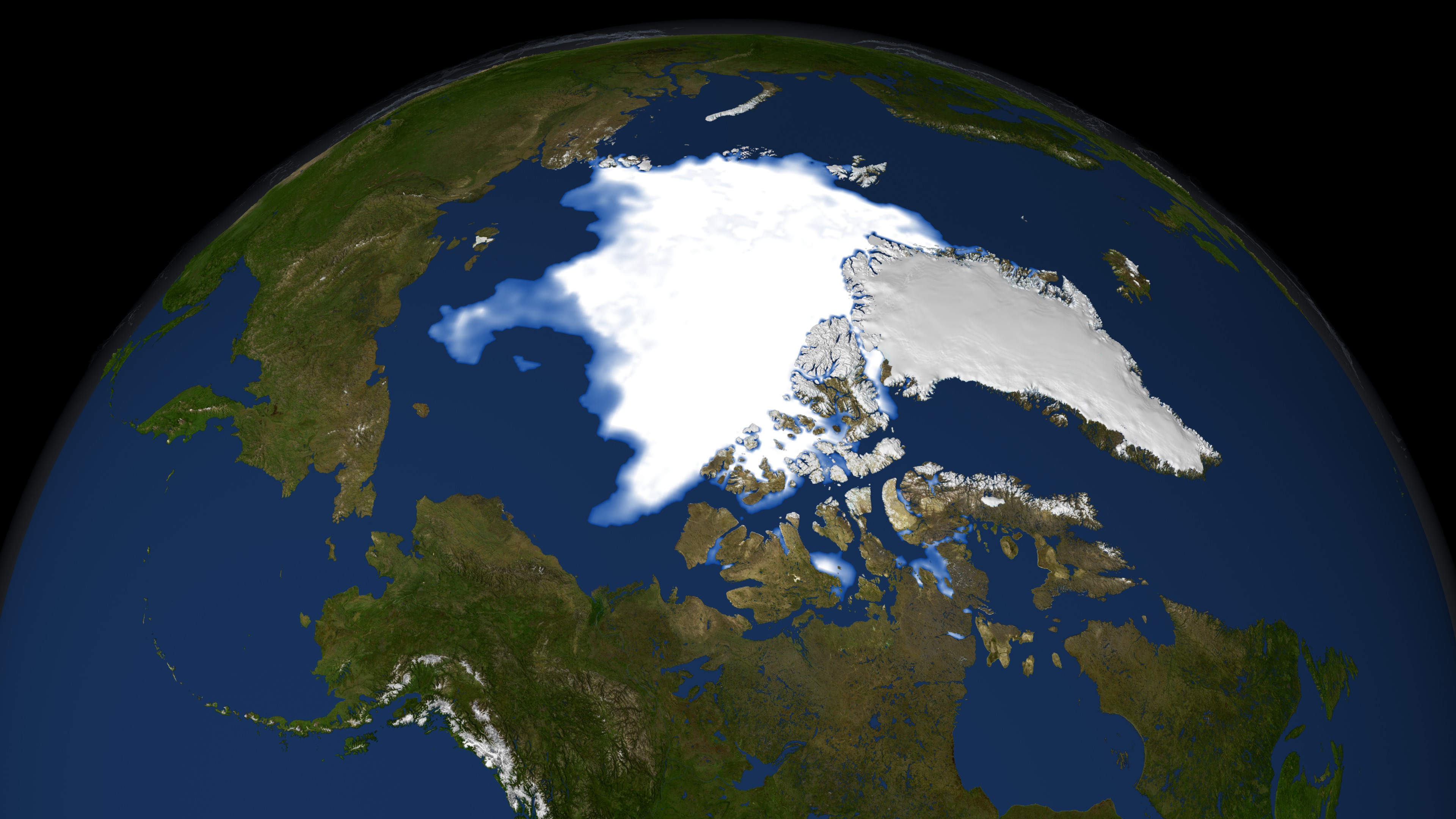
Earth
ID: 3802
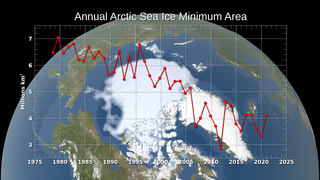
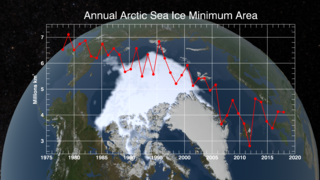
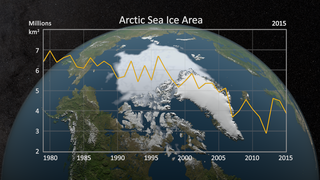
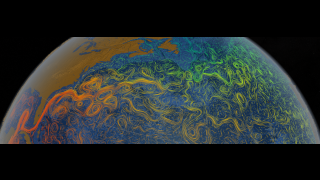
The continued significant reduction in the extent of the summer sea ice cover is a dramatic illustration of the pronounced impact increased global temperatures are having on the Arctic regions. There has also been a significant reduction in the relative amount of older, thicker ice. Satellite-based passive microwave images of the sea ice cover have provided a reliable tool for continuously monitoring changes in the extent of the Arctic ice cover since 1979. The ice parameters derived from satellite ice concentration data that are most relevant to climate change studies are sea ice extent and ice area. This visualization shows ice extent in the background and ice area in the foreground. Ice extent is defined here as the integrated sum of the areas of data elements (pixels) with at least 15% ice concentration while ice area is the integrated sum of the products of the area of each pixel and the corresponding ice concentration. Ice extent provides information about how far south (or north) the ice extends in winter and how far north (or south) it retreats toward the continent in the summer while the ice area provides the total area actually covered by sea ice which is useful for estimating the total volume and therefore mass, given the average ice thickness. For more information about these ice datasets, see The Journal of Geophysical Research VOL. 113, C02S07, doi:10.1029/2007JC004257, 2008

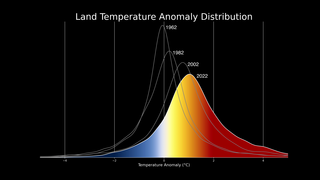
Sea Ice Yearly Minimum 1979-2010 (SSMI data)
There is a newer version of this story located here: https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/5170
In 2007, Arctic summer sea ice reached its lowest extent on record - nearly 25% less than the previous low set in 2005. At the end of each summer, the sea ice cover reaches its minimum extent and what is left is what is called the perennial ice cover which consists mainly of thick multi-year ice flows. The area of the perennial ice has been steadily decreasing since the satellite record began in 1979, at a rate of about 10% per decade.
This visualization shows the annual Arctic sea ice minimum from 1979 to 2010. A graph is overlaid that shows the area in million square kilometers for each year's minimum day. The 1979, 2007, and 2010 data points are highlighted on the graph.


