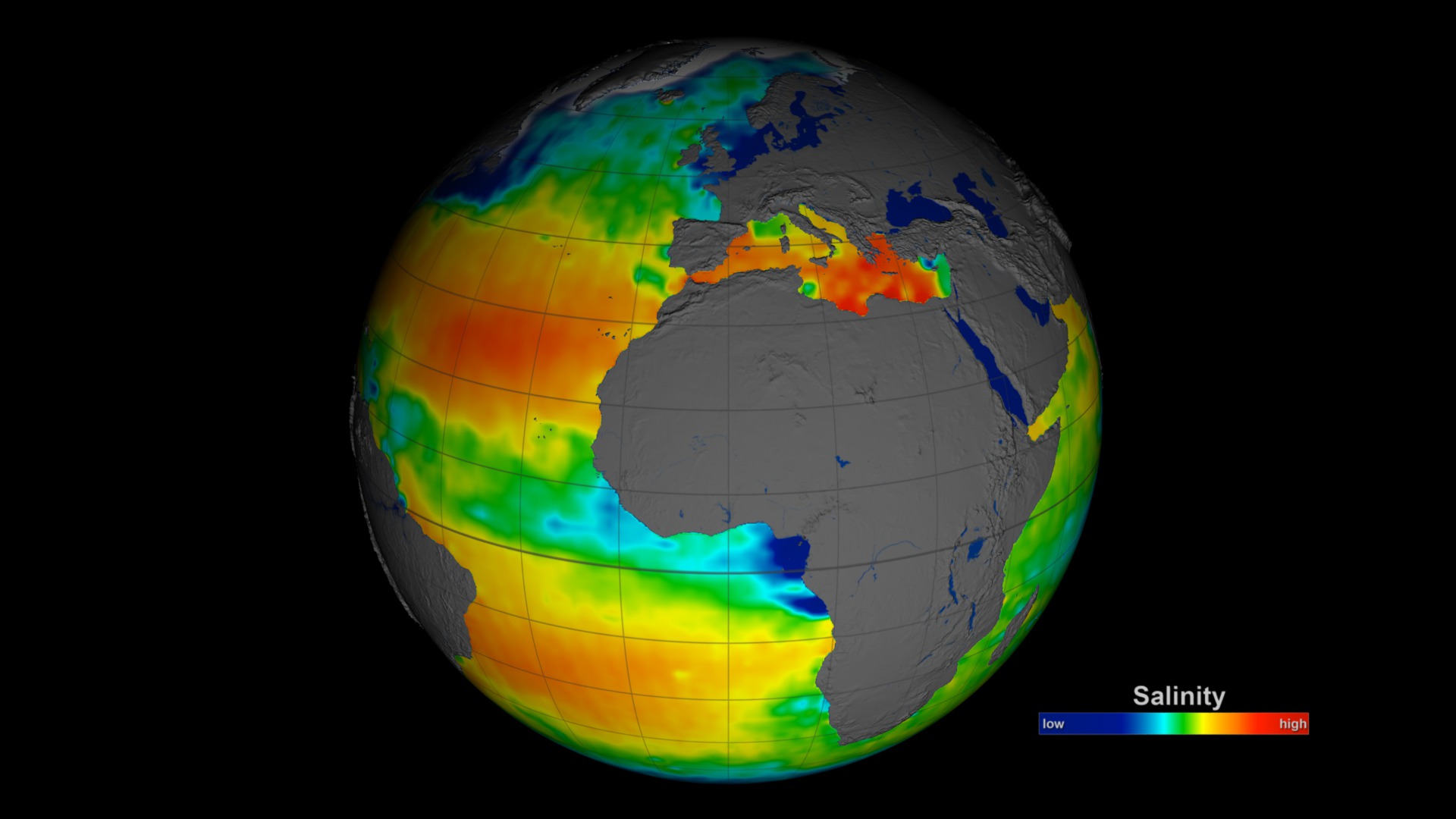
Aquarius Sea Surface Salinity 2011-2014 - Rotating Globes
3 years of sea surface salinity data displayed on a spinning globe focused on the northern hemisphere with date and color bar
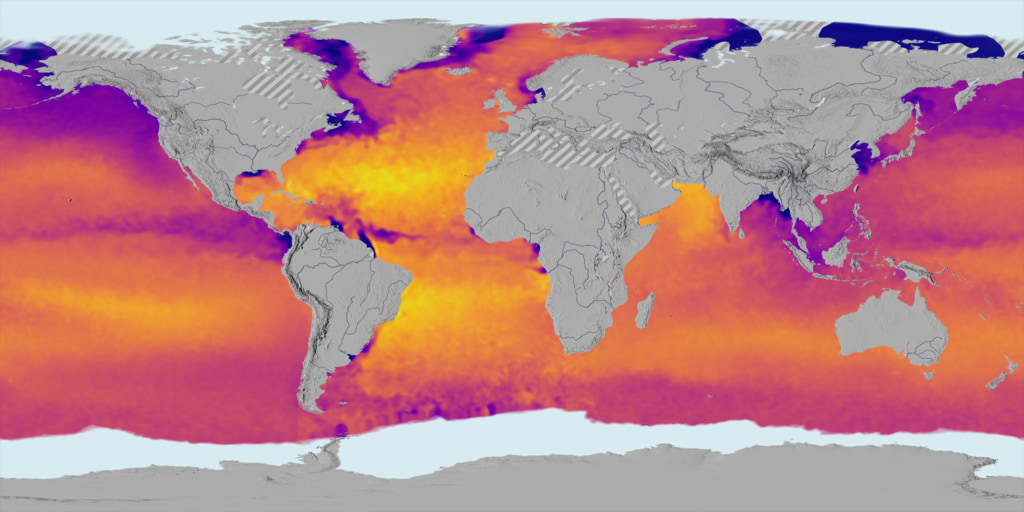
The Aquarius spacecraft is designed to measure global sea surface salinity. It is important to understand salinity, the amount of dissolved salts in water, because it will lead us to better understanding of the water cycle and can lead to improved climate models. Aquarius is a collaboration between NASA and the Space Agency of Argentina
