Earth
ID: 10863
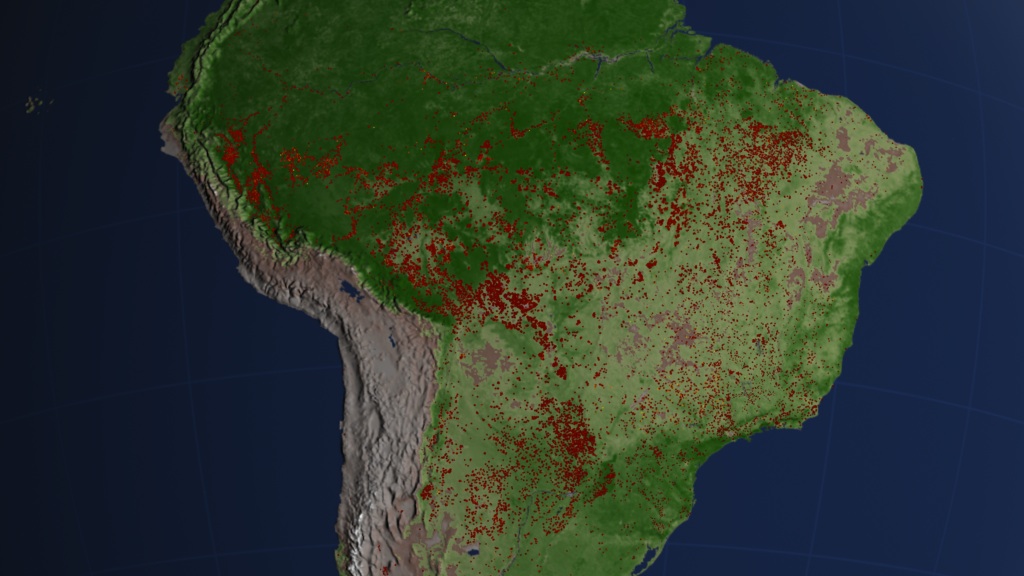
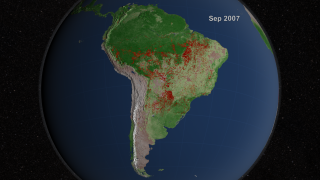
Human settlement patterns are the primary factor that drives the distribution of fires in the Amazon. Satellite imagery shows, for example, that fishbone-shaped patterns of burned and deforested land extend outward from roads in predictable ways. Likewise, fires are rare in thinly populated areas. In recent years, however, new research has made clear that subtle environmental factors -- including minor variations in ocean temperatures -- amplify human impacts and underpin much of the variability in the number of fires the region experiences from one year to the next. A study conducted by UC Irvine scientists and published last week in Science even showed that scientists can predict the severity of the South American fire season months in advance by analyzing ocean temperatures in the North Atlantic and Central Pacific Oceans. To make the discovery, the researchers compared about a decade of fire observations collected by NASA's Terra and Aqua satellites with records of sea surface temperatures maintained by NOAA. The video below offers a visual representation of the same decade of fire data the scientists used to conduct their study. Look closely to see if you can spot the especially intense fires seasons of 2005, 2007 and 2010.
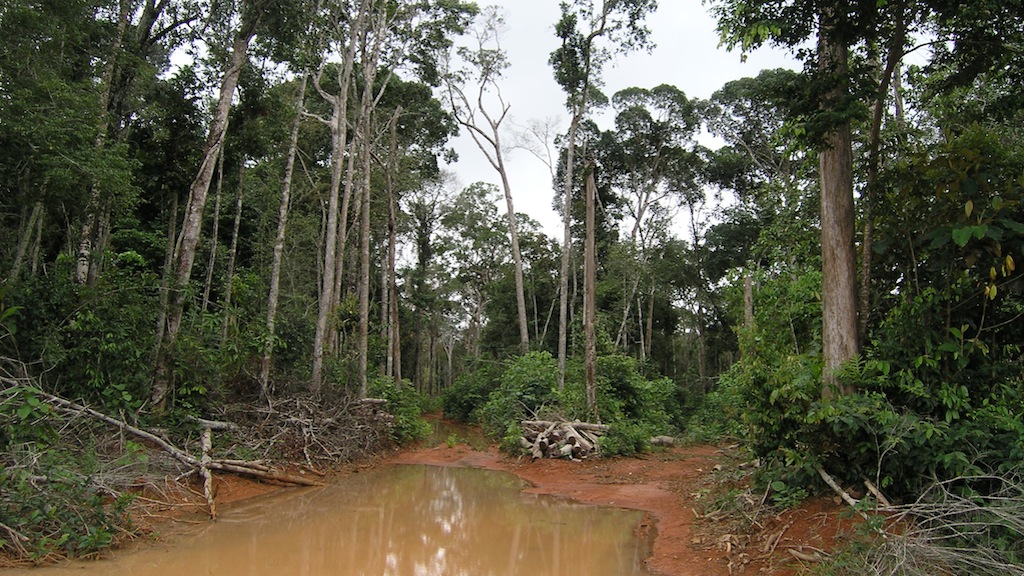
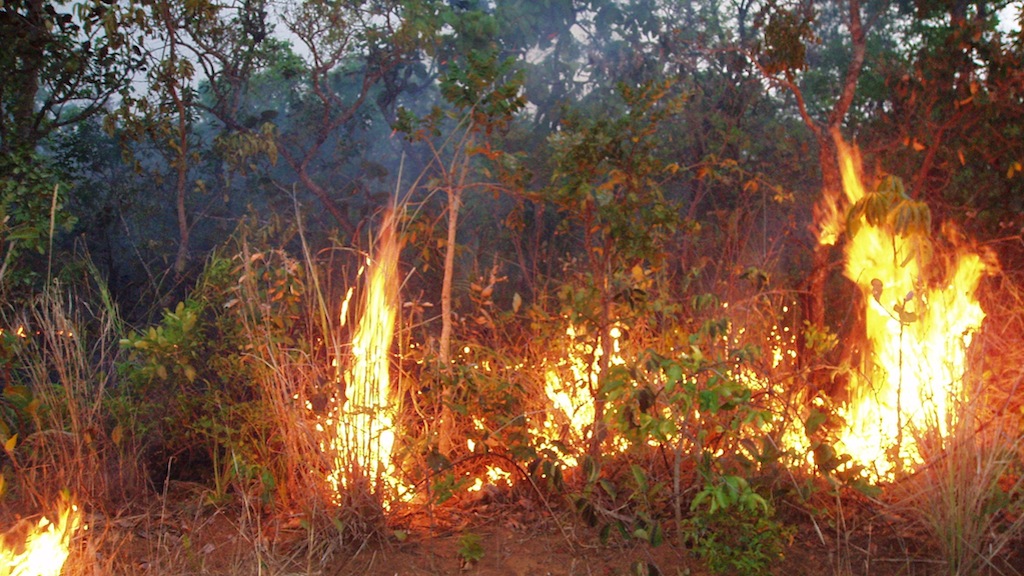
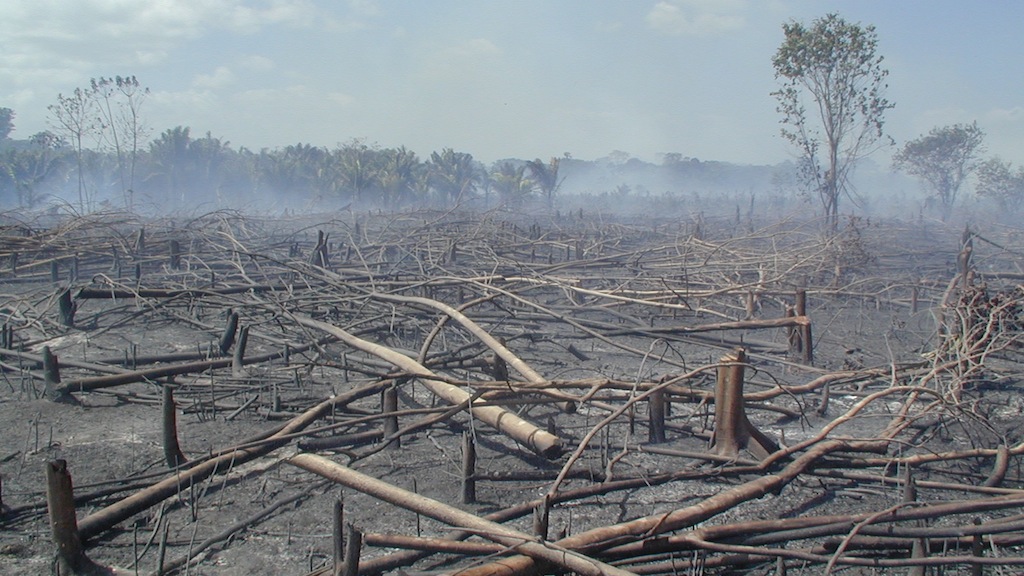



