Mirror Quadrants for XRISM

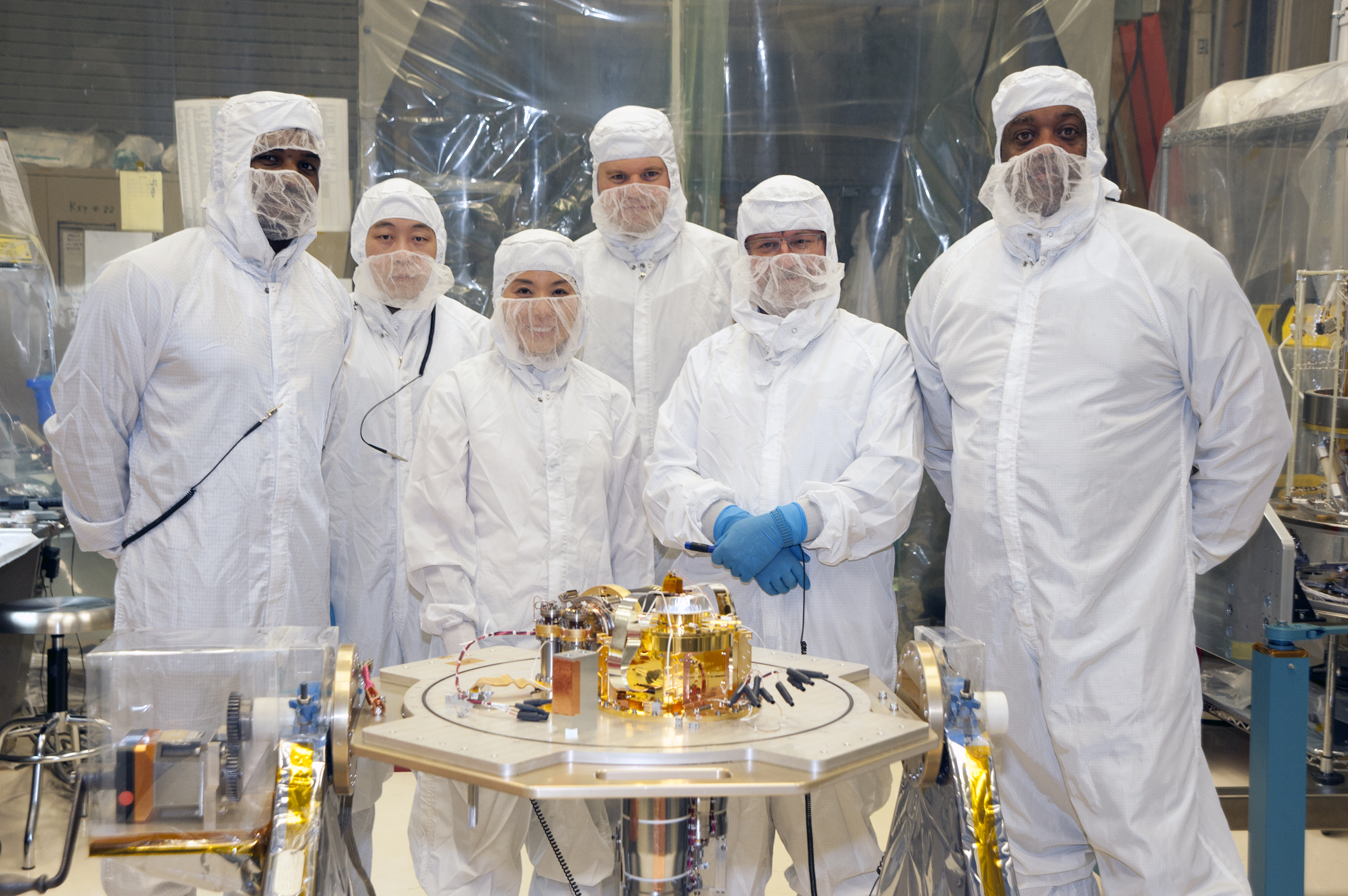
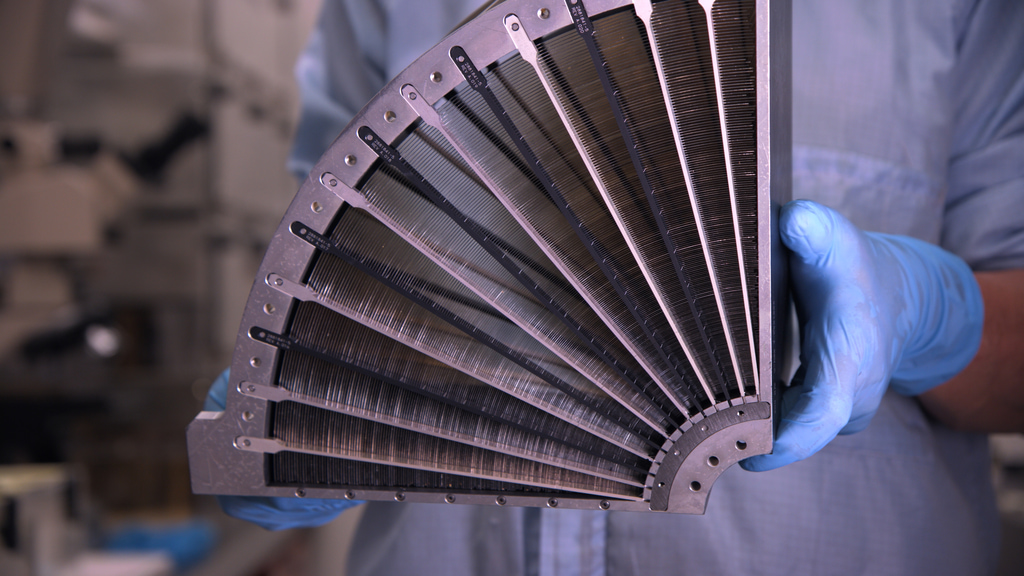
XRISM team member Yang Soong, a researcher at the University of Maryland, College Park, displays completed mirror elements for an X-ray Mirror Assembly developed for the JAXA/NASA mission.
Credit: Taylor Mickal/NASA
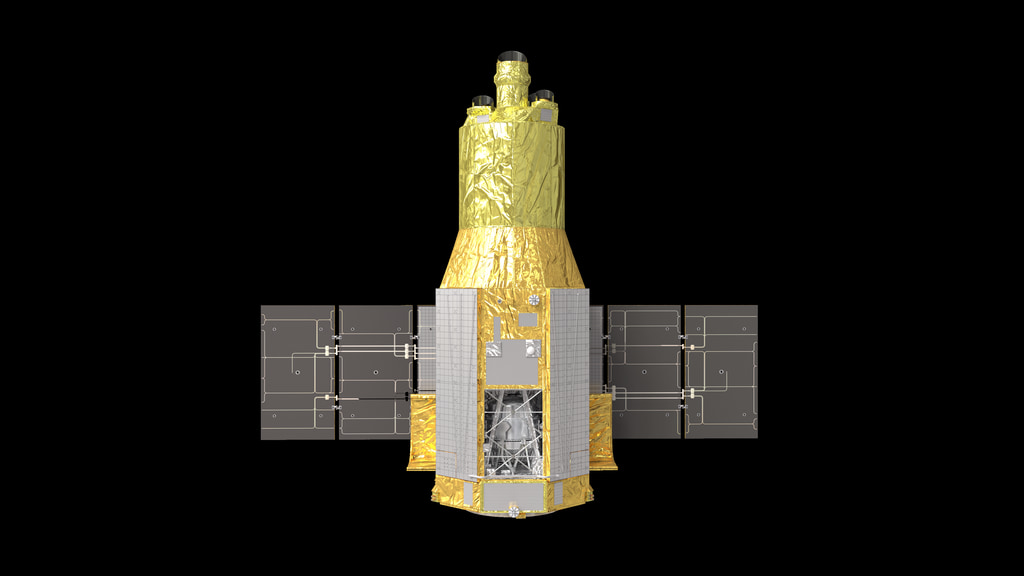
The X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM, pronounced “crism”) is a collaboration between the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and NASA, along with ESA participation, to investigate the X-ray universe using high-resolution imaging and spectroscopy. XRISM features two instruments: Resolve, an X-ray calorimeter spectrometer, and Xtend, an X-ray imager.
These images, taken in June 2019, show completed elements of one XRISM flight X-ray Mirror Assembly (XMA). Each XMA includes both a primary and a secondary mirror. Each mirror has four quadrants with 203 nested foil mirror segments apiece, for a total of 1,624 mirror segments in one XMA.
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center developed the X-ray Mirror Assemblies, as well as the Resolve detector and many of its subsystems. XRISM is expected to launch in 2023.

