Shadows near the Moon's South Pole
This video shows the movement of shadows near the Moon's South Pole, over the course of two lunar days, which is approximately two months on Earth. The visualization was created from data gathered by the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter spacecraft.
Music Provided by Universal Production Music: “Two Horizons” – Anthony d’Amario
Watch this video on the NASA Goddard YouTube channel.
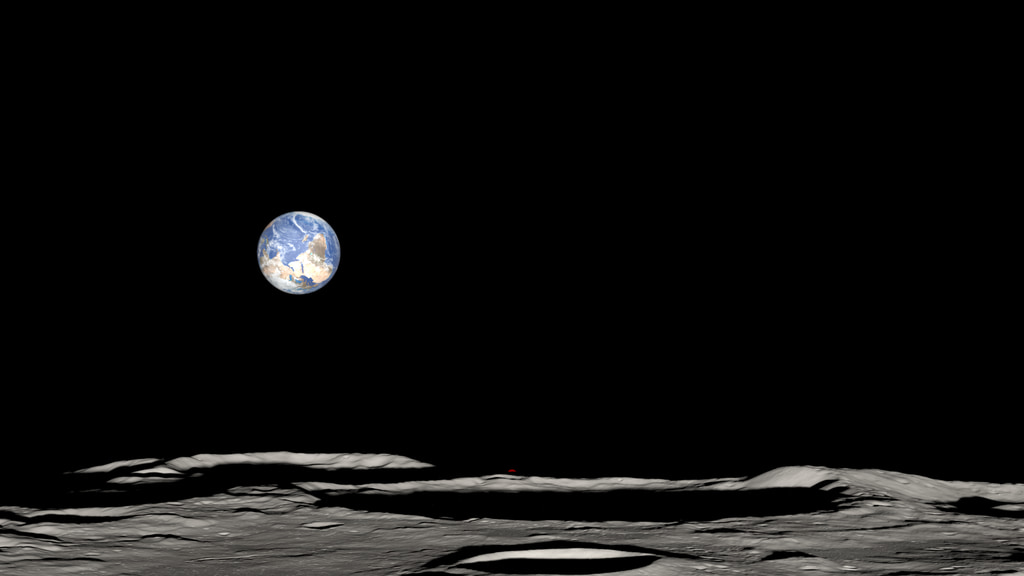
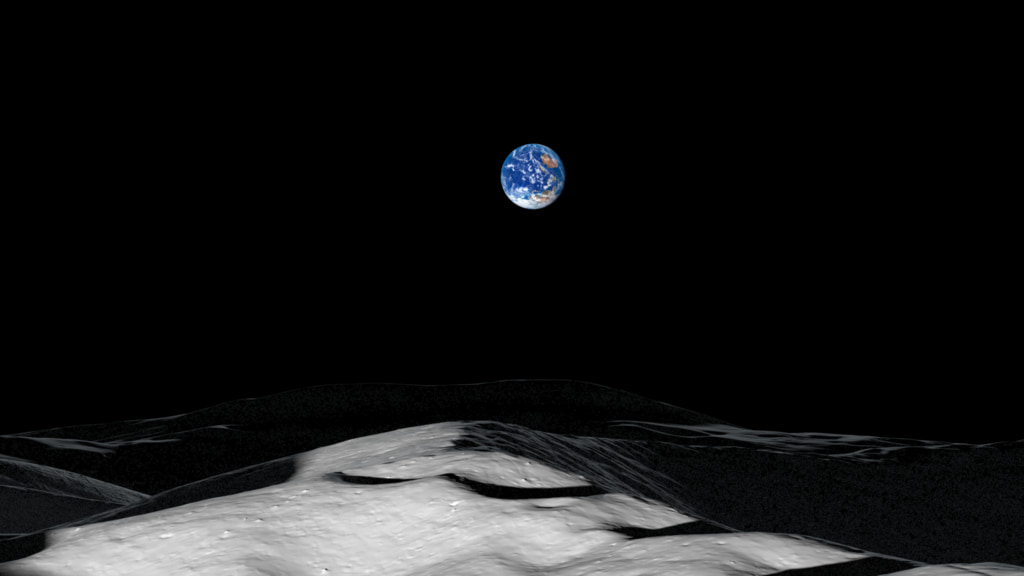
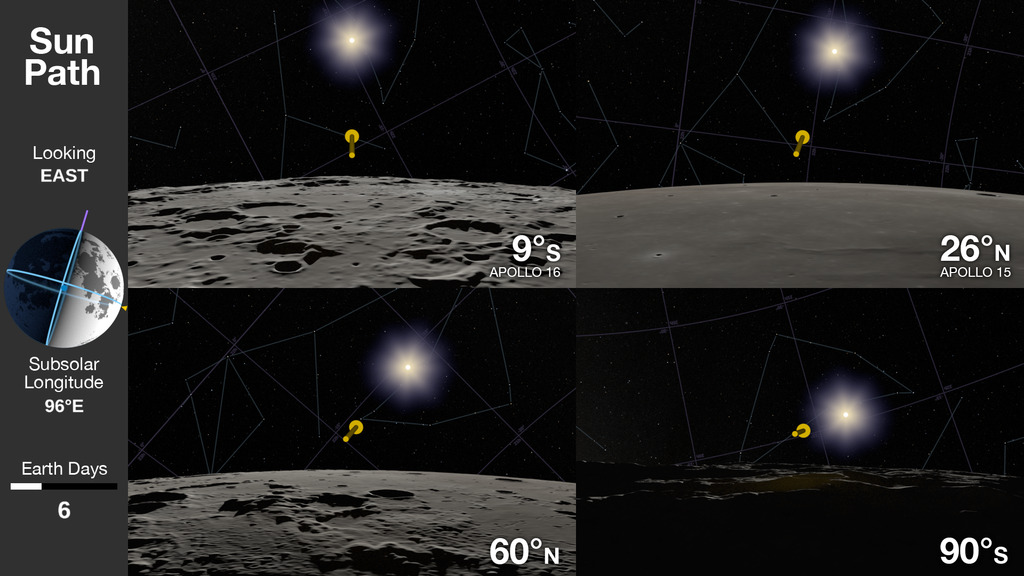
At the Moon's North and South Poles, the Sun is never more than 1.5° above or below the horizon. The resulting pattern of daylight and shadows is unlike anywhere else on the Moon — or the Earth. After zooming in on a small lunar highland area near the South Pole, this visualization recreates the illumination conditions there over a period of two lunar days, equal to two months on Earth.
This close to the pole, the Sun doesn't rise and set. Instead, as the Moon rotates on its axis, the Sun skims the horizon, traveling a full 360 degrees around the terrain. Mountains as far as 75 miles (120 kilometers) away cast shadows across the landscape. With the Sun at such a low angle, it can never reach the floors of some deep craters. Places the Sun never reaches are known as permanently shadowed regions. They are the locations of some of the coldest spots in the solar system, and because of that, they trap volatile chemicals, including water ice, that would immediately sublimate (transform directly from a solid to a gas) in the harsh, airless sunshine that falls in most other places on the Moon.