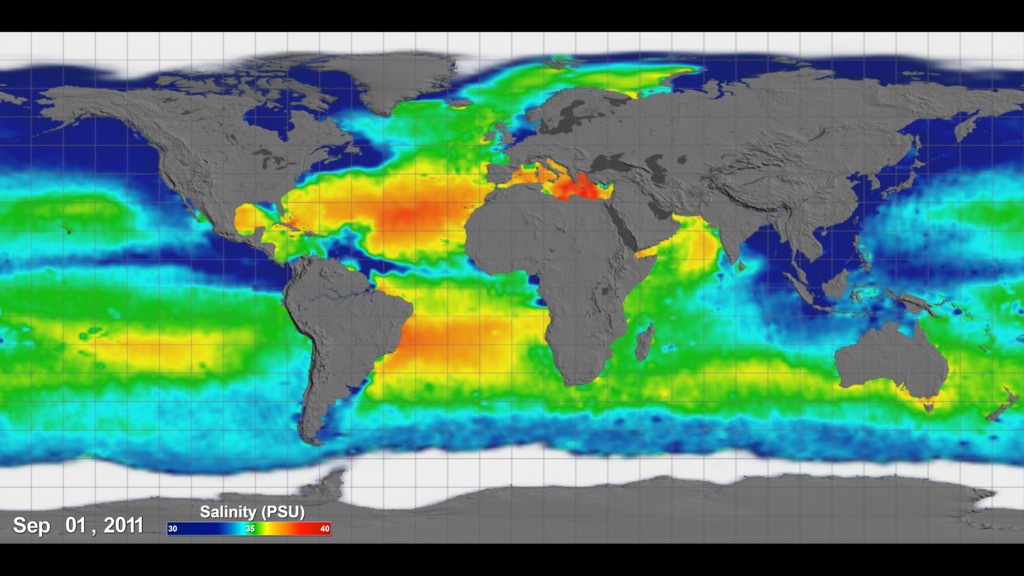
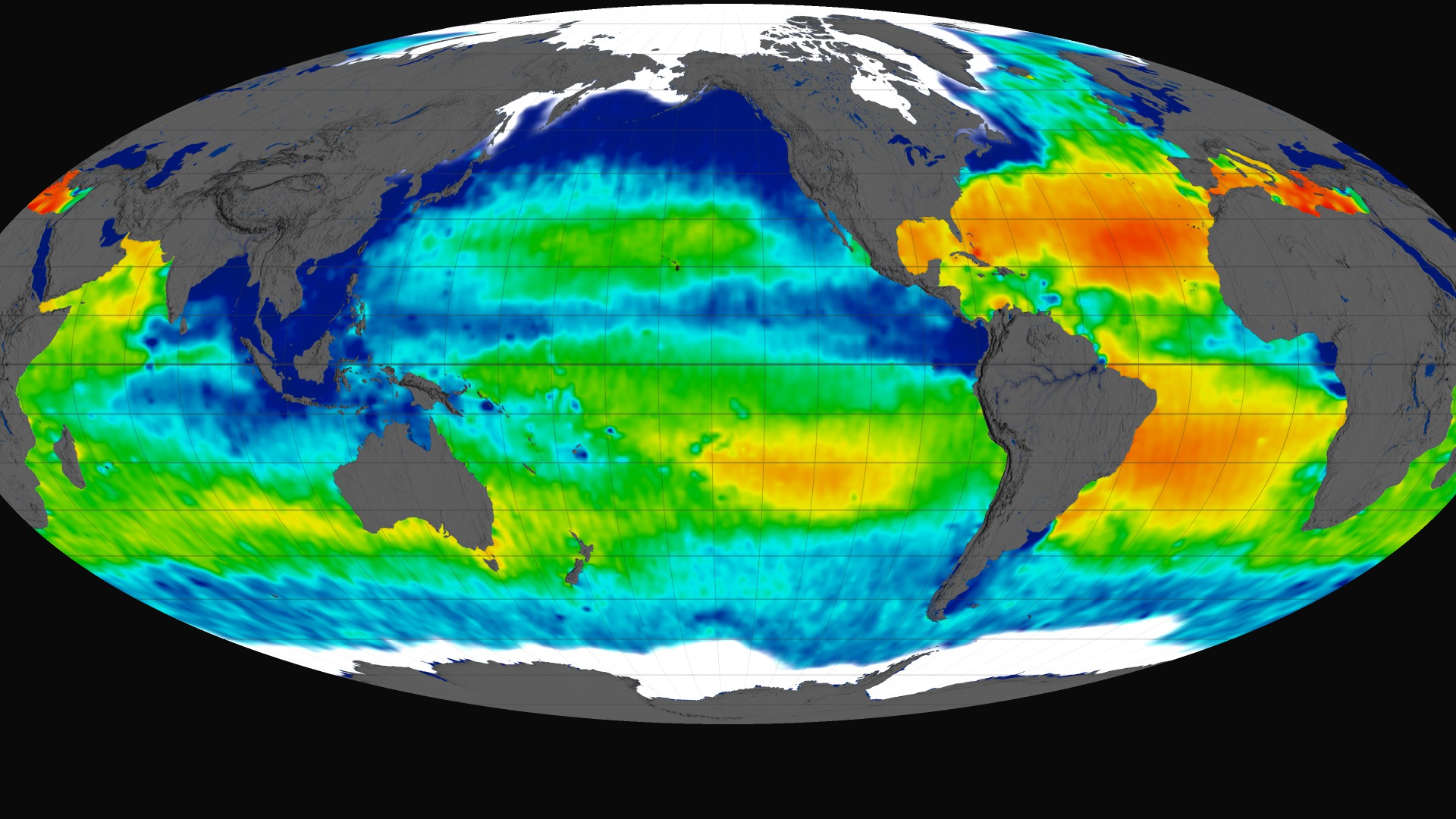
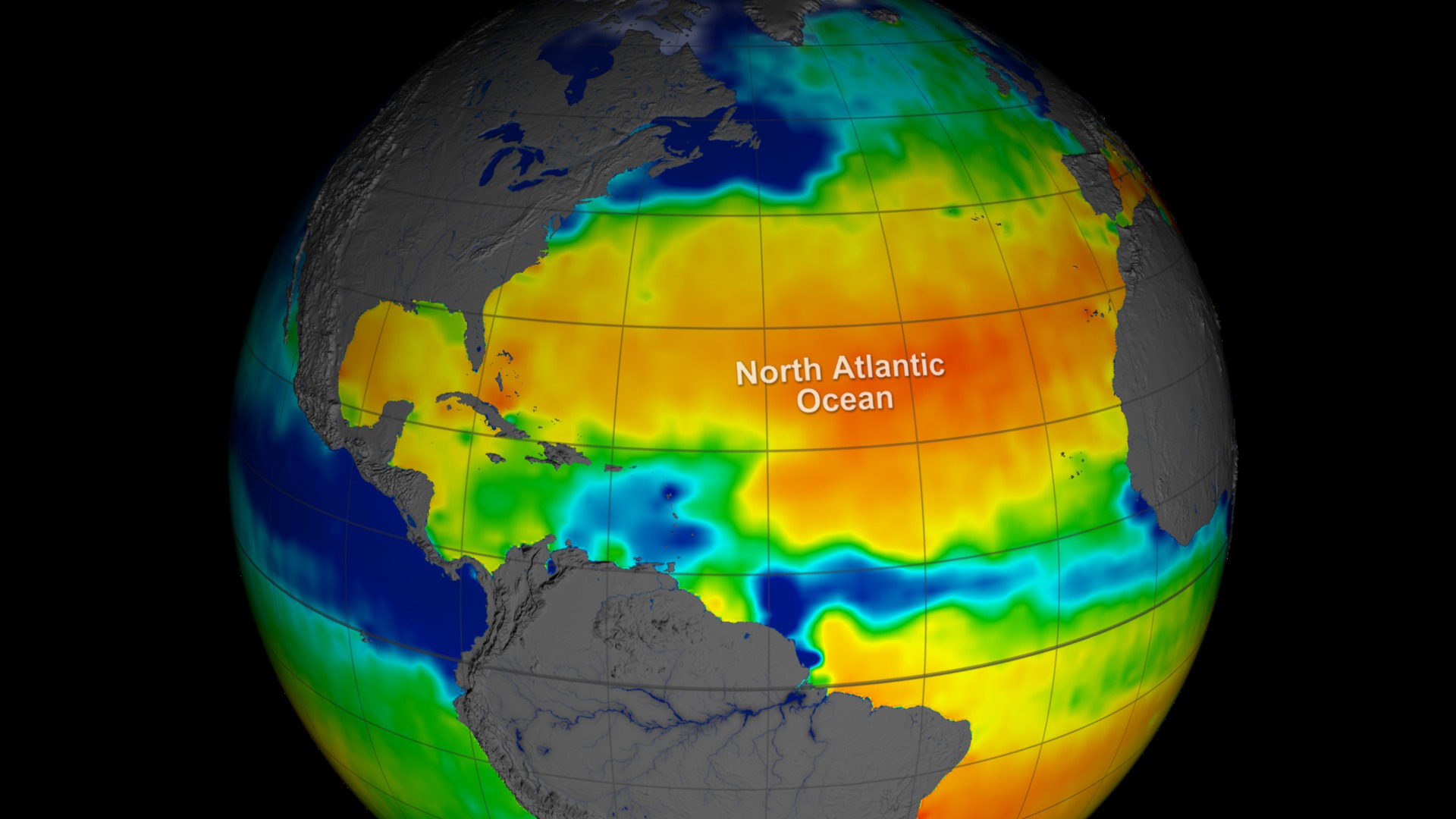
This visualization celebrates over three years of successful Aquarius observations. Sea surface salinity is shown on a spinning globe (with and without grid lines).
The range of time shown is September 2011 through September 2014. This visualization was generated based on version 3.0 of the Aquarius data products.
3 years of sea surface salinity data displayed on a spinning globe (with grid lines) focused on the northern hemisphere with date and color bar
3 years of sea surface salinity data displayed on a spinning globe with date and color bar
3 years of sea surface salinity data displayed on a spinning globe (with grid lines) with date and color bar
3 years of sea surface salinity data displayed on a spinning globe focused on the northern hemisphere. No dates or color bar

Print resolution still of the oceans around Africa

Print resolution still of the oceans around Asia

Print resolution still of the oceans around the Americas

Aquarius color bar showing salinity range from 30 to 40 PSU, going from blue to green to red
For More Information
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio
-
Animators
-
Kel Elkins
(USRA)
-
Greg Shirah
(NASA/GSFC)
-
Kel Elkins
(USRA)
-
Scientists
- Gary Lagerloef (ESR)
- Gene Feldman (NASA/GSFC)
- Norman Kuring (NASA/GSFC)
Series
This page can be found in the following series:Datasets used
-
SSS (Sea Surface Salinity) [Aquarius: Microwave Radiometer]
ID: 774
Note: While we identify the data sets used on this page, we do not store any further details, nor the data sets themselves on our site.
Release date
This page was originally published on Thursday, November 6, 2014.
This page was last updated on Wednesday, May 3, 2023 at 1:50 PM EDT.