Earth
ID: 11585
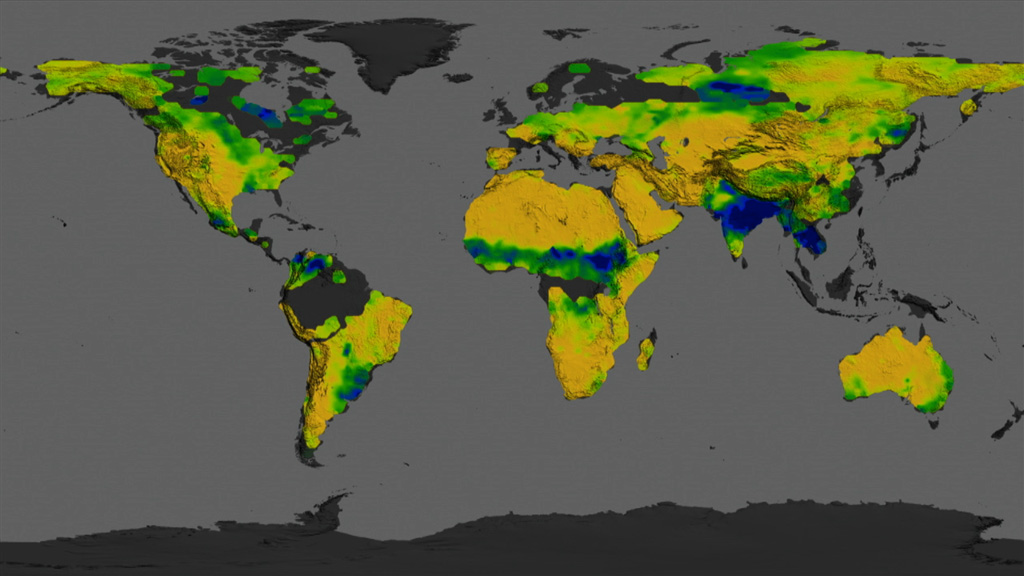
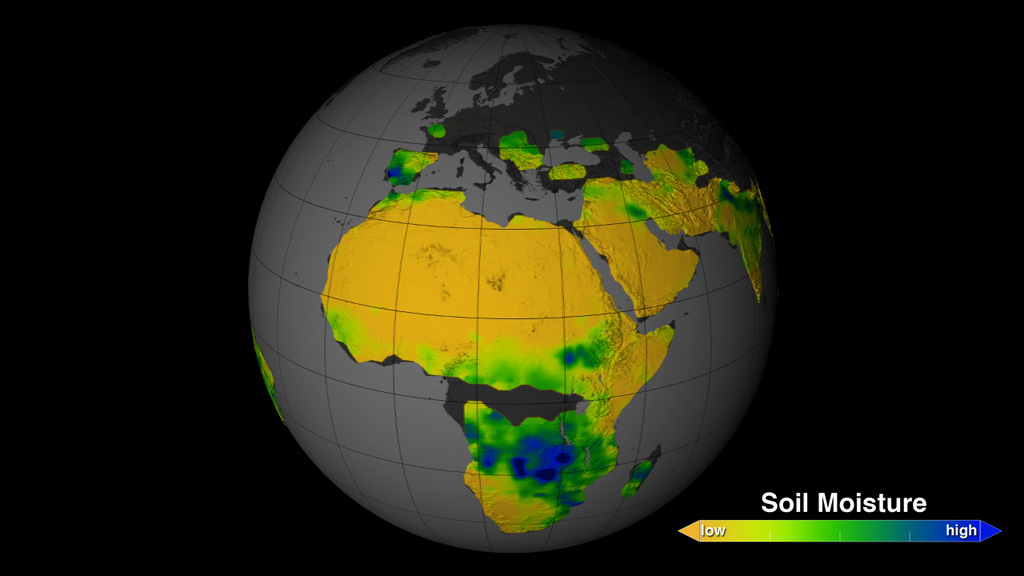
To improve weather forecasts and build better climate models, scientists are looking at changes in soil moisture. Soil moisture is a measurement of the amount of water contained within soil particles. In 2011, NASA and the Argentina space agency launched the Aquarius/SAC-D satellite to observe the salt content of the ocean surface. But researchers also developed a method for the satellite to provide global maps of soil moisture. Orbiting Earth at an altitude of 400 miles, the satellite measures the wetness of soil by detecting microwave energy that's naturally emitted from the top two inches of land. The maps show how severe weather and seasonal cycles affect soil conditions in different parts of the world—information that can be used to help predict the onset of floods or drought. Watch the video to learn more.



Mapping Soil Moisture





Related Stories
For More Information
Story Credits
Visualizers/Animators:
Trent L. Schindler (USRA)
Horace Mitchell (NASA/GSFC)
Video Editor:
Joy Ng (USRA)
Narration:
Kayvon Sharghi (USRA)
Joy Ng (USRA)
Narrator:
Joy Ng (USRA)
Producers:
Kayvon Sharghi (USRA)
Joy Ng (USRA)
Lead Scientists:
Rajat Bindlish (USDA-ARS Hydrology and Remote Sensing Laboratory)
Tom Jackson (USDA-ARS Hydrology and Remote Sensing Laboratory)
Lead Writer:
Kasha Patel (Wyle Information Systems)
Trent L. Schindler (USRA)
Horace Mitchell (NASA/GSFC)
Video Editor:
Joy Ng (USRA)
Narration:
Kayvon Sharghi (USRA)
Joy Ng (USRA)
Narrator:
Joy Ng (USRA)
Producers:
Kayvon Sharghi (USRA)
Joy Ng (USRA)
Lead Scientists:
Rajat Bindlish (USDA-ARS Hydrology and Remote Sensing Laboratory)
Tom Jackson (USDA-ARS Hydrology and Remote Sensing Laboratory)
Lead Writer:
Kasha Patel (Wyle Information Systems)
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Short URL to share this page:
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/11585
Keywords:
DLESE >> Narrated
SVS >> App
NASA Science >> Earth
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/11585
Keywords:
DLESE >> Narrated
SVS >> App
NASA Science >> Earth