The Sun appears to travel in a circle at the Earth's poles, too, but it also travels through a range of altitudes. From spring equinox to summer solstice, for example, the Sun is climbing higher in the sky, reaching an altitude of 23.4°. It only hugs the horizon for a few days around the equinoxes. At the Moon's poles, the Sun is always near the horizon, and the shadows are perpetually long, sweeping across the surface with the changing solar azimuth.
Music Only version (no narration).
Music Provided by Universal Production Music: “Two Horizons” – Anthony d’Amario
Visualization with icons. No audio.
Visualization only (No audio, no icons)
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio
Music Provided by Universal Production Music: "Two Horizons" – Anthony d’Amario
-
Visualizer
- Ernie Wright (USRA)
-
Producer
- David Ladd (USRA)
-
Video editor
- David Ladd (USRA)
-
Narrator
- David Ladd (USRA)
-
Scientist
- Noah Petro (NASA/GSFC)
-
Technical support
- Laurence Schuler (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
- Ian Jones (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
Release date
This page was originally published on Thursday, April 1, 2021.
This page was last updated on Monday, July 15, 2024 at 12:09 AM EDT.
Missions
This visualization is related to the following missions:Datasets used in this visualization
-
DEM (Digital Elevation Map) [LRO: LOLA]
ID: 653 -
LROC WAC Color Mosaic (Natural Color Hapke Normalized WAC Mosaic) [Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter: LRO Camera]
ID: 1015This natural-color global mosaic is based on the 'Hapke normalized' mosaic from LRO's wide-angle camera. The data has been gamma corrected, white balanced, and range adjusted to more closely match human vision.
See all pages that use this dataset
Note: While we identify the data sets used in these visualizations, we do not store any further details, nor the data sets themselves on our site.