Greenland on the move

A geologic hotspot shaped one of Earth's coldest places.
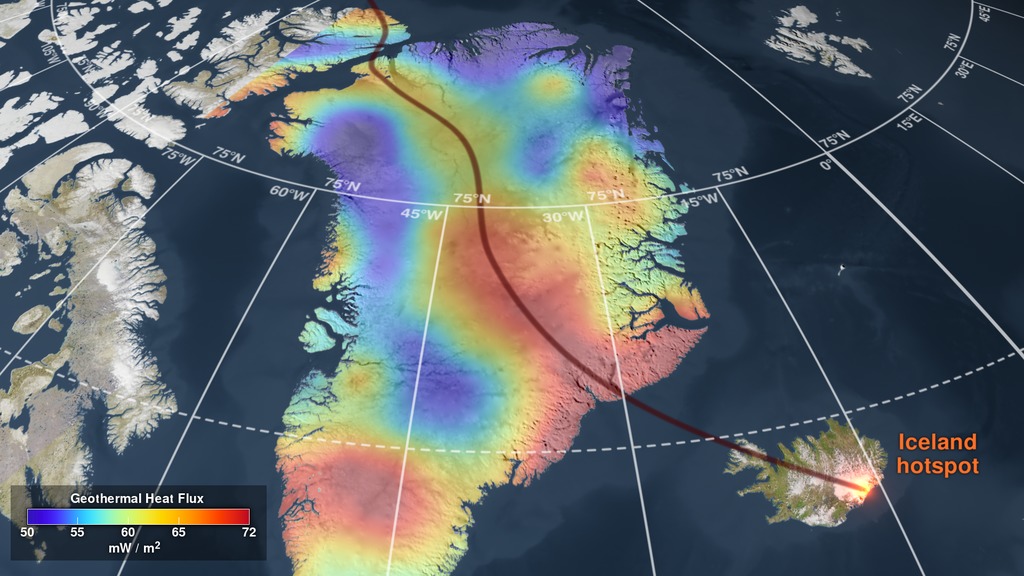
100 million years ago, Greenland was on the move. On its tectonic plate, it traveled from a more southern location northward to its current Arctic position, and along the way passed over a mantle plume or hotspot that left a record of its journey in Greenland's rocks. A plume is an upwelling of hot rock, or magma, from hundreds of miles below Earth's surface. When the magma reaches the base of Earth's outer layer, which includes the crust that makes up the sea floor and continents, it heats up the rock above, effectively cooking it and altering its chemistry. For magnetic rocks common in Earth crust, heating causes them to lose their magnetism. NASA researchers used the altered chemistry of these magnetic rocks to create a heat map of Greenland, where they found the "scar" of its millennia-long journey over the hotspot. The scar extends from the northwest region to the southeast region of Greenland. Because the northwest region of Greenland moved off the plume earlier it is significantly cooler than the southeast. Tracking the movements of land masses helps scientists understand their evolution through time. But more immediately, the heat information feeds sea-level-change models on Earth by helping scientists predict the behavior of the massive ice sheet that covers Greenland. Watch the video to learn more.
A heat map of Greenland’s reveals the path of the North American tectonic plate over geologic time.

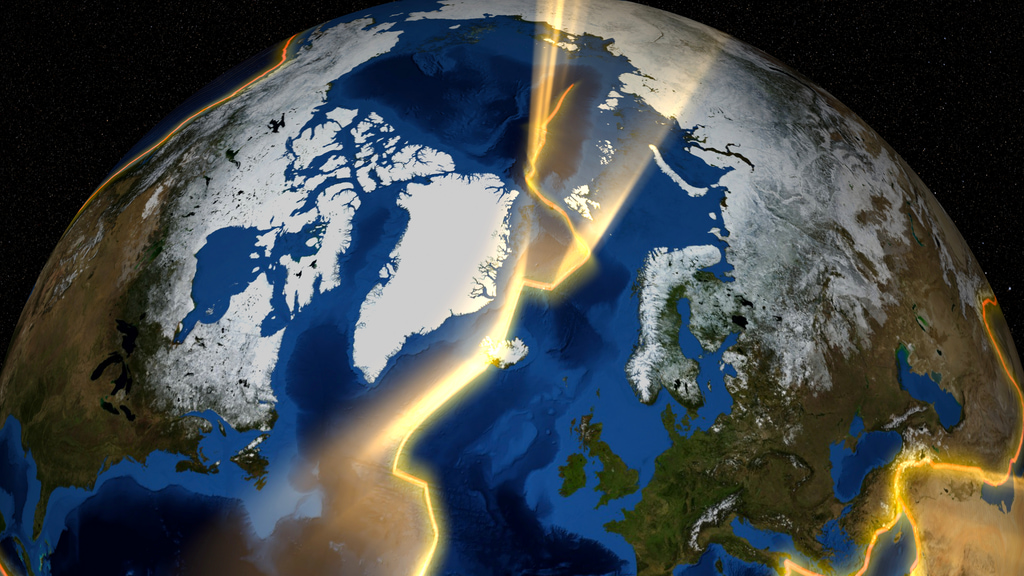
Greenland passed over the mantle plume, or hotspot, that currently sits beneath Iceland.

The mantle plume and Iceland currently sit on the tectonic plate boundary between the North American and Eurasian plates.

A mantle plume, or a hotspot, is an upwelling of magma from deep in the mantle, the layer of hot, malleable rock beneath the crust.
For More Information
See NASA.gov
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio
-
Animator
-
Ernie Wright
(USRA)
-
Ernie Wright
(USRA)
-
Scientist
- Yasmina Martos (University of Maryland College Park)
-
Producers
- Dan Gallagher (USRA)
- Jefferson Beck (USRA)
-
Writer
- Lonnie Shekhtman (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
Release date
This page was originally published on Monday, September 23, 2019.
This page was last updated on Wednesday, May 3, 2023 at 1:45 PM EDT.