A newer version of this visualization is available.
GEOS-5 Nature Run Collection
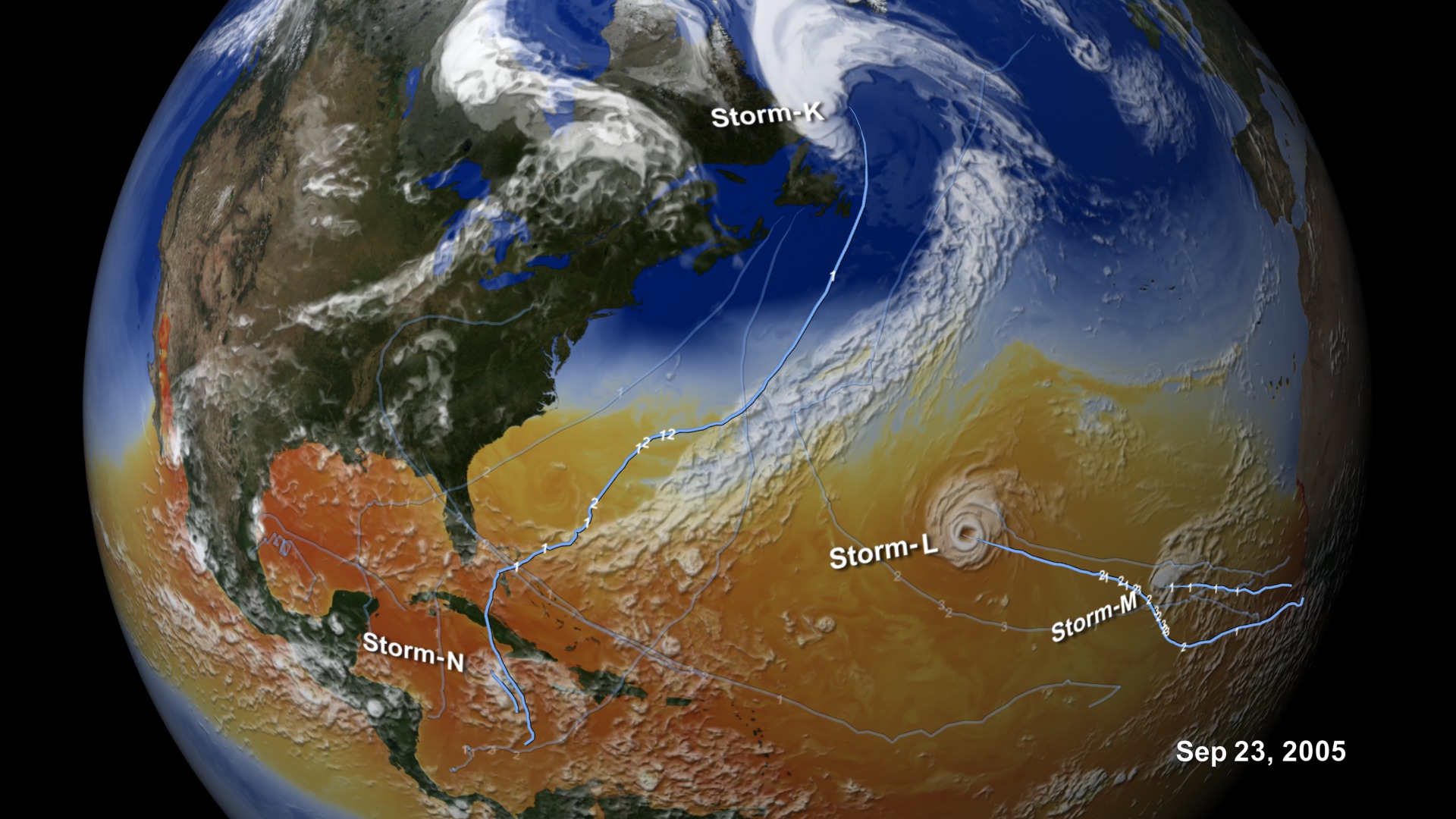
Through numerical experiments that simulate the dynamical and physical processes governing weather and climate variability of Earth's atmosphere, models create a dynamic portrait of our planet. This 10-kilometer global mesoscale simulation (Nature Run) using the NASA Goddard Earth Observing System Model (GEOS-5) explores the evolution of surface temperatures as the sun heats the Earth and fuels cloud formation in the tropics and along baroclinic zones; the presence of water vapor and precipitation within these global weather patterns; the dispersion of global aerosols from dust, biomass burning, fossil fuel emissions, and volcanoes; and the winds that transport these aerosols from the surface to upper-levels.
The full GEOS-5 simulation covered 2 years—from May 2005 to May 2007. It ran on 3,750 processors of the Discover supercomputer at the NASA Center for Climate Simulation, consuming 3 million processor hours and producing over 400 terabytes of data.
GEOS-5 development is funded by NASA's Modeling, Analysis, and Prediction Program.