Forecasting South American Fires




Related Stories
For More Information
Story Credits
Visualizers/Animators:
Lori Perkins (NASA/GSFC)
Greg Shirah (NASA/GSFC)
Interviewee:
Jim Randerson (University of California, Irvine)
Producer:
Kayvon Sharghi (USRA)
Lead Scientists:
Chris Justice (University of Maryland)
Louis Giglio (University of Maryland)
Luigi Boschetti Ph.D. (University Of Maryland College Park)
Lead Writer:
Adam P Voiland (Wyle Information Systems)
Lori Perkins (NASA/GSFC)
Greg Shirah (NASA/GSFC)
Interviewee:
Jim Randerson (University of California, Irvine)
Producer:
Kayvon Sharghi (USRA)
Lead Scientists:
Chris Justice (University of Maryland)
Louis Giglio (University of Maryland)
Luigi Boschetti Ph.D. (University Of Maryland College Park)
Lead Writer:
Adam P Voiland (Wyle Information Systems)
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center.
Forest photographs courtesy of NASA/GSFC/Doug Morton.
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center.
Forest photographs courtesy of NASA/GSFC/Doug Morton.
Science Paper:
http://www.sciencemag.org/content/334/6057/787.abstract
Short URL to share this page:
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/10863
Keywords:
SVS >> App
NASA Science >> Earth
http://www.sciencemag.org/content/334/6057/787.abstract
Short URL to share this page:
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/10863
Keywords:
SVS >> App
NASA Science >> Earth