Earth
ID: 12277
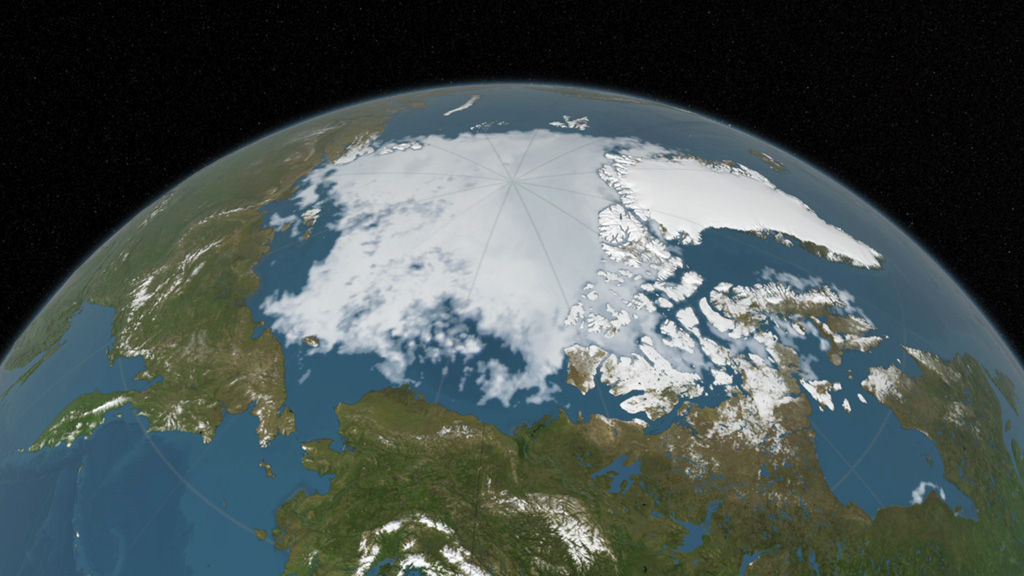
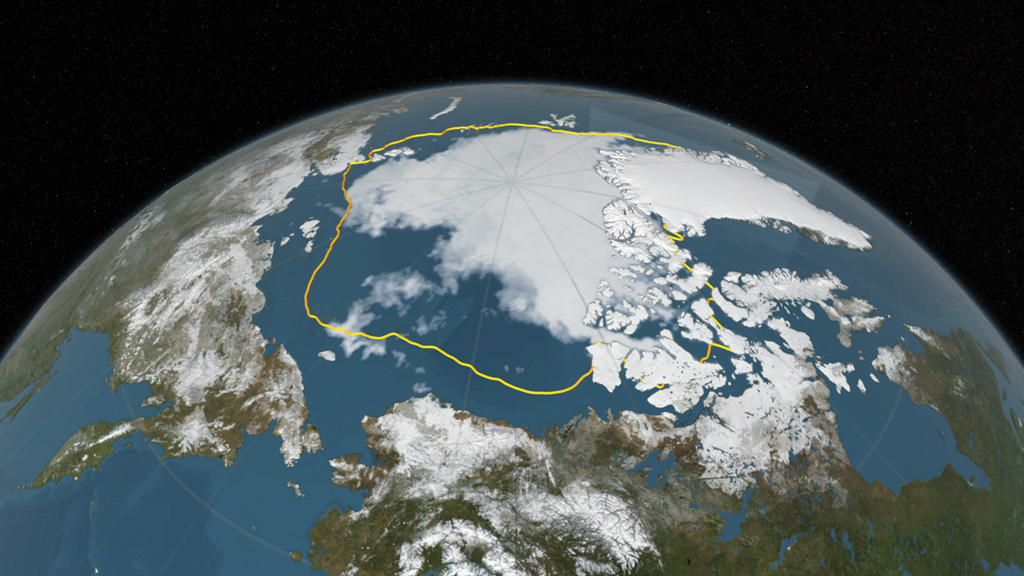
Arctic sea ice appeared to have reached its annual lowest extent on September 10, 2016. An analysis of satellite data showed that at 1.60 million square miles, the 2016 Arctic sea ice minimum extent is effectively tied with 2007 for the second lowest yearly minimum in the satellite record. Arctic sea ice shrinks every year during the spring and summer until it reaches its minimum yearly extent. It regrows during the frigid fall and winter months, when the sun is below the horizon in the Arctic. The Arctic sea ice cover helps regulate the planet’s temperature, influences the circulation of the atmosphere and ocean, and impacts Arctic communities and ecosystems, which is why scientists track how the extent and thickness of the sea ice is changing. Since satellites began monitoring sea ice in 1978, researchers have observed a steep decline in the average extent of Arctic sea ice for every month of the year. Watch the video to see the evolution of this year's Arctic sea ice cover from its wintertime maximum extent to its annual minimum.
