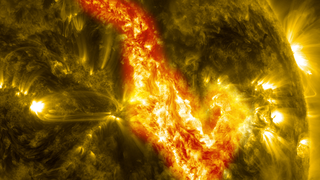
Filament Eruption Creates 'Canyon of Fire' on the Sun
In reality, the sun is not made of fire, but of something called plasma: particles so hot that their electrons have boiled off, creating a charged gas that is interwoven with magnetic fields.
These images were captured on Sept. 29-30, 2013, by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, which constantly observes the sun in a variety of wavelengths.
Different wavelengths help capture different aspect of events in the corona. The red images shown in the movie help highlight plasma at temperatures of 90,000° F and are good for observing filaments as they form and erupt. The yellow images, showing temperatures at 1,000,000° F, are useful for observing material coursing along the sun's magnetic field lines, seen in the movie as an arcade of loops across the area of the eruption. The browner images at the beginning of the movie show material at temperatures of 1,800,000° F, and it is here where the canyon of fire imagery is most obvious. By comparing this with the other colors, one sees that the two swirling ribbons moving farther away from each other are, in fact, the footprints of the giant magnetic field loops, which are growing and expanding as the filament pulls them upward.
Related
For More Information
Credits
Scott Wiessinger (USRA): Video Editor
Scott Wiessinger (USRA): Producer
Karen Fox (ADNET Systems, Inc.): Writer
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/SDO
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/11379
Mission:
SDO
Data Used:
SDO/AIA/304 Filter also referred to as: AIA 304
JOINT SCIENCE OPERATIONS CENTERSDO/AIA/193 Filter also referred to as: AIA 193
JOINT SCIENCE OPERATIONS CENTERSDO/AIA/171 Filter also referred to as: AIA 171
JOINT SCIENCE OPERATIONS CENTERThis item is part of these series:
Narrated Movies
SDO - Edited Features
Goddard Shorts
Five Years of Solar Dynamics Observatory
Goddard TV Tape:
G2013-089 -- Canyon of Fire on the Sun
Keywords:
SVS >> HDTV
GCMD >> Earth Science >> Sun-earth Interactions >> Solar Activity >> Solar Ultraviolet
SVS >> SDO
SVS >> Solar Dynamics Observatory
SVS >> Heliophysics
SVS >> Corona
NASA Science >> Sun
GCMD >> Earth Science >> Sun-earth Interactions >> Solar Activity >> Coronal Mass Ejections
SVS >> Extreme Ultraviolet Imaging
SVS >> EUV Imaging
GCMD keywords can be found on the Internet with the following citation: Olsen, L.M., G. Major, K. Shein, J. Scialdone, S. Ritz, T. Stevens, M. Morahan, A. Aleman, R. Vogel, S. Leicester, H. Weir, M. Meaux, S. Grebas, C.Solomon, M. Holland, T. Northcutt, R. A. Restrepo, R. Bilodeau, 2013. NASA/Global Change Master Directory (GCMD) Earth Science Keywords. Version 8.0.0.0.0