A newer version of this visualization is available.
Annual Arctic Sea Ice Minimum 1979-2014 with Area Graph
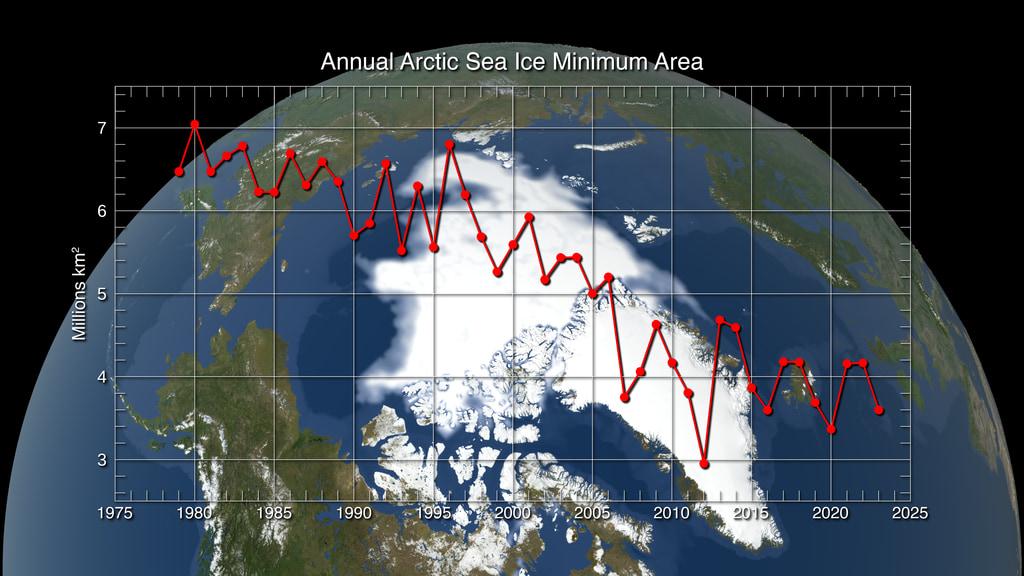
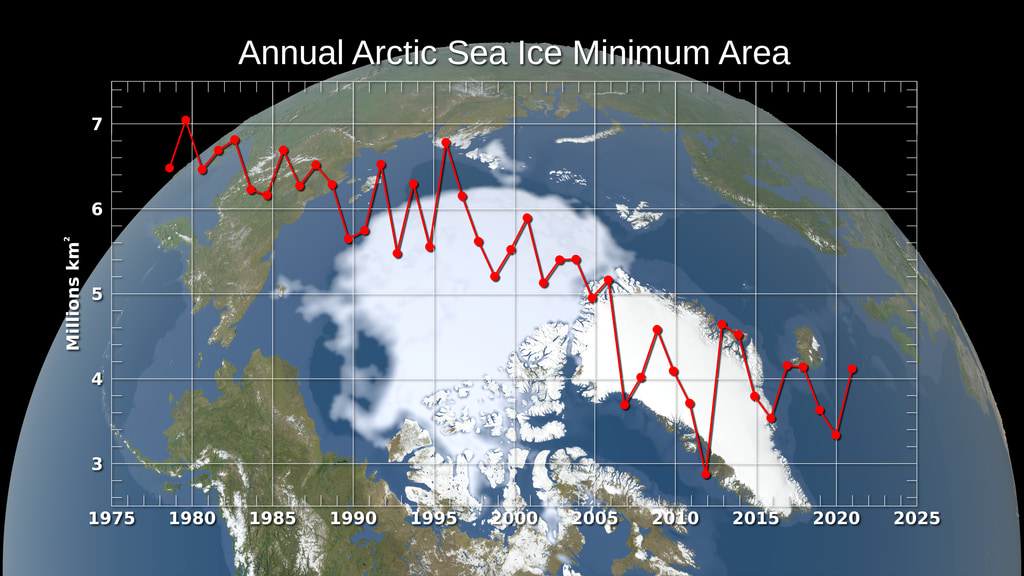
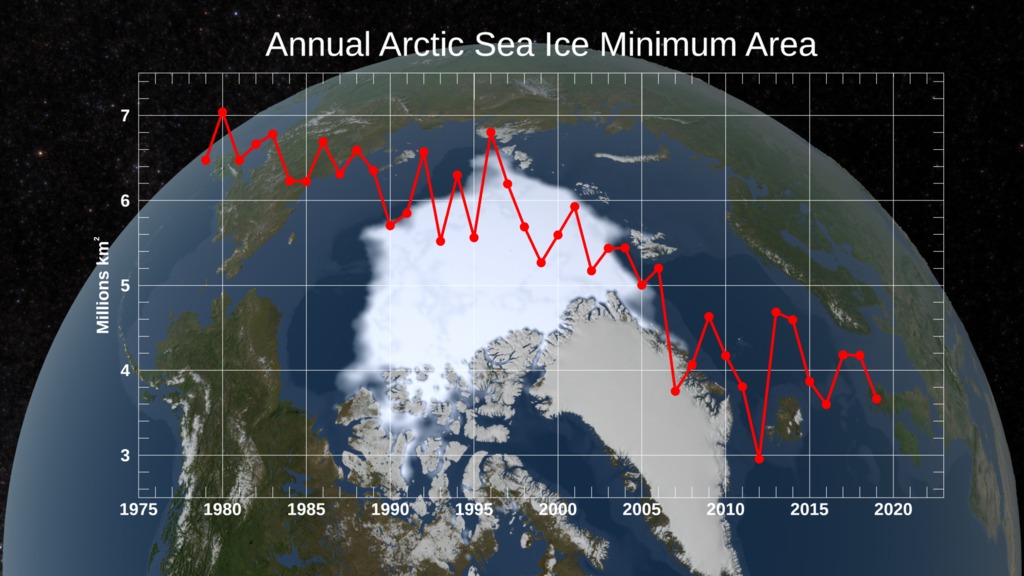
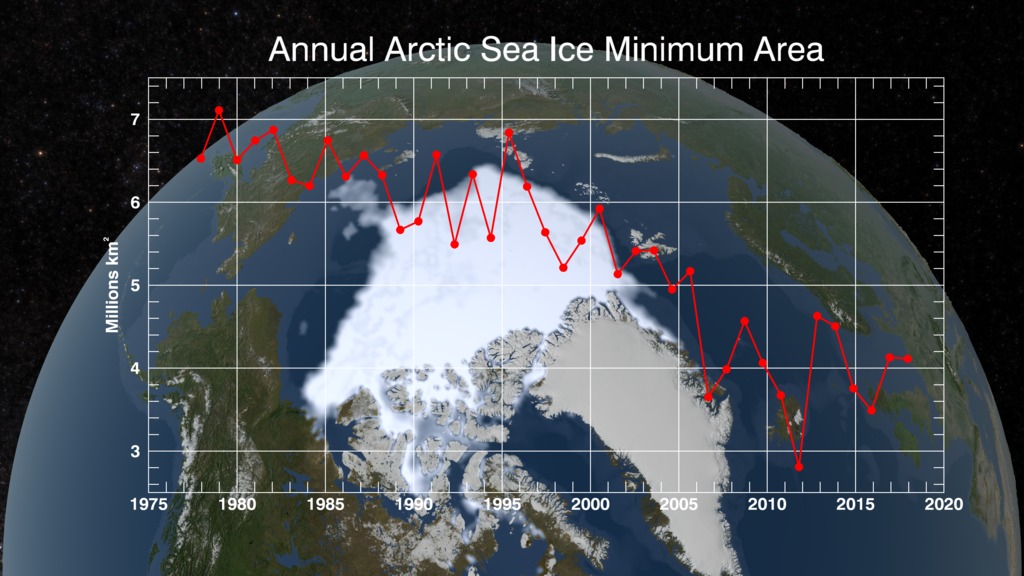
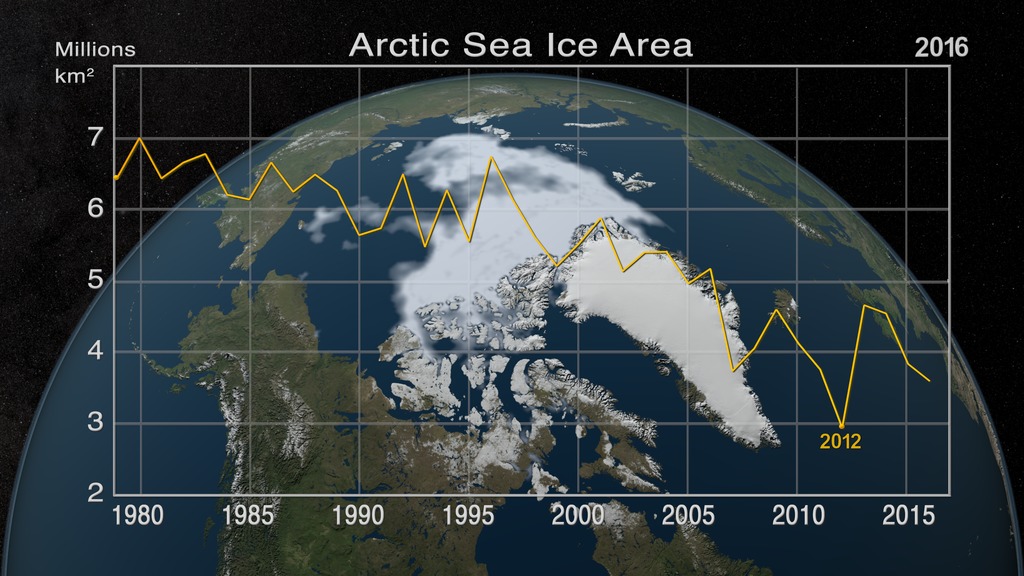
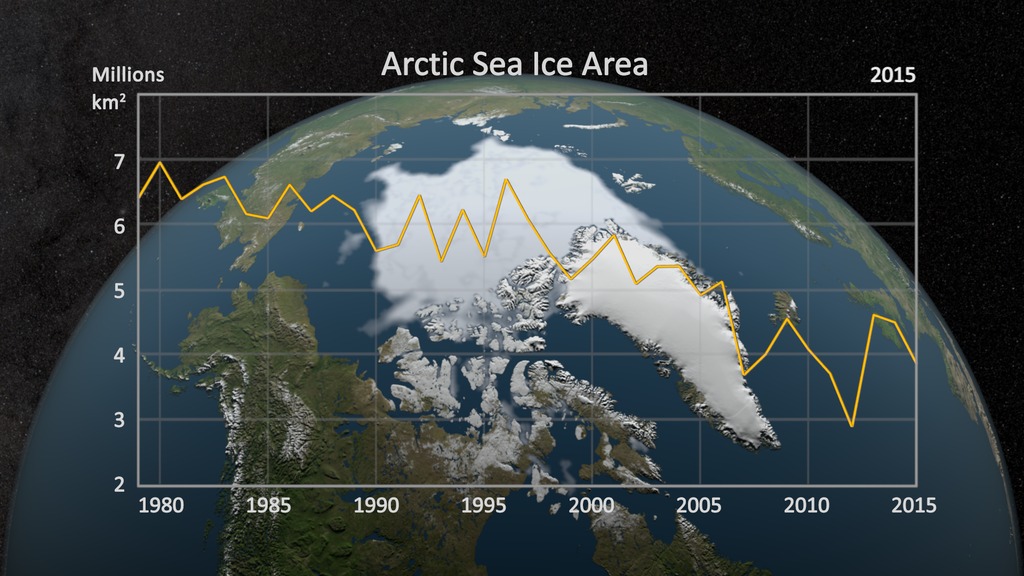
This animation shows the annual Arctic sea ice minimum with a graph overlay that depicts the area of the sea ice in millions of square kilometers.
Satellite-based passive microwave images of the sea ice have provided a reliable tool for continuously monitoring changes in the Arctic ice since 1979. Every summer the Arctic ice cap melts down to what scientists call its "minimum" before colder weather begins to cause ice cover to increase. The ice parameters derived from satellite ice concentration data that are most relevant to climate change studies are sea ice extent and sea ice area. This graph displays the area of the minimum sea ice coverage each year from 1979 through 2014. In 2014, the Arctic minimum sea ice covered an area of 4.527 million square kilometers.
This visualization shows the expanse of the annual minimum Arctic sea ice for each year from 1979 to 2014 as derived from SSMI data. A semi-transparent graph overlay shows the area in million square kilometers for each year's minimum day. The date shown in the upper right corner indicates the current year being displayed.
This animation shows the annual Arctic sea ice minimum from 1979 through 2014 with a date.
