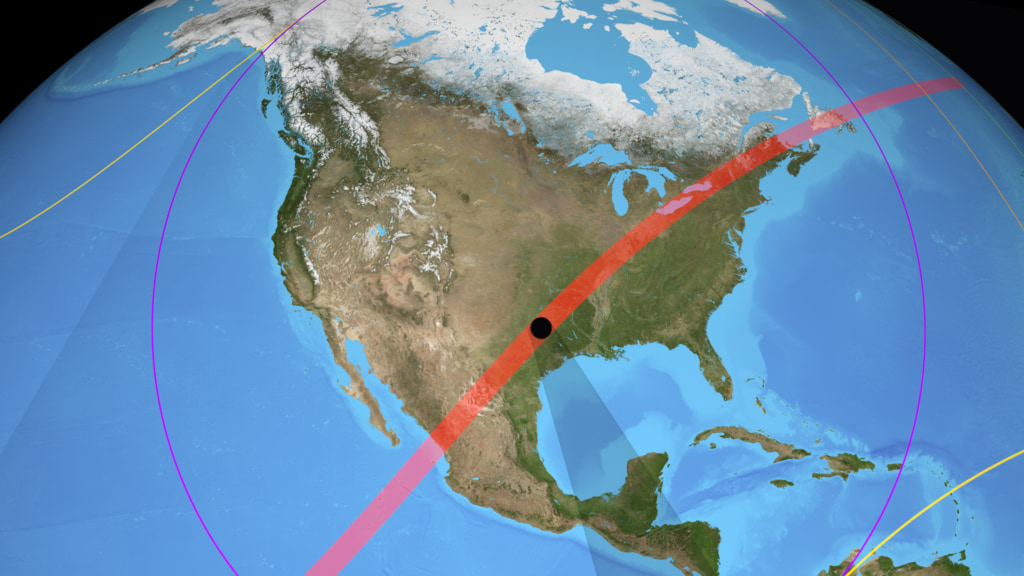
As this animation shows, the Moon's shadow dramatically, if temporarily, affects insolation in North America during the total solar eclipse of April 8, 2024. The effect is readily apparent to observers in the path of totality. As the umbra passes overhead, the temperature can drop by 10°F or more. The cooled column of air within the shadow cone can even influence cloud formation and the speed and direction of the wind.
The insolation map in the animation combines solar altitude with obscuration, the fraction of the Sun's area blocked by the Moon during the eclipse. It ignores a number of other factors, including atmospheric scattering, refraction, and cloud cover, that also play a big role in the amount of sunlight that reaches the ground.
A map-like view of the Earth shows insolation (sunlight intensity) over land during the April 8, 2024 total solar eclipse. This equirectangular projection is suitable for spherical displays and for spherical mapping in 3D animation software.

The color key for the insolation map.
The obscuration dataset used to calculate insolation. Obscuration, the fraction of the Sun's area covered by the Moon, is calculated at 10-second intervals from 15:42:10 to 20:52:20 UTC at a resolution of 360/8192 degrees per pixel (roughly 3.75 × 4.9 km at 40°N). The maps are global equirectangular projections centered on (0°, 0°), with white = 100% obscuration and black = 0%. The sharp borders are the terminator (the day-night line). The complete dataset can be downloaded as a single .zip file (194 MB).
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio
-
Visualizer
- Ernie Wright (USRA)
Release date
This page was originally published on Monday, March 25, 2024.
This page was last updated on Tuesday, March 26, 2024 at 12:36 PM EDT.
Series
This visualization can be found in the following series:Datasets used in this visualization
-
DE421 (JPL DE421)
ID: 752Planetary ephemerides
This dataset can be found at: http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/?ephemerides#planets
See all pages that use this dataset
Note: While we identify the data sets used in these visualizations, we do not store any further details, nor the data sets themselves on our site.