A newer version of this visualization is available.
North Polar Sea Ice Minimum, 2014
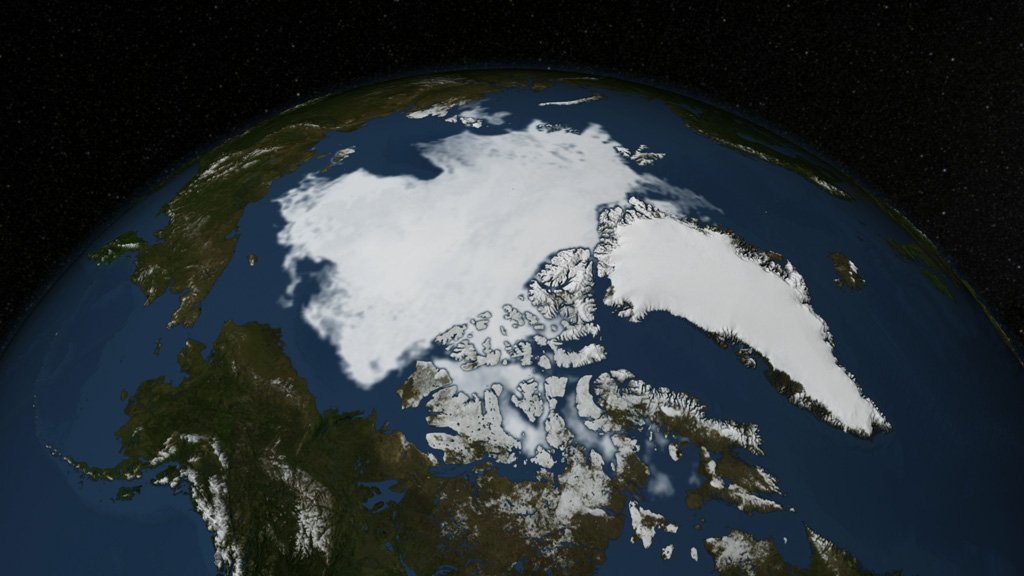
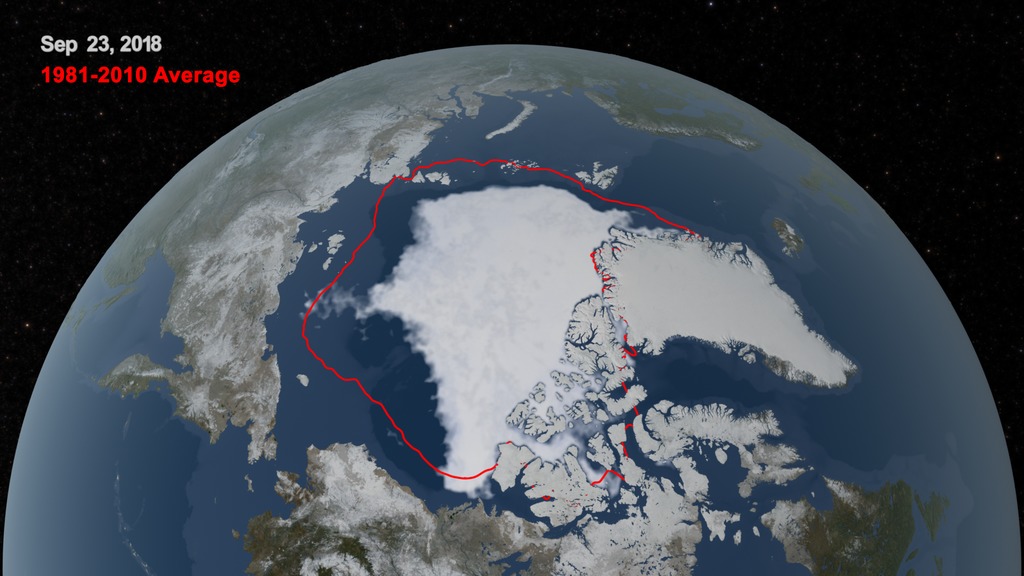
Sea ice acts as an air conditioner for the planet, reflecting energy from the Sun. On September 17, the Arctic Sea ice reached its minimum extent for 2014 — at 1.94 million square miles (5.02 million square kilometers), it’s the sixth lowest extent of the satellite record. With warmer temperatures and thinner, less resilient ice, the Arctic sea ice is on a downward trend. The red line in the still image indicates the average ice extent over the 30 year period between 1981 and 2011.