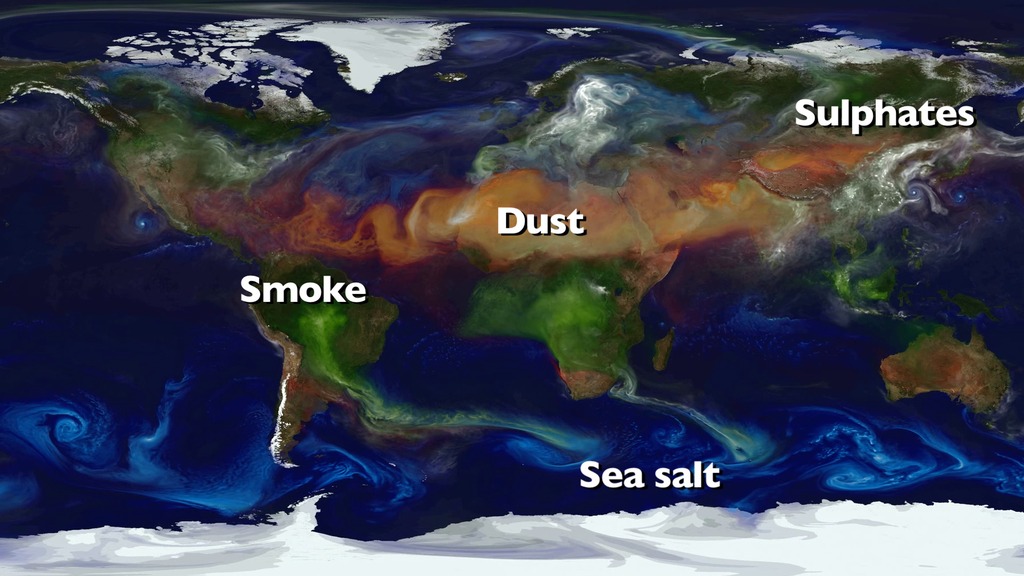
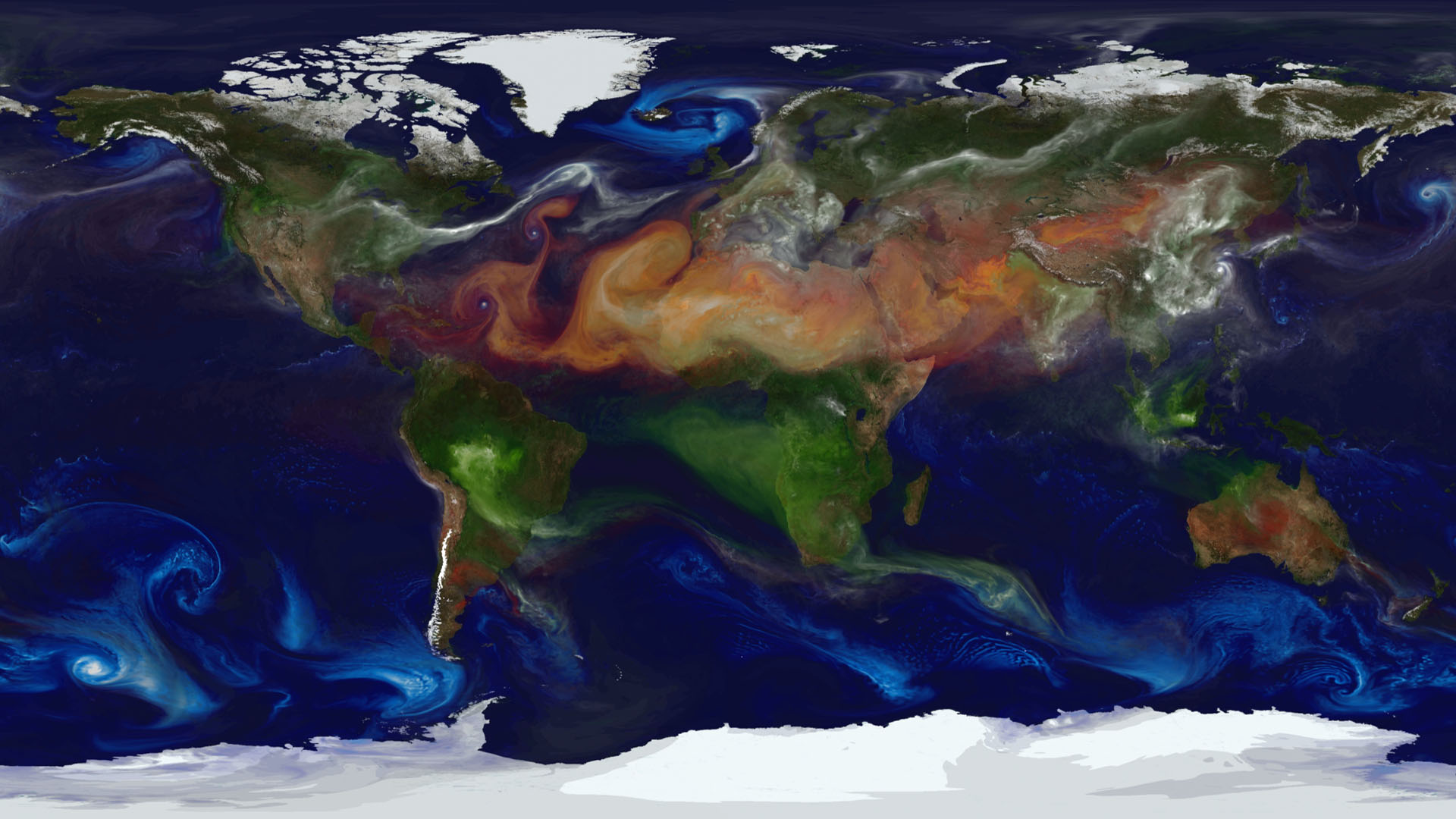
Dust (red), sea salt (blue), organic/black carbon (green), and sulfates (white) displayed by their extinction aerosol optical thickness.This simulation used GEOS-5 and the Goddard Chemistry Aerosol Radiation and Transport (GOCART) Model.
