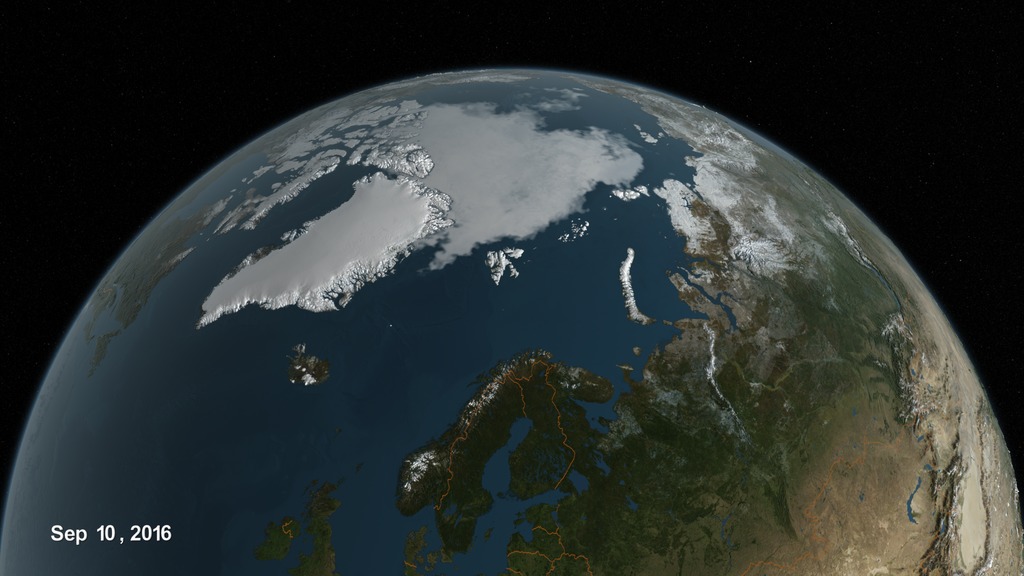
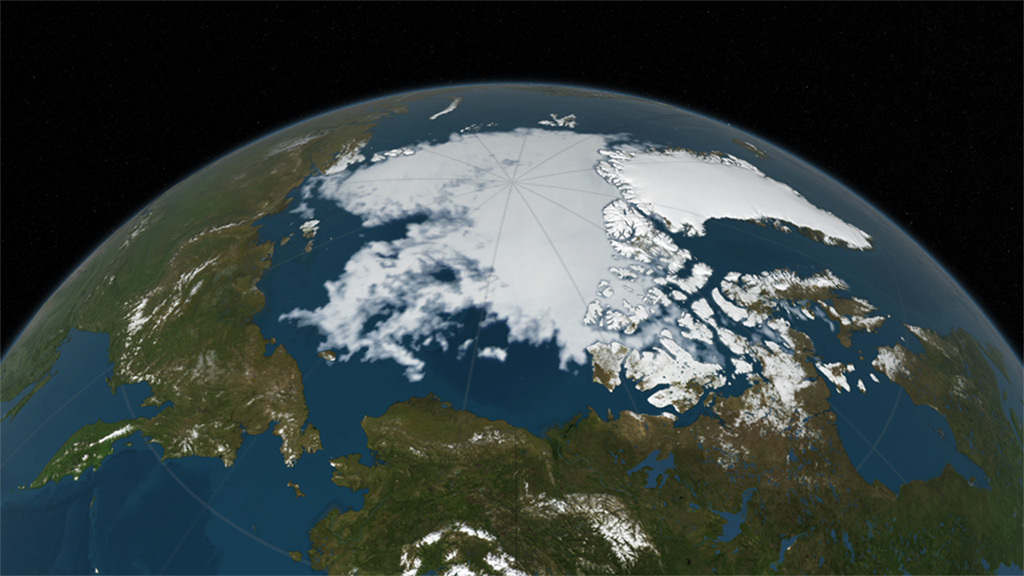
A New Forecast Model Predicts Arctic Sea Ice Extent
Arctic sea ice extent ebbs and flows with the seasons. During the summer months, the ice melts and the edge recedes northward, usually reaching its annual minimum sometime in September.
The ice extent is shaped by a variety of factors, including warmer temperatures, storms, and changes in the ocean, which makes it difficult to predict.
Sea ice plays an important role in maintaining Earth's temperature, so predicting how the ice extent might change helps us understand the warming climate.
Scientists have developed a new model to predict the sea ice minimum extent, using historical measurements and real-time satellite data. The model can begin predictions up to six months before the predicted minimum and continue to improve each day.

This forecasting model can predict sea ice extent in specific regions, like the seas north of Alaska.

The model uses satellites to detect open water and surface melting to help improve predictions.
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
-
Writer
- Maria-Jose Vinas Garcia (Telophase)
-
Producer
- Kathryn Mersmann (USRA)
-
Scientist
- Alek A. Petty (University of Maryland)
Release date
This page was originally published on Thursday, March 2, 2017.
This page was last updated on Wednesday, May 3, 2023 at 1:47 PM EDT.