Hubble Maps Jupiter in 4k Ultra HD
New imagery from the Hubble Space Telescope is revealing details never before seen on Jupiter. Hubble’s new Jupiter maps were used to create this Ultra HD animation.
Watch this video on the NASA Explorer YouTube channel.
These new maps and spinning globes of Jupiter were made from observations performed with NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. They are the first products to come from a program to study the solar system’s outer planets – Jupiter, Uranus, Neptune and, later, Saturn – each year using Hubble. The observations are designed to capture a broad range of features, including winds, clouds, storms and atmospheric chemistry. These annual studies will help current and future scientists see how these giant worlds change over time.
Scientists at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, and the University of California at Berkeley produced two global maps of Jupiter from the observations, which were made using Hubble’s high-performance Wide Field Camera 3.
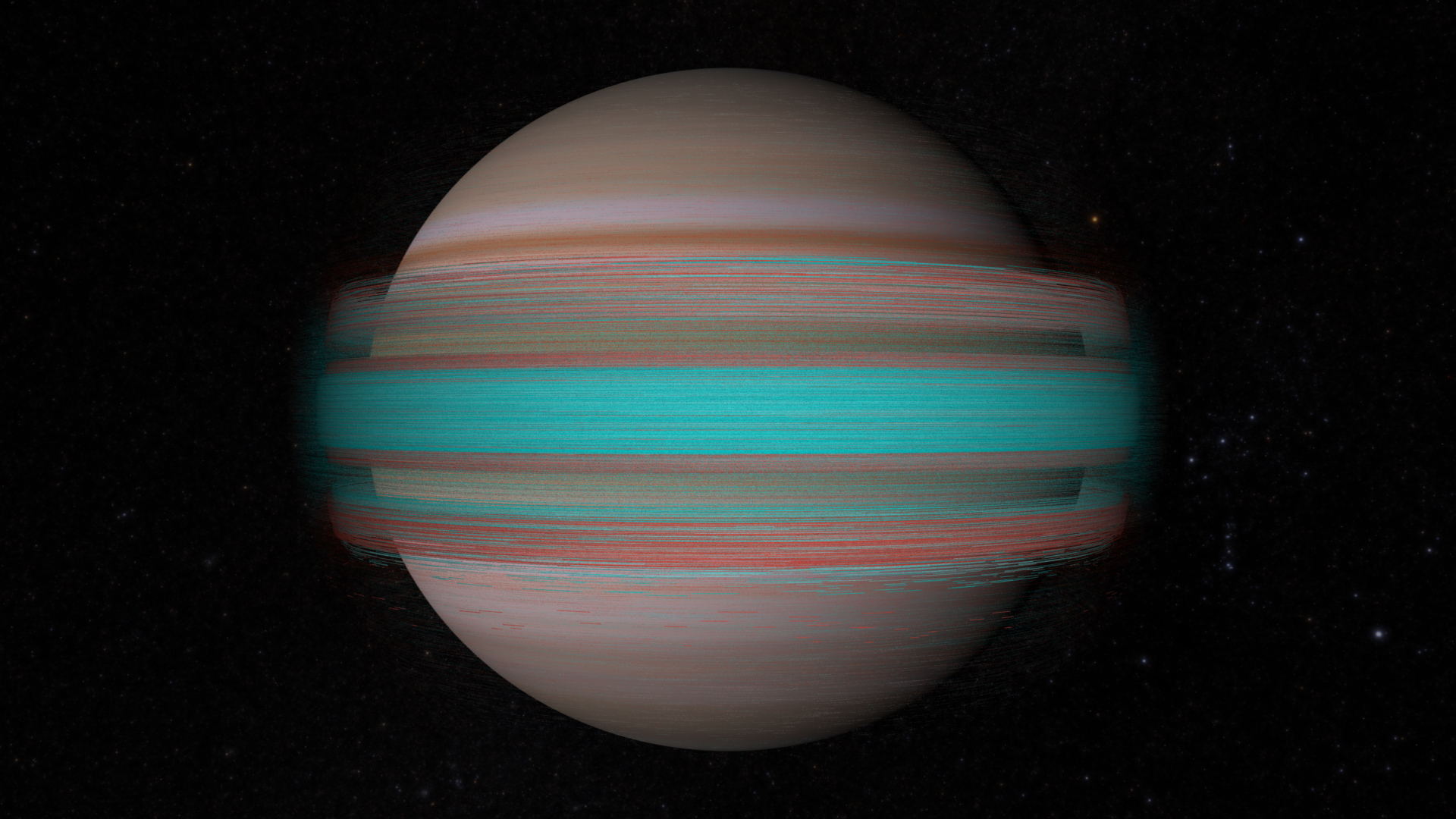
The two maps represent nearly back-to-back rotations of the planet, making it possible to determine the speeds of Jupiter’s winds. Already, the images have revealed a rare wave just north of the planet’s equator and a unique filament-like feature in the core of the Great Red Spot that had not been seen previously.
In addition, the new images confirm that the Great Red Spot continues to shrink and become more circular, as it has been doing for years. The long axis of this characteristic storm is about 150 miles (240 kilometers) shorter now than it was in 2014. Recently, the storm had been shrinking at a faster-than-usual rate, but the latest change is consistent with the long-term trend.
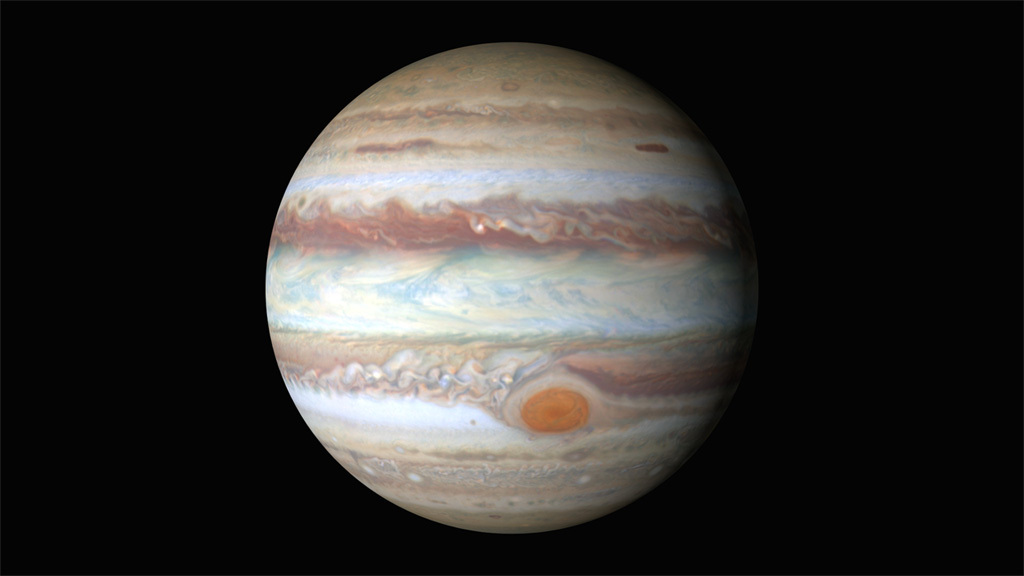
Spinning globe of Jupiter, made from first new Hubble map
Spinning globe of Jupiter, made from second new Hubble map