XRISM team member Yang Soong, a researcher at the University of Maryland, College Park, adjusts one quadrant of an X-ray Mirror Assembly developed for the JAXA/NASA mission.
Credit: Taylor Mickal/NASA

XRISM team member Yang Soong, a researcher at the University of Maryland, College Park, adjusts one quadrant of an X-ray Mirror Assembly developed for the JAXA/NASA mission.
Credit: Taylor Mickal/NASA

XRISM team member Yang Soong, a researcher at the University of Maryland, College Park, displays one of the 1,624 foil mirror segments used in an X-ray Mirror Assembly being built for the JAXA/NASA mission.
Credit: Taylor Mickal/NASA

An X-ray Mirror Assembly being built for the JAXA/NASA XRISM mission consists of a primary and secondary mirror, each containing 812 nested foil mirror segments. Team member Yang Soong, a researcher at the University of Maryland, College Park, looks on.
Credit: Taylor Mickal/NASA

XRISM team member Yang Soong, a researcher at the University of Maryland, College Park, displays a completed mirror quadrant from an X-ray Mirror Assembly being built for the JAXA/NASA mission.
Credit: Taylor Mickal/NASA

Completed quadrants of an X-ray Mirror Assembly being built for the JAXA/NASA XRISM mission are shown. Team member Lawrence Lozipone of Stinger Ghaffarian Technologies, Inc. appears in the background.
Credit: Taylor Mickal/NASA

Completed quadrants for an X-ray Mirror Assembly being developed for the JAXA/NASA XRISM mission appear in the foreground as team member Lawrence Lozipone of Stinger Ghaffarian Technologies, Inc. adjusts one for another assembly in the background.
Credit: Taylor Mickal/NASA

Credit: Taylor Mickal/NASA

Credit: Taylor Mickal/NASA

Credit: Taylor Mickal/NASA

Credit: Taylor Mickal/NASA

Credit: Taylor Mickal/NASA

Credit: Taylor Mickal/NASA

Credit: Taylor Mickal/NASA

Credit: Taylor Mickal/NASA

Credit: Taylor Mickal/NASA

Credit: Taylor Mickal/NASA

Credit: Taylor Mickal/NASA

Credit: Taylor Mickal/NASA
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. However, individual items should be credited as indicated above.
-
Science writers
- Francis Reddy (University of Maryland College Park)
- Jeanette Kazmierczak (University of Maryland College Park)
-
Producer
- Scott Wiessinger (USRA)
Release date
This page was originally published on Thursday, January 30, 2020.
This page was last updated on Wednesday, May 3, 2023 at 1:45 PM EDT.