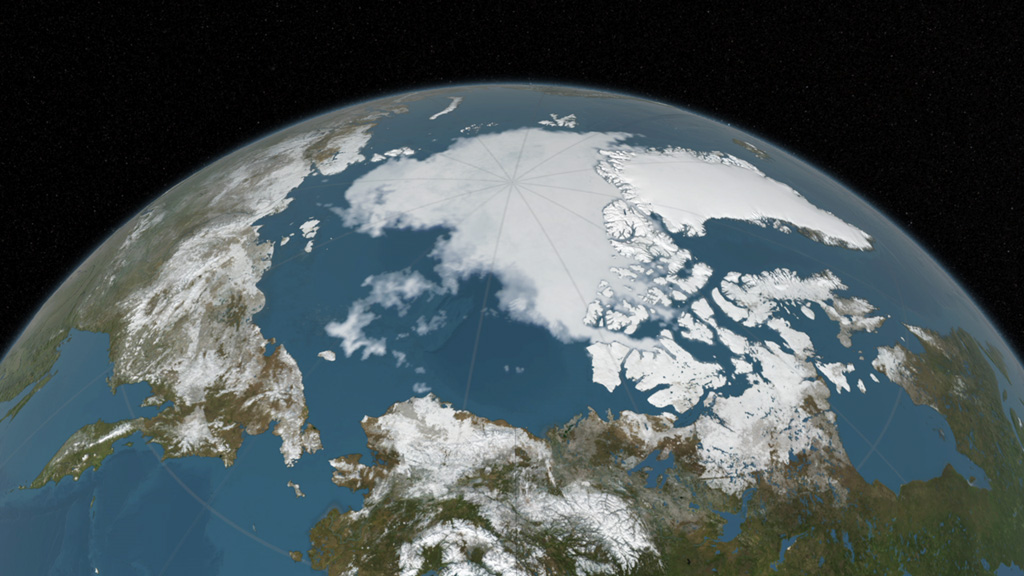


Arctic Sea Ice Update




Source Material
For More Information
Story Credits
Lead Visualizer/Animator:
Cindy Starr (Global Science and Technology, Inc.)
Visualizer/Animator:
Trent L. Schindler (USRA)
Producer:
Jefferson Beck (USRA)
Scientists:
Walt Meier (NASA/GSFC)
Nathan T. Kurtz (NASA/GSFC)
Project Support:
Leann Johnson (Global Science and Technology, Inc.)
Laurence Schuler (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
Ian Jones (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
Lead Writer:
Maria-Jose Vinas Garcia (Telophase)
Cindy Starr (Global Science and Technology, Inc.)
Visualizer/Animator:
Trent L. Schindler (USRA)
Producer:
Jefferson Beck (USRA)
Scientists:
Walt Meier (NASA/GSFC)
Nathan T. Kurtz (NASA/GSFC)
Project Support:
Leann Johnson (Global Science and Technology, Inc.)
Laurence Schuler (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
Ian Jones (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
Lead Writer:
Maria-Jose Vinas Garcia (Telophase)
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio
NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio
Short URL to share this page:
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/12277
Keywords:
SVS >> App
NASA Science >> Earth
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/12277
Keywords:
SVS >> App
NASA Science >> Earth