The graph overlay with transparency showing the annual sea ice area in millions of square kilometers
The date overlay with transparency

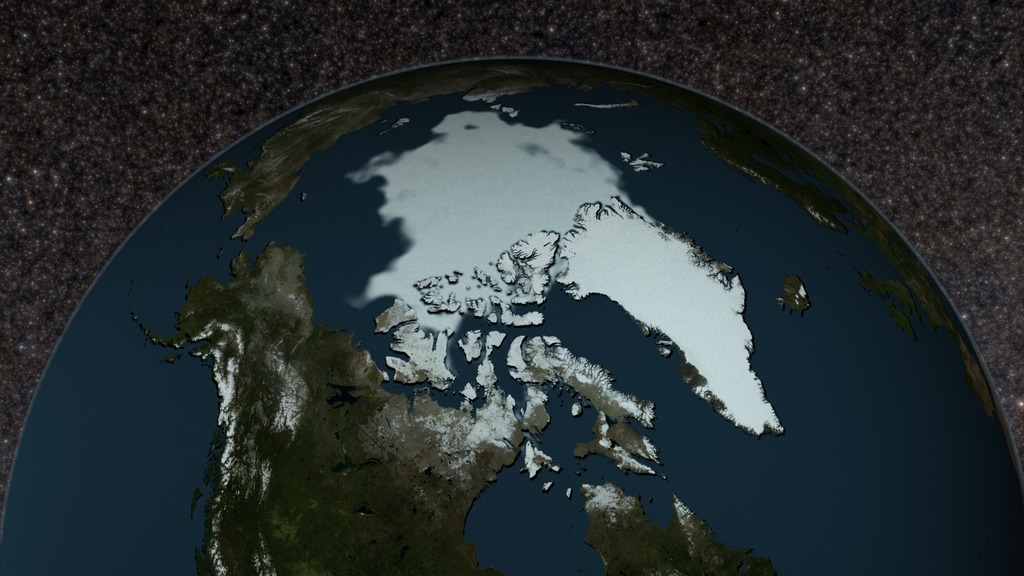
An image of the Arctic sea ice minimum on September 21, 1979

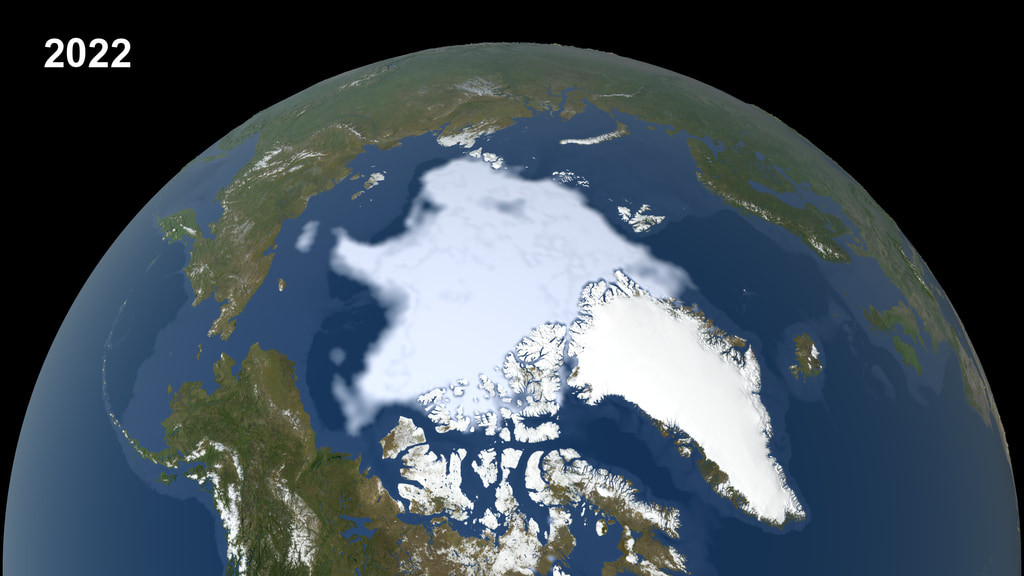
An image of the Arctic sea ice minimum on September 18, 2014
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio
The Blue Marble data is courtesy of Reto Stockli (NASA/GSFC).
-
Visualizer
- Cindy Starr (Global Science and Technology, Inc.)
-
Scientist
- Josefino Comiso (NASA/GSFC)
-
Sr. data analyst
- Robert Gersten (Wyle Information Systems)
-
Project support
- Laurence Schuler (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
- Ian Jones (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
- Eric Sokolowsky (Global Science and Technology, Inc.)
Release date
This page was originally published on Wednesday, April 8, 2015.
This page was last updated on Tuesday, November 14, 2023 at 12:06 AM EST.
Series
This visualization can be found in the following series:Datasets used in this visualization
-
Comiso's September Minimum Sea Ice Concentration
ID: 540
Note: While we identify the data sets used in these visualizations, we do not store any further details, nor the data sets themselves on our site.