Newer Versions
Related
Visualization Credits
Lori Perkins (NASA/GSFC): Lead Animator
Greg Shirah (NASA/GSFC): Animator
Josefino Comiso (NASA/GSFC): Scientist
Robert Gersten (RSIS): Project Support
Greg Shirah (NASA/GSFC): Animator
Josefino Comiso (NASA/GSFC): Scientist
Robert Gersten (RSIS): Project Support
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio Thanks to Rob Gerston (GSFC) for providing the data.
NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio Thanks to Rob Gerston (GSFC) for providing the data.
Short URL to share this page:
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/3802
Data Used:
Note: While we identify the data sets used in these visualizations, we do not store any further details nor the data sets themselves on our site.
This item is part of these series:
28 Year Arctic Temperature Trend
Arctic Sea Ice
Arctic Annual Sea Ice Minimum with Graph Overlay
Keywords:
DLESE >> Cryology
SVS >> HDTV
GCMD >> Earth Science >> Cryosphere >> Sea Ice
GCMD >> Earth Science >> Cryosphere >> Sea Ice >> Sea Ice Concentration
SVS >> iPod
NASA Science >> Earth
GCMD keywords can be found on the Internet with the following citation: Olsen, L.M., G. Major, K. Shein, J. Scialdone, S. Ritz, T. Stevens, M. Morahan, A. Aleman, R. Vogel, S. Leicester, H. Weir, M. Meaux, S. Grebas, C.Solomon, M. Holland, T. Northcutt, R. A. Restrepo, R. Bilodeau, 2013. NASA/Global Change Master Directory (GCMD) Earth Science Keywords. Version 8.0.0.0.0
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/3802
Data Used:
Comiso's September Minimum Sea Ice Concentration
Data Compilation - NASA/GSFC - 1979 - 2010DMSP/SSM/I
1979 - 2010
Defense Meteorological Satellite Program Special Sensor Microwave Imager
This item is part of these series:
28 Year Arctic Temperature Trend
Arctic Sea Ice
Arctic Annual Sea Ice Minimum with Graph Overlay
Keywords:
DLESE >> Cryology
SVS >> HDTV
GCMD >> Earth Science >> Cryosphere >> Sea Ice
GCMD >> Earth Science >> Cryosphere >> Sea Ice >> Sea Ice Concentration
SVS >> iPod
NASA Science >> Earth
GCMD keywords can be found on the Internet with the following citation: Olsen, L.M., G. Major, K. Shein, J. Scialdone, S. Ritz, T. Stevens, M. Morahan, A. Aleman, R. Vogel, S. Leicester, H. Weir, M. Meaux, S. Grebas, C.Solomon, M. Holland, T. Northcutt, R. A. Restrepo, R. Bilodeau, 2013. NASA/Global Change Master Directory (GCMD) Earth Science Keywords. Version 8.0.0.0.0