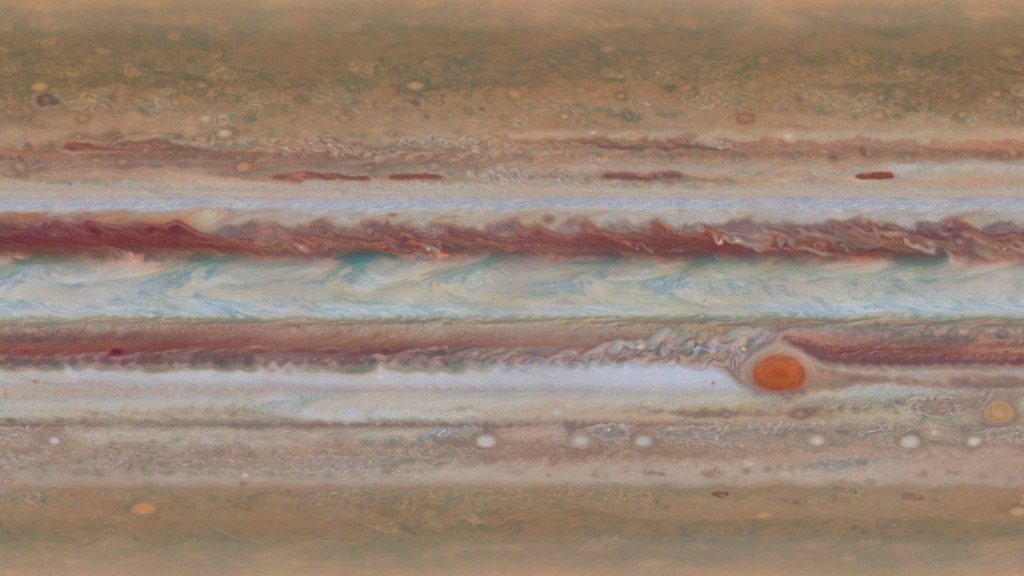
First global map of Jupiter (flat)

Second global map of Jupiter (flat)
The motions of clouds can be seen in this short sequence that alternates between the first and second maps of Jupiter.

The motions of clouds, with close-ups showing the movement of a unique filament, not seen before, in the Great Red Spot. The Great Red Spot is shown at blue (left) and red (right) wavelengths.

In Jupiter’s North Equatorial Belt, scientists spotted a rare wave that had been seen there only once before. It is similar to a wave that sometimes occurs in Earth’s atmosphere when cyclones are forming. This false-color close-up of Jupiter shows cyclones (arrows) and the wave (vertical lines). This image is available with and without annotations.
For More Information
See NASA.gov
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Space Telescope Science Institute
-
Science writer
- Elizabeth Zubritsky (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
-
Scientists
- Amy A. Simon (NASA/GSFC)
- Michael H. Wong (University of California at Berkeley)
- Glenn Orton (NASA/JPL CalTech)
-
Animator
- Greg Bacon (STScI/Aura)
-
Editor
- Dan Gallagher (USRA)
-
Technical support
- Michael Randazzo (Advocates in Manpower Management, Inc.)
- Aaron E. Lepsch (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
Missions
This page is related to the following missions:Tapes
The media on this page originally appeared on the following tapes:-
Jupiter in 4k Ultra HD
(ID: 2015085)
Tuesday, October 13, 2015 at 4:00AM
Produced by - Dan Jacob (Global Science and Technology, Inc.)
Release date
This page was originally published on Tuesday, October 13, 2015.
This page was last updated on Monday, January 6, 2025 at 1:28 AM EST.




![Music credit: "Triangulate" by Gianluigi Gallo [PRS]; El Murmullo Sarao SGAE, Universal Sarao SGAE; SaraoMusic; Killer Tracks Production MusicWatch this video on the NASA Goddard YouTube channel.](/vis/a010000/a012500/a012570/Hubble_Jupiter_Opposition_thumbnail.png)