Print-resolution still, no date

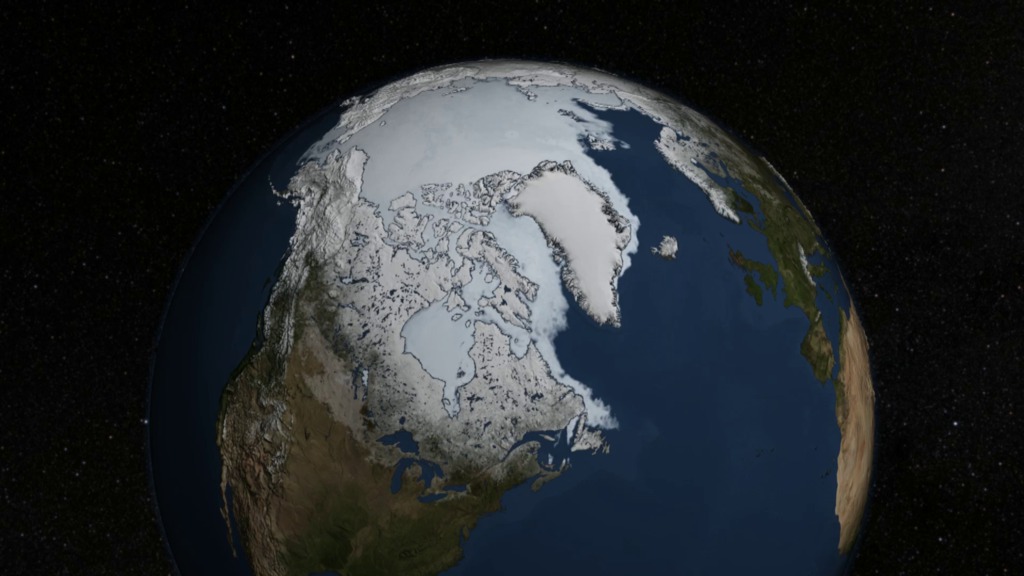
Print-resolution still, with date
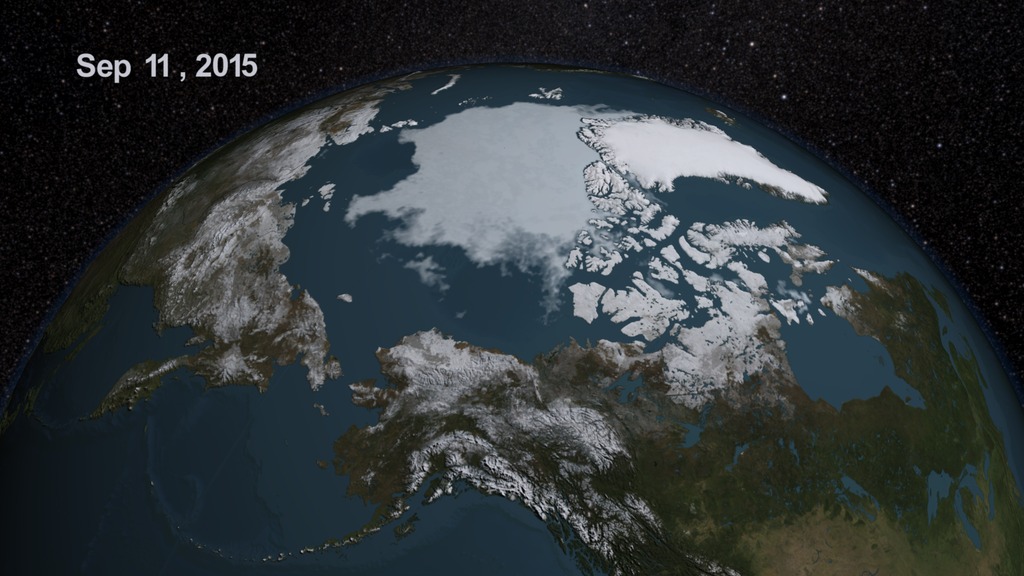
Sea ice extent animation, with date
Sea ice extent animation, without date
Dates only

Print-resolution still with a graph overlay
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio
-
Animator
- Trent L. Schindler (USRA)
-
Visualizer
-
Cindy Starr
(Global Science and Technology, Inc.)
-
Cindy Starr
(Global Science and Technology, Inc.)
-
Producer
- Joy Ng (USRA)
-
Scientists
- Walt Meier (NASA/GSFC)
- Nathan T. Kurtz (NASA/GSFC)
-
Project support
- Laurence Schuler (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
- Ian Jones (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
Missions
This page is related to the following missions:Datasets used
-
BMNG (Blue Marble: Next Generation) [Terra and Aqua: MODIS]
ID: 508Credit: The Blue Marble data is courtesy of Reto Stockli (NASA/GSFC).
This dataset can be found at: http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Newsroom/BlueMarble/
See all pages that use this dataset -
10 km Daily Sea Ice Concentration [SHIZUKU (GCOM-W1): AMSR2]
ID: 795Credit: AMSR2 data courtesy of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA).
See all pages that use this dataset -
10 km Daily 89 GHz Brightness Temperature [SHIZUKU (GCOM-W1): AMSR2]
ID: 796Credit: AMSR2 data courtesy of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA).
See all pages that use this dataset
Note: While we identify the data sets used on this page, we do not store any further details, nor the data sets themselves on our site.
Release date
This page was originally published on Monday, September 22, 2014.
This page was last updated on Wednesday, May 3, 2023 at 1:50 PM EDT.