ID: 30775
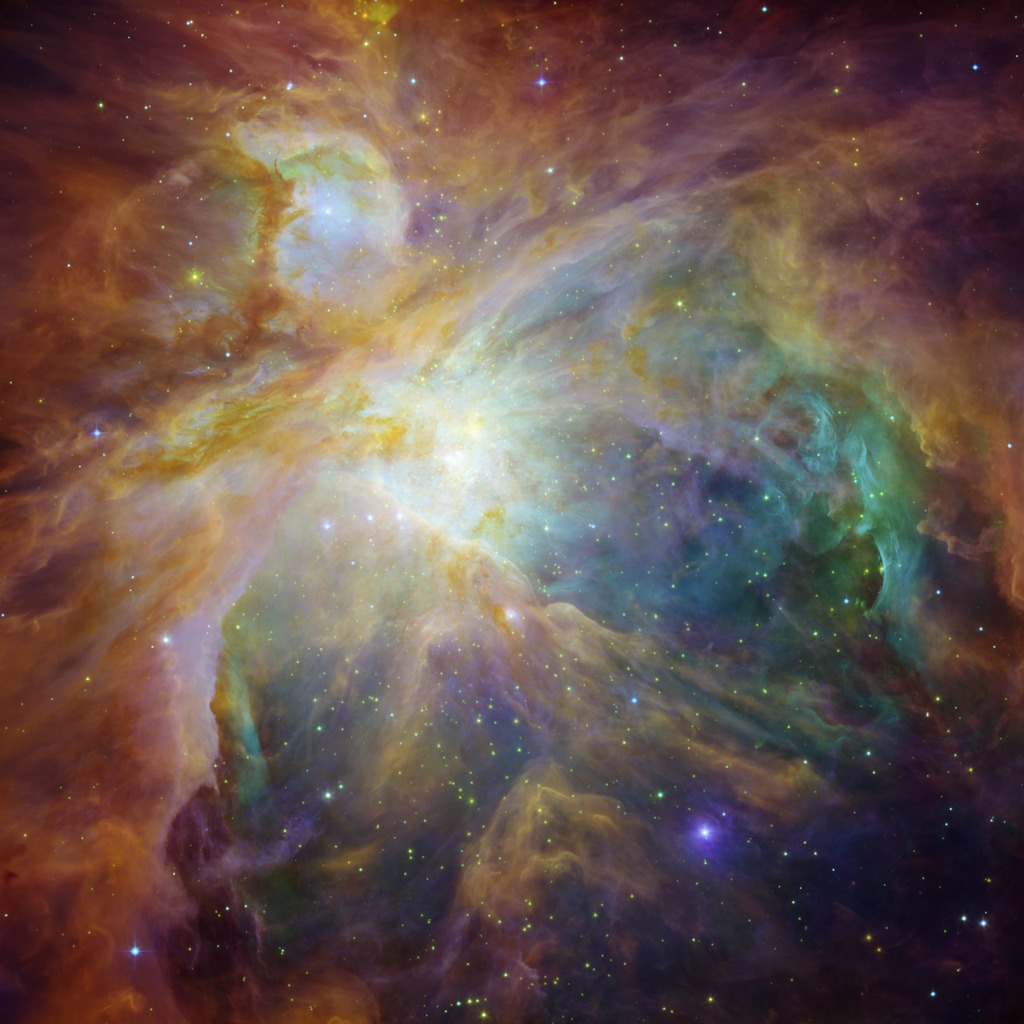

A composite image from NASA's Hubble and Spitzer Space Telescopes looks more like an abstract painting than a cosmic snapshot. The magnificent masterpiece shows the Orion nebula in an explosion of infrared, ultraviolet and visible-light colors. It was "painted" by hundreds of baby stars on a canvas of gas and dust, with intense ultraviolet light and strong stellar winds as brushes.
At the heart of the artwork is a set of four monstrously massive stars, collectively called the Trapezium. These behemoths are approximately 100,000 times brighter than our sun. Their community can be identified as the yellow smudge near the center of the composite.
The swirls of green were revealed by Hubble's ultraviolet and visible-light detectors. They are hydrogen and sulfur gases heated by intense ultraviolet radiation from the Trapezium's stars.
Wisps of red, also detected by Spitzer, indicate infrared light from illuminated clouds containing carbon-rich molecules called polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. On Earth, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are found on burnt toast and in automobile exhaust.
Additional stars in Orion are sprinkled throughout the image in a rainbow of colors. Spitzer exposed infant stars deeply embedded in a cocoon of dust and gas (orange-yellow dots). Hubble found less embedded stars (specks of green) and stars in the foreground (blue). Stellar winds from clusters of newborn stars scattered throughout the cloud etched all of the well-defined ridges and cavities.
Located 1,500 light-years away from Earth, the Orion nebula is the brightest star in the sword of the hunter constellation. The cosmic cloud is also our closest massive star-formation factory, and astronomers suspect that it contains several thousand young stars.
Hubble and Spitzer Composite of the Orion Nebula

At the heart of the artwork is a set of four monstrously massive stars, collectively called the Trapezium. These behemoths are approximately 100,000 times brighter than our sun. Their community can be identified as the yellow smudge near the center of the composite.
The swirls of green were revealed by Hubble's ultraviolet and visible-light detectors. They are hydrogen and sulfur gases heated by intense ultraviolet radiation from the Trapezium's stars.
Wisps of red, also detected by Spitzer, indicate infrared light from illuminated clouds containing carbon-rich molecules called polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. On Earth, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are found on burnt toast and in automobile exhaust.
Additional stars in Orion are sprinkled throughout the image in a rainbow of colors. Spitzer exposed infant stars deeply embedded in a cocoon of dust and gas (orange-yellow dots). Hubble found less embedded stars (specks of green) and stars in the foreground (blue). Stellar winds from clusters of newborn stars scattered throughout the cloud etched all of the well-defined ridges and cavities.
Located 1,500 light-years away from Earth, the Orion nebula is the brightest star in the sword of the hunter constellation. The cosmic cloud is also our closest massive star-formation factory, and astronomers suspect that it contains several thousand young stars.
Related
For More Information
Credits
Frank Summers (STScI): Project Support
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA, ESA, T. Megeath (University of Toledo) and M. Robberto (STScI)
NASA, ESA, T. Megeath (University of Toledo) and M. Robberto (STScI)
Short URL to share this page:
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/30775
Missions:
Hubble
Spitzer Space Telescope
Keywords:
SVS >> Infrared
SVS >> Hyperwall
SVS >> Hubble Space Telescope
SVS >> Astrophysics
SVS >> Universe
SVS >> Spitzer
SVS >> Nebula
SVS >> Star Formation
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/30775
Missions:
Hubble
Spitzer Space Telescope
Keywords:
SVS >> Infrared
SVS >> Hyperwall
SVS >> Hubble Space Telescope
SVS >> Astrophysics
SVS >> Universe
SVS >> Spitzer
SVS >> Nebula
SVS >> Star Formation