This projection of the aerosols simulation onto a rotating globe tracks wildfires and human-initiated burning (red-yellow dots) as detected by NASA's MODIS instrument aboard the Terra and Aqua satellites.
A zoomed in version of aerosols and fires on a rotating globe.
Total precipitable water (white) and rainfall (colors 0-15 millimeters/hour; red=highest).
Surface winds (white 0-40 meters/second) and upper-level (250 hPa) winds (colors 0-175 meters/second; red=faster).
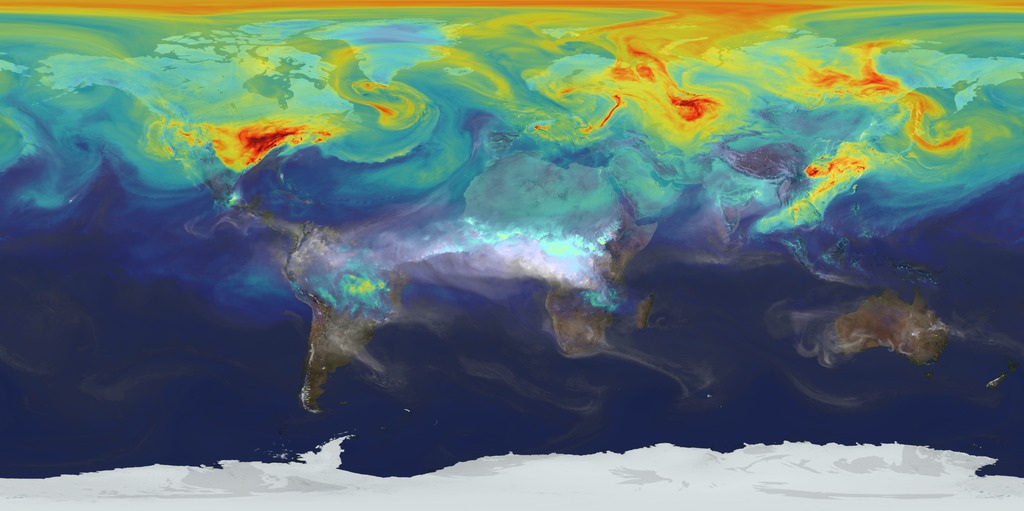
Surface temperature (colors 270-310 Kelvin) and outgoing longwave radiation at the top of the atmosphere (white) representative of clouds in the model.
For More Information
See the following sources:
- gmao.gsfc.nasa.gov/research/aerosol/
- gmao.gsfc.nasa.gov/research/aerosol/modeling/nr1_movie/
- gmao.gsfc.nasa.gov/systems/geos5
- gmao.gsfc.nasa.gov/systems/geos5/
- http://gmao.gsfc.nasa.gov/research/aerosol
- http://gmao.gsfc.nasa.gov/research/aerosol/modeling/nr1_movie/
- http://gmao.gsfc.nasa.gov/systems/geos5/
- http://www.nccs.nasa.gov/discover_front.html
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center
Model data processing provided by Discover supercomputer, NASA Center for Climate Simulation
-
Animator
- William Putman (NASA/GSFC)
-
Scientist
- William Putman (NASA/GSFC)
Release date
This page was originally published on Thursday, March 7, 2013.
This page was last updated on Monday, July 15, 2024 at 12:13 AM EDT.
Missions
This visualization is related to the following missions:Series
This visualization can be found in the following series:Datasets used in this visualization
-
GEOS-5 Cubed-Sphere (GEOS-5 Atmospheric Model on the Cubed-Sphere)
ID: 663The model is the GEOS-5 atmospheric model on the cubed-sphere, run at 14-km global resolution for 30-days. GEOS-5 is described here http://gmao.gsfc.nasa.gov/systems/geos5/ and the cubed-sphere work is described here http://sivo.gsfc.nasa.gov/cubedsphere_overview.html.
See all pages that use this dataset -
GOCART (Goddard Chemistry Aerosol and Transport (GOCART) )
ID: 712 -
[Terra and Aqua: MODIS]
ID: 775
Note: While we identify the data sets used in these visualizations, we do not store any further details, nor the data sets themselves on our site.